From Raw Materials to Retail: Ensuring Ethical Treatment Throughout
Sourcing Strategies for Raw Materials
Effective raw material acquisition hinges on a robust sourcing strategy. This involves meticulously identifying reliable suppliers, evaluating their capacity and capabilities, and establishing clear contracts to ensure consistent quality and timely delivery. Analyzing market trends and anticipating future supply chain disruptions are critical components for long-term sustainability. A well-defined sourcing strategy minimizes risk and maximizes value throughout the entire supply chain.
Different industries have unique sourcing needs. For instance, the pharmaceutical industry requires stringent adherence to regulatory guidelines, while the fashion industry prioritizes ethical sourcing and environmental responsibility. Understanding these specific requirements is crucial for selecting appropriate suppliers and building a sustainable supply chain.
Supplier Relationship Management
Strong supplier relationships are paramount for consistent raw material supply. Cultivating trust and open communication channels with suppliers fosters a collaborative environment, enabling proactive issue resolution and joint problem-solving. This collaborative approach is critical for mitigating potential disruptions to production and maintaining supply chain resilience. Transparent and consistent communication is essential for maintaining a healthy and productive partnership.
Quality Control and Inspection
Maintaining high-quality raw materials is essential for product quality and customer satisfaction. Implementing stringent quality control procedures at the sourcing stage is vital for identifying and mitigating potential defects or inconsistencies. This often involves rigorous inspection processes and establishing clear quality standards that suppliers must adhere to. Meeting these standards ensures the end product meets the required quality benchmarks, enhancing brand reputation and customer trust.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Raw material acquisition is inherently susceptible to risks, including price fluctuations, supply shortages, and geopolitical instability. Developing proactive risk mitigation strategies is critical for minimizing potential disruptions to production. Diversifying supplier sources and establishing contingency plans are key components of a robust risk management framework. These strategies protect against unforeseen events and ensure business continuity.
Regularly evaluating market conditions and geopolitical landscapes is essential for anticipating potential risks. Building strong relationships with multiple suppliers allows for flexibility in case of disruptions from a single source. Furthermore, robust inventory management strategies can help buffer against unexpected supply shortages.
Ethical Sourcing Considerations
Ethical sourcing practices are becoming increasingly important for businesses. This includes considering labor standards, environmental impact, and human rights throughout the supply chain. Prioritizing ethical sourcing demonstrates a commitment to social responsibility, which can enhance brand image and attract environmentally conscious consumers. Companies must ensure that their suppliers adhere to ethical standards, preventing exploitation and promoting sustainable practices.
Cost Optimization Strategies
Optimizing raw material costs is a key objective in procurement. Implementing cost-effective sourcing strategies and negotiating favorable pricing with suppliers are essential steps. Analyzing market trends and exploring alternative raw materials can lead to significant cost savings while maintaining quality standards. Regularly benchmarking supplier prices and exploring innovative sourcing methods can help keep costs under control.
Manufacturing Processes: Ensuring Safe and Equitable Conditions
Importance of Safe Working Environments
Manufacturing processes, while crucial for economic growth and providing essential goods, must prioritize the safety and well-being of workers. A safe working environment is not just a moral imperative, but a practical necessity. Accidents and injuries not only cause immense suffering for individuals and their families, but also lead to significant financial losses for companies in terms of compensation claims, lost productivity, and potential legal repercussions. Implementing comprehensive safety protocols, including regular safety training, risk assessments, and the provision of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), is essential for preventing accidents and fostering a culture of safety within the manufacturing facility.
Furthermore, a safe working environment contributes significantly to employee morale and productivity. Employees who feel valued and protected are more likely to be engaged and committed to their work. This translates into higher output, reduced absenteeism, and a more positive overall work environment. A strong focus on safety is a testament to the company's commitment to its employees, which can attract and retain top talent in a competitive job market.
Ethical Considerations in Production
Beyond physical safety, manufacturing processes must also adhere to ethical considerations. Fair wages, reasonable working hours, and the prohibition of exploitative labor practices are fundamental principles that should underpin all production activities. Companies have a responsibility to ensure that their supply chains and manufacturing processes do not contribute to human rights abuses, such as child labor or forced labor. Transparency and accountability are vital in this regard, allowing for greater scrutiny and preventing the perpetuation of unethical practices.
This includes fair compensation for workers, regardless of their position or skill level, and ensuring that working conditions meet established labor standards. Moreover, fair treatment extends to the entire workforce, encompassing equal opportunities and respect for all individuals. Implementing ethical standards throughout the production process is crucial for fostering a just and equitable society while also maintaining a positive public image.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
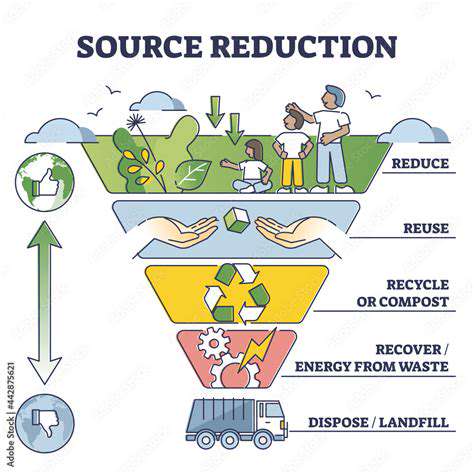
Modern manufacturing processes must increasingly incorporate sustainable practices. Minimizing environmental impact is paramount, encompassing the reduction of waste, the responsible use of resources, and the adoption of environmentally friendly technologies. Implementing strategies to minimize waste generation, reduce water consumption, and control air emissions are crucial steps towards environmental sustainability. This not only protects the planet but also contributes to long-term economic viability by reducing operational costs associated with waste disposal and environmental regulations.
