The Future of Fashion: Embracing Sustainable Practices
The fashion industry is increasingly recognizing the environmental impact of traditional textile production. Consumers are demanding greater transparency and accountability from brands, pushing them to explore sustainable alternatives. This includes using recycled materials, organic cotton, innovative plant-based fibers like Tencel and pineapple leather, and responsibly sourced wool. The transition towards these materials is not just about reducing environmental damage; it also opens doors for a more ethical supply chain, ensuring fair labor practices throughout the production process.
Ethical Production Practices: Fair Labor and Wages
Ethical considerations extend beyond the materials themselves. Consumers are demanding that brands prioritize fair labor practices and ensure workers are paid a living wage. This includes safe working conditions, fair compensation, and the right to organize. Transparency in the supply chain is crucial in allowing consumers to trace the origins of their garments and hold companies accountable for their labor practices. Brands that embrace ethical production are not only demonstrating social responsibility but also building trust with their customers.
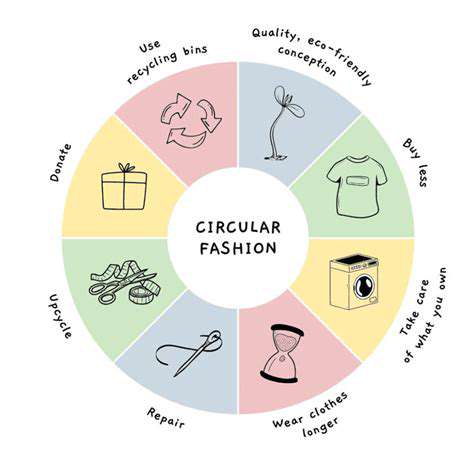
Circular Fashion Models: Reducing Waste and Extending Lifespan
The concept of fast fashion is being challenged by the growing awareness of waste generation. Circular fashion models, which prioritize reducing textile waste and extending the lifespan of garments, are becoming increasingly important. This can include initiatives like clothing rental services, repair and upcycling programs, and encouraging consumers to purchase durable, higher-quality garments that can be worn for longer periods. These models aim to minimize the environmental footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future for the fashion industry.
Consumer Education and Awareness: Empowering Informed Choices
Consumers play a critical role in driving the demand for ethical and eco-conscious fashion choices. Increased awareness of the environmental and social impact of clothing production empowers consumers to make more informed decisions. Educational resources, transparent labeling, and clear communication from brands about their sustainability efforts are essential in guiding consumers towards responsible consumption. Educated consumers are more likely to demand ethical and sustainable practices from the brands they support.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Fashion
Technological advancements are offering innovative solutions to enhance sustainability in the fashion industry. From biodegradable packaging to 3D printing that reduces material waste, technology is transforming the way clothes are designed, produced, and consumed. The use of data analytics can help brands optimize production processes, reduce waste, and track the environmental impact of their products more effectively. This integration of technology is critical in creating a more efficient and eco-friendly fashion system.
Circular Design and the Rise of Upcycling
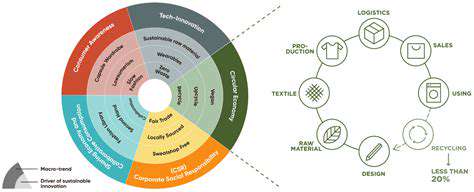
Circular Design Principles
Circular design, a significant shift from traditional linear models, prioritizes the reuse, repair, and recycling of materials throughout a product's lifecycle. This approach aims to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency. By embracing circularity, businesses can significantly reduce their environmental footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future. It's a fundamental concept in the modern approach to product development and manufacturing, driving innovation and long-term value creation.
A key principle within circular design is the concept of designing out waste from the outset. This involves considering the entire lifecycle of a product, from material sourcing to end-of-life disposal, to identify and eliminate waste generation points. Products are designed to be easily disassembled, repaired, and reused, ensuring their value is retained for as long as possible.
