From Raw Materials to Retail: Auditing for Ethical Practices: New Technologies
Developing a Multi-Stakeholder Approach to Ethical Audits
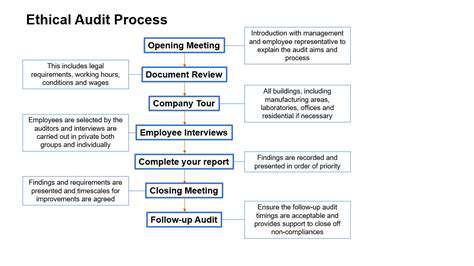
Understanding the Diverse Needs of Stakeholders
Creating effective multi-stakeholder solutions demands comprehensive insight into each party's unique requirements. Beyond primary users, consideration must extend to administrators, secondary beneficiaries, and affected communities. Recognizing and addressing these varied expectations is fundamental to developing genuinely inclusive solutions. Mapping stakeholders' motivations enables designs that foster meaningful participation.
Defining Clear Roles and Responsibilities
Precise delineation of each participant's duties forms the backbone of successful implementation. This encompasses data management protocols, update procedures, and governance frameworks. Well-defined expectations prevent operational bottlenecks while ensuring coordinated effort toward shared objectives. Ambiguity in role assignment frequently leads to duplicated efforts and diminished effectiveness.
Facilitating Collaboration and Communication
Robust interaction mechanisms serve as the lifeblood of multi-party initiatives. Establishing structured touchpoints through digital platforms and face-to-face meetings proves invaluable. Open dialogue cultivates mutual understanding and reinforces collective commitment to project goals. Such transparency transforms potential conflicts into opportunities for constructive problem-solving.
Integrating Diverse Data Sources
Modern solutions frequently require synthesizing information from multiple streams including APIs, legacy systems, and manual inputs. Seamless data integration creates holistic perspectives that empower informed decision-making across all user groups. Attention to standardization protocols and validation procedures ensures consistency throughout the information lifecycle.
Ensuring Data Security and Privacy
Protecting sensitive information represents a non-negotiable requirement in collaborative environments. Implementation of enterprise-grade encryption, role-based access controls, and compliance monitoring forms essential safeguards. Maintaining regulatory compliance while preserving stakeholder confidence demands proactive security measures from project inception. Neglecting this aspect risks both legal consequences and reputational damage.
Testing and Iteration for Stakeholder Feedback
Continual refinement through real-world testing provides critical validation of system effectiveness. Structured feedback mechanisms including user trials and focus groups yield actionable insights. Regular incorporation of stakeholder perspectives ensures solutions remain aligned with evolving requirements throughout the development cycle. This adaptive approach maximizes both functionality and user acceptance.
The Future of Ethical Audits: Adapting to Change
The Rise of AI in Ethical Auditing
Advanced analytics are transforming compliance verification through unprecedented processing capabilities. Machine learning systems can identify subtle irregularities across massive datasets that escape human detection. This enhances oversight quality while allowing professionals to concentrate on strategic evaluation. Predictive modeling further enables preemptive identification of compliance risks before they escalate.
However, algorithmic auditing introduces unique challenges requiring careful management. Training data quality directly impacts system objectivity, making bias mitigation protocols essential. Developing standardized evaluation frameworks ensures artificial intelligence applications meet rigorous fairness criteria. Concurrently, evolving regulatory guidance must address appropriate implementation boundaries for these emerging technologies.
Adapting to Emerging Ethical Challenges
Rapid technological and social changes continuously redefine corporate responsibility expectations. Auditors must develop flexible methodologies capable of addressing novel concerns arising from digital transformation and globalization. Staying current with international standards and industry innovations remains critical for maintaining audit relevance.
The ethical dimensions of automation and artificial intelligence demand specialized assessment frameworks. Evaluation criteria must encompass potential discrimination vectors, data integrity vulnerabilities, and societal impact considerations. Organizations ignoring these dimensions face increasing scrutiny from regulators and consumers alike.
Globalized operations require auditors to navigate complex cultural and legal landscapes with sensitivity. Effective oversight demands understanding how ethical principles manifest differently across jurisdictions while maintaining consistent corporate standards. This includes developing region-specific compliance indicators without compromising overarching ethical commitments.
Sustainability considerations now represent fundamental audit components rather than optional supplements. Professionals must evaluate environmental impact metrics, circular economy implementation, and climate resilience strategies with equal rigor as financial controls. This expansion of scope necessitates continuous education in emerging environmental science and policy developments.
The digital workplace revolution further complicates compliance monitoring. Remote work environments require innovative approaches to data governance, cybersecurity verification, and behavioral compliance assessment. Audit methodologies must evolve to effectively evaluate distributed operations while maintaining rigorous ethical standards.