Compostable Materials: The Ultimate Sustainable Goal for Fashion
The increasing awareness of environmental concerns has spurred a significant shift towards sustainable practices in various industries. Compostable fabrics represent a crucial step in this revolution, offering a viable alternative to traditional materials like petroleum-based synthetics. These fabrics, derived from renewable resources, decompose naturally, minimizing their environmental footprint and reducing reliance on finite resources.
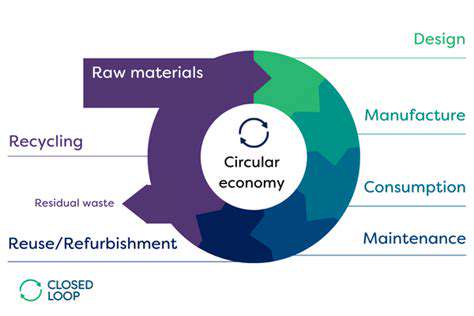
The potential for widespread adoption of compostable fabrics is immense, offering a pathway to a more circular economy where materials are used, repurposed, and returned to the earth, rather than ending up in landfills. This transition promises a more sustainable future for fashion and beyond.
Bio-Based Materials: The Foundation of Compostability
Compostable fabrics are fundamentally different from conventional textiles in their source materials. Unlike synthetic fabrics made from petroleum, compostable fabrics utilize bio-based polymers. These polymers are derived from renewable sources such as agricultural byproducts, plant starches, and even certain types of algae. This reliance on nature-derived materials distinguishes them and makes them a truly sustainable alternative.
The process of converting these bio-based materials into usable fabrics involves a complex interplay of scientific techniques and sustainable agricultural practices. This ensures that the entire lifecycle of the material, from its origins to its final decomposition, is environmentally friendly.
Environmental Benefits: Reducing Landfill Waste
Traditional textiles, especially those made from synthetic materials, often end up in landfills, where they persist for hundreds of years, contributing to the problem of plastic pollution. Compostable fabrics, in contrast, decompose naturally, returning essential nutrients to the soil. This significantly reduces the environmental impact of textile waste.
The decomposition process is accelerated by the natural breakdown of microorganisms in compost environments. This natural process not only eliminates the need for landfills but also enriches the soil, making it more fertile and suitable for agriculture. This is a profound benefit for the planet.
Technological Advancements: Enhancing Performance and Aesthetics
Early compostable fabrics often faced limitations in terms of durability and aesthetic appeal. However, significant advancements in biotechnology and textile engineering have led to compostable fabrics with improved strength, moisture-wicking properties, and a wide range of colors and textures. This evolution allows for the creation of diverse garments and applications.
These advancements also enable the creation of compostable fabrics that can be used in a wide range of applications, from clothing and upholstery to packaging and industrial materials. The enhanced performance and aesthetics open up new possibilities for a more sustainable future.
Challenges and Considerations: Cost and Scalability
One of the primary challenges associated with the widespread adoption of compostable fabrics is the cost. Currently, the production of these fabrics can be more expensive than conventional synthetic materials. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on reducing production costs and increasing efficiency to make compostable fabrics more accessible.
Future Prospects: Integrating Compostable Fabrics into Everyday Life
The future of compostable fabrics looks promising. As research and development continue, the cost is expected to decrease, and the range of applications will expand. The potential for incorporating compostable fabrics into everyday life is significant, from clothing and home textiles to industrial materials and packaging. This will contribute to a significant reduction in textile waste and a more sustainable future.
Consumer demand and government regulations also play a critical role in driving the adoption of compostable fabrics. With increasing awareness and support for sustainable practices, compostable fabrics have the potential to revolutionize the fashion and materials industries.
The Advantages of Compostable Materials in Fashion

Compostable Materials: A Sustainable Alternative
Compostable materials offer a crucial step towards a more sustainable future. Using these materials in everyday products and packaging significantly reduces our reliance on non-biodegradable options, lessening the burden on landfills and promoting environmental health. The decomposition process, achievable through composting, returns valuable nutrients to the soil, fostering a healthy ecosystem.
Enhanced Environmental Impact
The primary advantage of compostable materials lies in their ability to decompose naturally. This contrasts sharply with conventional plastics, which can persist in the environment for centuries. By opting for compostable alternatives, we contribute to a cleaner planet by reducing the accumulation of waste in landfills and the subsequent environmental pollution. This reduction in waste significantly minimizes the strain on our natural resources.
Reduced Landfill Burden
Landfills are overflowing with non-biodegradable waste, leading to environmental problems. Compostable materials, on the other hand, break down into natural components, reducing the volume of waste in landfills and minimizing the negative impact on the surrounding environment. This reduction in landfill waste is a significant step towards a more sustainable future.
By choosing compostable materials, we can lessen the strain on our already overburdened landfill systems. This positive environmental impact leads to a more sustainable and healthier planet.
Economic Benefits
The production of compostable materials can create new economic opportunities. The development and manufacturing of these materials can stimulate job growth in the related industries. Furthermore, the reduced need for waste disposal and landfill management translates into significant cost savings for municipalities and businesses. This results in a more sustainable and efficient resource management system.
Improved Soil Health
Compostable materials, when composted, enrich the soil with essential nutrients. This process helps to improve soil structure, water retention, and overall fertility, promoting healthy plant growth. The nutrients released during decomposition are readily absorbed by plants, leading to improved yields and a more robust ecosystem.
Healthier Food Production
Compostable materials play a crucial role in supporting healthier food production practices. By using compostable packaging and materials, farmers and food producers can reduce their environmental footprint and contribute to more sustainable agriculture. This promotes a healthier environment for both humans and the natural world. The use of compostable materials can lead to more environmentally friendly and sustainable farming practices.
In today's interconnected global economy, ethical considerations in supply chains are no longer optional; they are fundamental. Companies face increasing pressure from consumers, investors, and regulatory bodies to demonstrate responsible sourcing practices. This necessitates a shift from a transactional approach to a collaborative one, recognizing the interconnectedness of businesses and their impact on the broader community.