Sustainable manufacturing practices extend beyond the factory floor to encompass the entire supply chain. By collaborating with suppliers who share similar values and employing environmentally friendly materials, manufacturers can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and promote a more responsible approach to production. This commitment to sustainability demonstrates a company's long-term vision and its dedication to creating a healthier planet for future generations.
Equitable Distribution of Benefits
The benefits of successful manufacturing processes should be distributed equitably among all stakeholders, including workers, communities, and the environment. This requires a careful consideration of the social and economic impacts of manufacturing activities on local communities. Companies should actively engage with local communities to understand their needs and concerns, and to contribute positively to their economic development. This might involve supporting local businesses, providing educational opportunities, or investing in community infrastructure.
Moreover, the benefits of increased productivity and economic growth should be shared with employees through fair wages, competitive benefits packages, and opportunities for professional development. This fosters a sense of shared prosperity and motivates workers to contribute to the overall success of the manufacturing process. A just and equitable distribution of benefits is essential for creating a sustainable and harmonious relationship between the manufacturing industry and the societies in which it operates.
Effective communication is paramount to a positive tenant experience. Providing multiple, readily accessible channels for tenants to contact property management, such as email, phone, and a dedicated online portal, significantly improves response times and reduces frustration. This approach ensures tenants feel heard and valued, fostering a sense of connection and trust with the property management team.
Transportation and Logistics: Minimizing Environmental Footprint
Optimizing Supply Chains for Sustainability
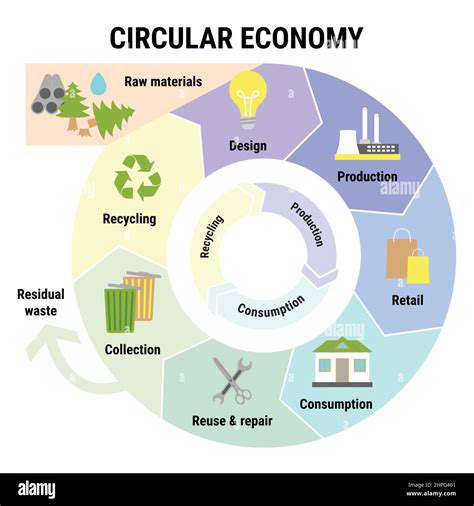
Modern transportation and logistics systems are integral to the global economy, but their environmental impact is significant. Optimizing supply chains to minimize this footprint involves a multifaceted approach, from reducing the distances goods travel to employing more fuel-efficient modes of transport. This includes exploring alternative transportation options like rail and water, and strategically locating warehouses to minimize delivery distances. Sustainable practices within the supply chain, such as using recycled materials and packaging, also contribute to a reduced carbon footprint.
Implementing technologies that track shipments in real-time can help optimize routes, reduce idling time, and minimize fuel consumption. Furthermore, analyzing data to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies within the supply chain allows for targeted improvements and cost savings while promoting sustainability.
The Role of Sustainable Transportation Modes
Transitioning from traditional, fossil fuel-dependent transportation methods to more sustainable alternatives is crucial. This includes promoting the use of electric vehicles (EVs) in delivery fleets, investing in advanced rail infrastructure, and exploring the potential of alternative fuels like hydrogen. Developing and implementing robust public transportation systems in urban areas can significantly reduce reliance on individual vehicles and lower overall emissions.
Investing in infrastructure to support these sustainable modes, such as charging stations for EVs or dedicated rail lines, is equally important. Governments can play a critical role in incentivizing this shift through policies and regulations that favor sustainable transportation.
Reducing Packaging Waste and Material Efficiency
Excessive packaging contributes significantly to waste and environmental pollution. Implementing strategies to reduce packaging materials and utilizing eco-friendly alternatives is vital. This includes using recyclable or biodegradable materials, minimizing packaging volume, and optimizing product designs to reduce the need for excessive packaging.
Promoting reusable packaging solutions and implementing effective waste management systems within the supply chain are also important components in minimizing the environmental impact of packaging materials.
Technological Advancements in Logistics
Technological advancements are transforming transportation and logistics, offering opportunities to improve efficiency and minimize environmental impact. Real-time tracking systems, predictive analytics, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) can optimize routes, reduce delivery times, and minimize fuel consumption. These technologies contribute to a more sustainable and cost-effective supply chain.
Sustainable Packaging Innovations
Innovations in packaging materials and designs are crucial for reducing the environmental footprint of the logistics industry. Biodegradable and compostable materials, along with lightweight and recyclable packaging, are crucial elements in this effort. Companies must actively seek out and implement these innovative solutions to minimize their environmental impact.
Carbon Footprint Measurement and Mitigation
Accurate measurement of the carbon footprint of transportation and logistics activities is essential for identifying areas of improvement. Employing robust methodologies for calculating emissions, from fuel consumption to transportation distances, is critical for developing effective mitigation strategies. Companies can use this data to identify areas where they can reduce their environmental impact and set realistic targets for sustainability.
Adopting carbon offsetting strategies and investing in carbon capture technologies can further reduce the environmental burden of transportation and logistics operations. Transparency in reporting carbon emissions is also essential to building trust and accountability within the industry.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations play a vital role in shaping the sustainability of transportation and logistics. Incentivizing the adoption of sustainable practices, such as investing in charging infrastructure and promoting alternative fuels, can accelerate the transition to a greener industry. Regulations on emissions and fuel efficiency standards are crucial for pushing the industry toward a more sustainable future. International cooperation on these issues is also vital for fostering global progress.