Material Selection and Sourcing
The careful selection of materials is critical in circular design. Using recycled or renewable materials whenever possible, and prioritizing those with low environmental impact, is essential. This reduces the reliance on virgin resources and minimizes the strain on the planet's ecosystems. Furthermore, transparent and ethical sourcing practices are crucial to ensure that materials are obtained responsibly and sustainably, respecting human rights and environmental standards.
Innovative material science plays a crucial role in developing sustainable alternatives and improving the recyclability of existing materials. This includes developing biodegradable and compostable materials, as well as exploring advanced recycling technologies to recover valuable resources from waste streams.
Product Durability and Reparability
Designing for durability and reparability is a key aspect of circular design. Products should be built to last, with high-quality components and robust construction. This ensures that products can withstand regular use and are easier to repair when issues arise, extending their lifespan.
This approach not only reduces the need for frequent replacements but also promotes a culture of repair and maintenance, minimizing the generation of electronic waste and fostering a more sustainable consumption pattern. This approach also encourages a shift away from 'planned obsolescence,' a common practice in traditional manufacturing, which promotes the rapid replacement of products.
Product Lifecycle Management
Circular design considers the entire lifecycle of a product, from design and manufacturing to use and disposal. This holistic approach allows for a comprehensive analysis of environmental impacts and the identification of potential improvements at each stage. This means taking responsibility for the entire journey of a product, from cradle to grave, and optimizing each step to reduce environmental harm.
Economic Benefits of Circular Design
Circular design is not just environmentally beneficial; it also offers significant economic advantages. By reducing waste and maximizing resource efficiency, businesses can lower production costs and increase profitability. Circular design can lead to new revenue streams from the reuse and recycling of materials, creating a more sustainable business model.
The shift towards circular design fosters innovation in product development and manufacturing, leading to the creation of new jobs and industries. This can stimulate economic growth while mitigating environmental risks. Furthermore, increased resource efficiency can lead to cost savings in the long run.
Consumer Engagement and Education
Consumer engagement is crucial to the success of circular design initiatives. Educating consumers about the benefits of circular products and practices empowers them to make sustainable choices. This includes providing clear information about product durability, reparability, and recycling options. This also encourages them to actively participate in the circular economy by choosing products with longer lifespans and actively participating in repair and reuse initiatives.
By fostering a culture of conscious consumption, consumers can become active agents of change, contributing to a more sustainable future. Encouraging responsible consumption habits, such as repair and reuse, is essential for the success of a circular economy.
Sustainable Sourcing and Labor Practices
Ethical Material Selection
Sustainable sourcing isn't just about the materials themselves; it's about understanding the entire supply chain. This means considering the environmental impact of cultivating or extracting raw materials, from the use of pesticides and fertilizers in cotton farming to the mining practices for metals like gold or the impact of synthetic fabrics on the planet. Companies committed to ethical sourcing meticulously research and vet their suppliers, ensuring that their practices align with environmental standards and fair labor practices throughout the entire process. Transparent communication about these sourcing decisions is crucial for building consumer trust and holding companies accountable.
Transparency in material sourcing is paramount. Consumers deserve to know where their clothes come from and how they were made. Detailed information about the origin of materials, the manufacturing processes, and the working conditions involved should be readily available, fostering greater awareness and enabling informed purchasing decisions. This transparency allows consumers to make conscious choices, supporting brands committed to ethical practices and contributing to a more sustainable fashion industry.
Fair Labor Practices
Beyond the materials, sustainable sourcing extends to the workers who create the garments. Ethical fashion demands fair wages, safe working conditions, and opportunities for professional development for all those involved in the production process. This includes ensuring that workers are not exploited and receive fair compensation for their labor. Fair labor practices are essential for creating a just and equitable fashion system.
