From Global Supply Chains to Local Impact: New Perspectives

The Role of Technology and Innovation in Localizing Supply Chains
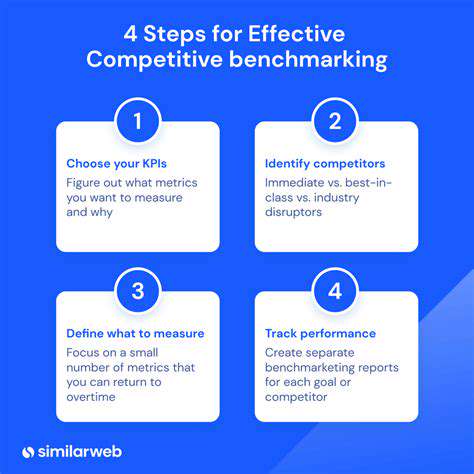
The Evolution of Localized Supply Chains
The globalized supply chains of the past are rapidly evolving, with a growing recognition of the need for localized alternatives. Companies are increasingly recognizing the vulnerabilities inherent in long, complex international supply chains, particularly regarding geopolitical instability, economic downturns, and disruptions like pandemics. This shift towards localization is not simply a reaction to these challenges, but a strategic decision driven by the desire for greater resilience, cost efficiency, and responsiveness to local market demands.
Technology plays a crucial role in facilitating this evolution. From sophisticated logistics platforms to advanced data analytics, companies can optimize their localized supply chains, ensuring efficient flow of goods and services within a given region. This localization process requires a fundamental shift in mindset, moving away from the one-size-fits-all approach and embracing the unique characteristics of different geographical markets.
Technological Advancements Driving Localization
Several technological advancements are driving the localization of supply chains. For instance, advancements in 3D printing technology are enabling on-demand manufacturing, reducing reliance on distant suppliers and facilitating the production of customized goods closer to the consumer. Furthermore, the Internet of Things (IoT) provides real-time data on inventory levels, transportation, and production processes, enabling companies to make informed decisions and optimize their supply chains in real-time.
Data analytics also plays a vital role. By analyzing data from various sources, businesses can identify trends, predict potential disruptions, and optimize their supply chain strategies for greater efficiency and cost savings. These advancements are not just confined to large corporations; smaller businesses can leverage these technologies to build more resilient and responsive supply chains.
Localization and Increased Resilience
Localized supply chains enhance resilience by reducing reliance on international partners and global networks. This approach minimizes the impact of unforeseen events on production and delivery, such as political conflicts, trade wars, or natural disasters. By distributing production and distribution hubs across different geographic regions, companies can create a more robust and stable supply chain that is less vulnerable to external shocks.
Cost Optimization Through Localization
Localization can lead to significant cost savings. Reduced transportation costs, lower tariffs, and streamlined logistics processes are key benefits. Companies can reduce the time it takes for goods to reach consumers, minimizing warehousing costs and inventory holding expenses. By moving closer to their markets, companies can also reduce their exposure to fluctuating exchange rates and import-export costs.
Sustainability and Social Impact of Localized Supply Chains
Localized supply chains often have a positive social and environmental impact. Supporting local businesses and communities fosters economic growth and creates jobs within the region. Companies can also reduce their carbon footprint by minimizing transportation distances and reducing their reliance on long-haul shipping. This can contribute to a more sustainable and socially responsible business model by reducing environmental impact and fostering local economic development.
Building a Future of Localized Resilience
Localizing Resources for Enhanced Accessibility
A key aspect of building a future of localized resources is ensuring that information is readily available and understandable to diverse communities. This necessitates translation and adaptation of content to specific cultural contexts, ensuring that the intended message resonates with the target audience. Localized resources also include adapting formats and presentation styles, considering linguistic nuances and cultural sensitivities.
The goal is to create a seamless experience for users regardless of their language or cultural background. This fosters inclusivity and empowers individuals to access the information they need, promoting better understanding and collaboration.
Leveraging Technology for Effective Localization
Modern technologies play a pivotal role in streamlining the localization process. Automated translation tools, coupled with human review, can significantly reduce costs and timelines. These technologies also enable the creation of more accurate and culturally appropriate translations. Furthermore, these tools can handle a multitude of languages and formats, making the process more efficient and comprehensive.
Developing Robust Localization Strategies
Effective localization requires a well-defined strategy. This strategy should encompass the identification of target audiences, the selection of appropriate translation methods, and the implementation of quality assurance procedures. Careful planning is crucial for achieving desired outcomes and avoiding errors.
A robust strategy also involves establishing clear communication channels between stakeholders, including developers, translators, and end-users.
Addressing Cultural Nuances for Accurate Representation
Localization is not just about translating words; it's about understanding and representing cultural nuances. This includes recognizing and adapting to cultural values, beliefs, and traditions. Failure to account for these subtleties can lead to misinterpretations and potentially harmful outcomes. A deep understanding of the target culture is essential for successful localization.
Ensuring Quality Control Throughout the Process
Maintaining high quality throughout the localization process is critical. This requires rigorous quality assurance measures at each stage. This includes thorough proofreading, editing, and validation by native speakers. Implementing consistent standards ensures that the translated content accurately reflects the original message while adhering to cultural appropriateness.
Prioritizing User Experience in Localized Resources
A key consideration in localization is the user experience. The translated content should be easy to understand and navigate, regardless of the language or cultural background. This includes adapting design elements, ensuring accessibility features are incorporated, and providing clear instructions and support materials.
Promoting Inclusivity through Localized Content
Ultimately, localized resources are about fostering inclusivity and creating a more equitable environment for all. By providing information in multiple languages and culturally sensitive formats, we empower individuals to participate more fully in society and access critical resources. This inclusivity leads to a richer understanding and appreciation of diverse perspectives, contributing to a more harmonious and collaborative world.