Resale Platforms: Giving Clothes a Second Life, Again and Again
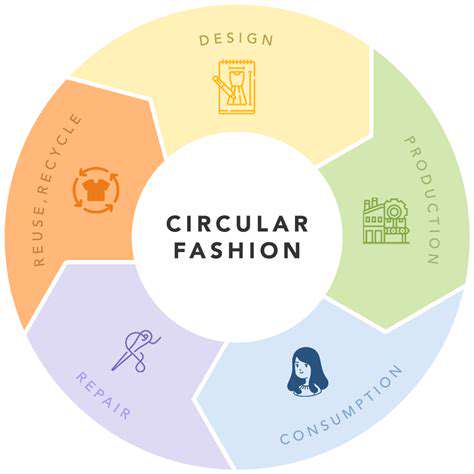
The Rise of the Circular Fashion Economy
The Growing Demand for Sustainable Practices
Consumers are increasingly conscious of the environmental impact of their purchasing decisions, and this heightened awareness is significantly influencing the fashion industry. Consumers are actively seeking out brands that prioritize sustainability and ethical production methods. This shift towards conscious consumption is driving the demand for circular fashion, a model that prioritizes reducing waste and maximizing resource efficiency throughout the entire lifecycle of a garment.
The rise of social media and online platforms has amplified this trend, allowing consumers to easily compare brands and their sustainability efforts. Information about manufacturing processes, material sourcing, and ethical labor practices is readily available, empowering consumers to make informed choices.
Innovative Design and Material Choices
Circular fashion is not just about recycling; it's about reimagining the entire design process. Innovative designers are exploring new materials and techniques to create garments that are durable, repairable, and easily upcycled or recycled at the end of their life cycle. This approach moves beyond the traditional 'fast fashion' model, emphasizing longevity and reduced environmental impact.
The Importance of Durability and Repair
A crucial aspect of circular fashion is the emphasis on durability. Garments designed for longevity are less likely to end up in landfills, and they encourage consumers to repair and reuse items rather than discarding them after a single wear. By investing in products that can withstand multiple uses, circular fashion fosters a more sustainable relationship with clothing.
Repair services and workshops are also becoming increasingly popular, providing consumers with the tools and knowledge to extend the lifespan of their garments. This empowers individuals to take an active role in the circular fashion system.
The Role of Technology in Circularity
Technology plays a significant role in enabling circular fashion. Digital platforms facilitate the sharing and renting of clothing, reducing the need for individual ownership and promoting resource efficiency. Advanced recycling technologies are being developed to process textile waste more effectively, minimizing environmental harm.
Furthermore, technologies like 3D printing and bio-based materials are enabling the creation of innovative, sustainable fabrics and designs, further enhancing the circularity of the fashion industry.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the circular fashion movement is growing rapidly, there are still challenges to overcome. One significant hurdle is the high cost of implementing sustainable practices. Adopting new technologies, developing innovative materials, and establishing recycling infrastructure all require significant investment.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and economic growth. Investing in sustainable solutions can create new jobs, stimulate economic activity, and drive the development of a more environmentally responsible fashion system.
Consumer Behavior and Shifting Attitudes
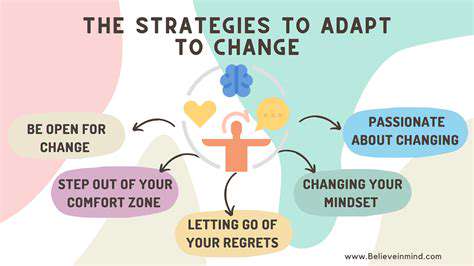
Ultimately, the success of circular fashion hinges on a shift in consumer behavior. Consumers must be willing to embrace new models of consumption, prioritizing durability and repairability over frequent purchases. This requires a fundamental change in mindset, moving away from disposable fashion and towards a more sustainable approach to clothing.
Educating consumers about the benefits of circular fashion and providing them with access to sustainable options are crucial steps in fostering this shift. Brands need to communicate their commitment to sustainability clearly and transparently to build consumer trust and encourage adoption of circular practices.
Environmental Benefits and Economic Opportunities
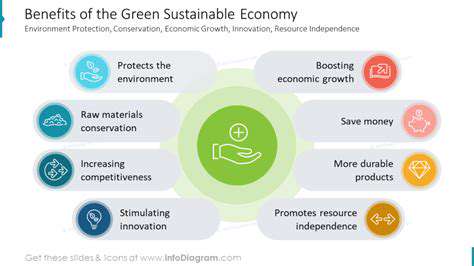
Environmental Sustainability
Environmental sustainability is crucial for the well-being of both present and future generations. Protecting natural resources and ecosystems is essential for maintaining a healthy planet. This involves reducing our environmental footprint through responsible consumption and production patterns. Sustainable practices, such as using renewable energy sources and minimizing waste, are vital to mitigate the effects of climate change and preserve biodiversity.
Implementing sustainable solutions across industries and communities is not just about environmental protection; it's also about creating a resilient and adaptable future. Investing in renewable energy, promoting efficient resource management, and fostering sustainable agriculture are vital steps towards a more environmentally conscious and responsible society.
Economic Opportunities
The transition to a sustainable economy presents significant economic opportunities. Investing in renewable energy technologies, for example, creates new jobs and fosters innovation. Sustainable agriculture practices can increase yields and improve food security, while also reducing environmental impact. This shift towards a circular economy, where waste is minimized and resources are reused, can lead to considerable cost savings and greater efficiency.
Sustainable business practices can enhance a company's reputation and attract environmentally conscious consumers. Companies adopting sustainable practices often find that they improve their bottom line, reduce operational costs, and gain a competitive advantage. This positive feedback loop incentivizes further innovation and investment in sustainable solutions, creating a virtuous cycle of economic growth and environmental responsibility.
Social Equity
Sustainable development recognizes that environmental protection and economic growth should be pursued in a way that addresses social equity. This means ensuring that the benefits of sustainability are distributed fairly and that vulnerable communities are not disproportionately impacted by environmental changes or economic transitions. Sustainable policies should consider the social impact and strive to create a more just and equitable society.
Addressing social inequities often necessitates community engagement and empowerment. Supporting local communities in adopting sustainable practices can create economic opportunities and enhance their resilience to environmental challenges. Promoting access to clean water, sanitation, and sustainable energy sources for marginalized communities is essential for achieving genuine social equity.
Policy and Regulation
Effective policies and regulations are essential to drive the transition towards a sustainable economy. Governments need to implement policies that incentivize sustainable practices and discourage environmentally harmful activities. This includes setting emission reduction targets, promoting sustainable transportation, and supporting the development of renewable energy infrastructure.
Strong regulations and enforcement mechanisms are crucial to ensure that businesses and individuals comply with environmental standards and contribute to a more sustainable future. International cooperation and agreements are also vital for addressing global environmental challenges, such as climate change and biodiversity loss. These collaborative efforts are critical for creating a shared vision and driving collective action towards a more sustainable world.