Companies need to actively monitor and audit their supply chains to ensure that labor standards are met. They need to establish clear procedures for addressing worker concerns and grievances, creating a supportive and respectful environment for everyone involved in the production process. By prioritizing fair labor practices, companies can build a more responsible and sustainable fashion industry.
Environmental Impact Reduction
The environmental impact of the fashion industry is significant, encompassing everything from water pollution to greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable sourcing plays a vital role in minimizing this impact. Brands need to carefully evaluate the environmental footprint of their materials and manufacturing processes, implementing strategies to reduce waste, conserve water, and minimize their carbon footprint. This involves exploring innovative technologies and materials with lower environmental impacts.
Sustainable practices, such as using recycled or organic materials, reducing water consumption in dyeing processes, and minimizing packaging waste, are crucial steps toward a more environmentally conscious fashion industry. Innovative approaches and technologies are vital in lowering the environmental impact of production and reducing waste.
Waste Minimization and Circularity
The fashion industry is notorious for its waste, from discarded garments to textile scraps. A key component of sustainable sourcing is minimizing waste throughout the entire lifecycle of a garment, from design and production to consumption and disposal. Embracing circularity, which involves designing products for durability, repairability, and recyclability, is crucial in reducing the environmental burden of fashion.
Promoting the reuse and repurposing of garments, encouraging clothing swaps and donation programs, and exploring innovative ways to recycle textile waste all contribute to a more circular approach to fashion. Implementing these strategies can significantly reduce the environmental impact of the industry, fostering a more sustainable and responsible approach to clothing production and consumption.
Transparency and Traceability
Transparency and traceability are vital components of sustainable sourcing. Consumers need to know the origins of the materials, the manufacturing processes, and the working conditions involved in producing a garment. This knowledge empowers consumers to make informed choices and hold brands accountable for their sustainability efforts.
Providing detailed information about the supply chain, including the names of suppliers and the specific materials used, fosters trust and allows for greater scrutiny. Transparency enables consumers to support brands committed to ethical and sustainable practices, driving a shift towards a more responsible fashion industry.
The Role of Technology in Driving Sustainability

The Automation of Tasks
Technological advancements have led to significant automation of various tasks across numerous industries. From manufacturing plants employing robotic arms to customer service chatbots handling inquiries, technology is streamlining processes and freeing up human workers for more complex and strategic roles. This automation not only boosts efficiency but also reduces errors, leading to higher quality outputs and increased productivity. This shift in task allocation is reshaping the workforce, demanding adaptation and new skill sets from employees.
The implementation of automation technologies has been crucial in improving operational efficiency and reducing costs. By removing the need for human intervention in repetitive and mundane tasks, companies can focus on areas that require creative problem-solving and strategic thinking. This shift has led to a significant transformation in the way businesses operate, demanding that employees adapt to new roles and responsibilities.
Enhanced Communication and Collaboration
Technology has revolutionized communication, enabling instant and global collaboration across geographical boundaries. Video conferencing tools, instant messaging platforms, and cloud-based project management systems have fostered seamless communication and collaboration, regardless of location. This interconnectedness has significantly improved teamwork and productivity, allowing teams to work together more efficiently and effectively. This interconnectedness has also led to a more dynamic and responsive work environment.
Data-Driven Decision Making
The ability to collect, analyze, and interpret data has become a critical component of modern businesses. Technological tools provide businesses with the ability to gather insights from vast amounts of data, enabling them to make informed and data-driven decisions. This empowers companies to understand customer preferences, market trends, and operational inefficiencies with greater accuracy, leading to better strategic planning and optimized resource allocation. Data analysis tools help businesses make better decisions and adapt to changing market conditions more effectively.
Improved Accessibility and Inclusivity
Technology has significantly broadened access to information and opportunities, making them more inclusive for diverse populations. Online learning platforms, accessible websites, and assistive technologies have removed barriers and fostered greater inclusivity. This increased accessibility has empowered individuals with disabilities and those in remote areas, creating more equitable opportunities for participation in the global economy. The proliferation of digital tools has created more opportunities for individuals from various backgrounds.
