Brand Responsibility for Human Rights in Supply Chains
Understanding the Need for Proactive Applications
In our fast-changing digital era, companies are realizing that merely ticking regulatory boxes isn't enough. Forward-thinking businesses now prioritize applications that stay ahead of the curve, ensuring both competitiveness and longevity. Truly innovative applications don't just react - they predict challenges and evolve with shifting landscapes, driving progress while minimizing operational hazards. This philosophy represents a fundamental shift from passive compliance to active problem-solving and opportunity creation.
Where traditional models wait for issues to emerge, proactive systems implement solutions preemptively. This difference in approach creates more durable, flexible infrastructures that weather challenges more effectively.
Key Features of a Proactive Application
Distinctive characteristics set proactive applications apart from basic compliance tools. They incorporate live data interpretation, intelligent notification frameworks, and self-adjusting protocols. These elements enable organizations to anticipate operational hiccups, make data-backed choices, and implement fixes before minor issues become major crises. Additionally, they maintain seamless compatibility with both current operational needs and future technological developments.
Rather than just satisfying present requirements, these systems are built with tomorrow's demands in mind, creating an exceptionally responsive and sturdy digital environment.
Enhanced Security Through Proactive Measures
Security takes center stage in proactive systems through advanced threat identification and neutralization protocols. By employing pattern-recognition algorithms, these applications spot potential weak points before malicious actors can exploit them. This preventive security model dramatically decreases the likelihood of damaging data incidents.
Improved Operational Efficiency and Agility
Proactive applications revolutionize workflow efficiency through intelligent automation. They handle repetitive analytical tasks, report generation, and even certain decision processes autonomously. This liberation of human resources enables companies to pivot rapidly when market conditions shift or new prospects emerge.
Data-Driven Insights and Decision-Making
These advanced systems transform raw data into actionable intelligence. By continuously processing information streams and recognizing meaningful patterns, they provide invaluable foresight about both potential pitfalls and promising avenues. This intelligence foundation supports smarter strategic planning and preemptive solution development.
Future-Proofing Your Applications
Adopting proactive development methodologies safeguards technological investments against obsolescence. By integrating tomorrow's technologies today, companies avoid expensive system replacements and maintain market leadership. This strategic foresight doesn't just reduce risk - it creates a platform for continuous innovation and competitive advantage in our rapidly evolving tech ecosystem. The result is digital infrastructure that remains relevant and effective despite future uncertainties.
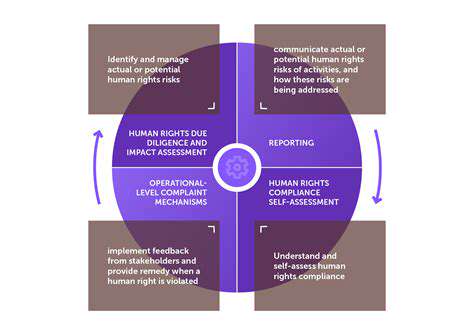
Identifying and Mitigating Risks in Complex Supply Chains
Understanding the Complexity of Modern Supply Chains
Today's supply networks form intricate global webs connecting countless suppliers, producers, and distributors across borders. This complexity breeds numerous vulnerabilities - from political unrest to natural catastrophes and material shortages. Mapping these interdependent relationships and their inherent weak points forms the foundation of effective risk management.
Untangling these connections requires meticulous examination of each supply link, from raw material origins to final delivery. Analysts must evaluate disruption potential at every stage and understand how problems might ripple through the entire network.
Identifying Key Risk Areas
Thorough risk analysis pinpoints specific vulnerabilities in transportation, production, storage, and distribution networks. Geopolitical factors - like trade conflicts or regional instability - can severely disrupt operations, demanding careful assessment of political climates in sourcing and manufacturing regions.
Overdependence on single suppliers presents another critical vulnerability. Relying exclusively on one source for essential components creates dangerous exposure. Supplier diversification often provides crucial protection against this risk.
Implementing Robust Mitigation Strategies
After identifying risks, organizations must deploy tailored countermeasures. These might include expanding supplier networks, creating disruption contingency plans, or enhancing inventory control systems. Each solution should match the specific risk profile, considering both probable impact and likelihood.
Cultivating strong supplier relationships proves equally vital. Transparent communication and cooperation offer early warning about potential issues and facilitate collaborative solutions. This partnership approach builds the trust necessary for anticipating and resolving challenges.
The Role of Technology in Risk Management
Modern technologies dramatically enhance supply chain visibility and real-time monitoring capabilities. Live tracking systems, analytical tools, and predictive algorithms help companies spot emerging threats before they cause operational damage. These technological solutions enable rapid response to unfolding situations, maintaining business continuity despite uncertainties.
The Importance of Transparency and Communication
Clear visibility throughout supply networks is essential for effective risk control. Open information channels between all partners - suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors - allow timely risk communication and coordinated response planning. This transparency builds mutual trust, resulting in more resilient supply systems.
This openness should extend to consumers as well. Clearly communicating product origins and manufacturing processes builds customer trust while encouraging responsible purchasing decisions. It also reinforces corporate accountability across the entire supply network.
Ethical Considerations in Supply Chain Risk Management
Ethical principles must form the foundation of any responsible supply chain strategy. This includes upholding fair employment standards, environmental responsibility, and ethical material sourcing. Companies must evaluate the broader social and ecological consequences of their supply operations. Neglecting these considerations can trigger serious reputational damage and legal consequences.