The Creation of New Industries and Jobs
Technological advancements have spurred the creation of entirely new industries and job sectors. The rise of the internet, mobile technology, and artificial intelligence has led to the development of innovative businesses and career paths that were unimaginable just a few decades ago. From software development and data science to e-commerce and digital marketing, technology has generated countless new opportunities for employment and entrepreneurial endeavors. The rapid pace of technological change creates a constant need for upskilling and reskilling to maintain relevance in the job market.
The Impact on Consumer Experience
Technology has fundamentally transformed the consumer experience, offering unparalleled convenience and personalized interactions. Online shopping, mobile banking, and personalized recommendations have revolutionized how consumers interact with businesses. This personalized approach has led to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty, and fostered a more dynamic and engaging market. The ability to tailor products and services to individual needs has significantly improved the consumer experience and driven business growth.
The Future of Fashion: A Collective Responsibility
Sustainable Practices: A Crucial Shift
The fashion industry's environmental footprint is undeniable, and the future of fashion hinges on a fundamental shift towards sustainability. This means embracing eco-friendly materials like organic cotton, recycled fibers, and innovative plant-based alternatives. Moving beyond the current fast-fashion model, which often prioritizes speed over substance, requires a conscious effort to minimize waste and pollution throughout the entire production cycle, from sourcing raw materials to manufacturing and distribution.
Adopting circular economy principles, where products are designed for reuse and recyclability, is another key element. Brands need to actively consider the lifecycle of their garments, aiming for designs that can be repaired, repurposed, or recycled at the end of their useful life. This not only reduces environmental damage but also fosters a more responsible and ethical approach to consumption.
Ethical Labor Practices: Fair Treatment for All
The ethical treatment of workers is paramount in the future of fashion. Transparency and accountability are essential, and consumers deserve to know the conditions under which their clothes are made. This includes fair wages, safe working environments, and the right to organize for workers in the global supply chain. Brands must actively engage in ethical sourcing and labor practices, partnering with suppliers who prioritize human rights and worker well-being.
Technological Advancements: Innovation in Design and Production
Technological advancements are poised to revolutionize the fashion industry. From 3D printing and digital design tools to innovative materials and sustainable manufacturing processes, technology offers exciting opportunities to streamline production, reduce waste, and create more personalized experiences for consumers. This includes using data analytics to understand consumer preferences and trends, optimizing production processes for efficiency and minimizing environmental impact.
Consumer Awareness and Conscious Consumption
Consumers play a critical role in shaping the future of fashion. Educating consumers about the environmental and social impact of their choices is crucial. Promoting conscious consumption, encouraging the repair and reuse of garments, and supporting brands committed to ethical and sustainable practices are all ways that consumers can contribute to a more responsible fashion industry.
By understanding the lifecycle of their garments, from sourcing to disposal, consumers can make informed decisions that align with their values and support a more sustainable and equitable future for fashion.
Inclusivity and Diversity: Representation for All
The future of fashion must embrace inclusivity and diversity. This means representing a wider range of body types, ethnicities, and gender identities in the industry’s designs and marketing materials. Removing the limitations of traditional beauty standards is crucial for fostering a more representative and equitable fashion landscape. This inclusivity should also extend to the diversity of voices in the design process and the workforce, ensuring that everyone has a platform to contribute their unique perspective.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Fashion Design: Meeting Diverse Needs
Beyond representation, the future of fashion must prioritize accessibility and inclusivity in design. This means creating garments that are adaptable and inclusive of people with varying needs and abilities, ensuring that everyone can participate in the joy of fashion. Designing for diverse body types, mobility challenges, and cultural needs is essential to creating a more inclusive and accessible fashion industry. This also includes making fashion more affordable for everyone, reducing the financial barriers to expressing oneself through clothing.