The Power of Upcycling in Creative Expression: New Art Forms
Sustainable Style Choices
Choosing sustainable fashion transcends mere environmentalism—it's a declaration of personal principles. When you select garments crafted from recycled fibers or ethically harvested textiles, you're directly diminishing ecological harm while championing equitable labor conditions. This mindful approach to consumption considers not just the final product but the entire lifecycle, from raw materials to community effects.
Eco-conscious apparel frequently emphasizes longevity over temporary fads. Acquiring premium, durable clothing pieces that withstand years of use dramatically decreases the necessity for constant repurchasing, thereby curbing fabric waste and its environmental consequences.
Ethical Production Practices
Moral manufacturing standards form the foundation of sustainable personal expression. This encompasses guaranteeing living wages, secure workplaces, and human rights observance across all production stages. Patronizing companies dedicated to ethical operations cultivates a more just and accountable fashion sector.
Supply chain visibility is essential for comprehending the genuine consequences of your wardrobe decisions. Organizations that disclose details about their manufacturing techniques, materials, and workforce policies enable buyers to make educated choices and demand corporate responsibility.
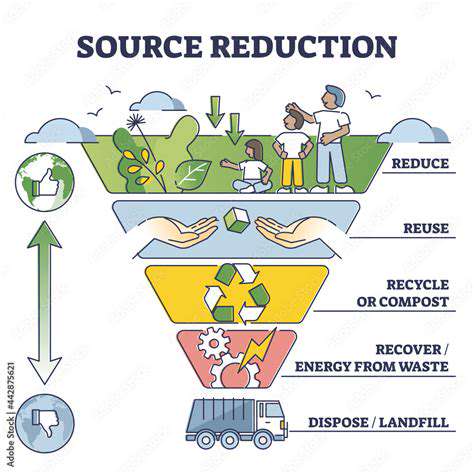
Circular Fashion Models
Adopting circular fashion principles represents a vital component of eco-conscious individuality. These systems concentrate on waste reduction and garment longevity through mending, repurposing, and materials recovery. Implementing circular strategies can substantially lessen the fashion industry's ecological footprint.
This paradigm moves beyond the traditional linear consumption model to embrace a restorative repair-reuse-recycle methodology. Such comprehensive thinking sparks creativity and inspires novel approaches to minimize textile waste across a product's complete lifespan.
Eco-Friendly Materials
Environmentally responsible self-expression frequently incorporates apparel created from sustainable fabrics. Materials like organic cotton, regenerated polyester, or cutting-edge botanical fibers decrease the ecological consequences of clothing manufacture and use. Recognizing various materials' environmental impacts is fundamental for making prudent selections.
Personal Style and Sustainability
Incorporating sustainable methods into your aesthetic identity is an evolving exploration. It requires investigating diverse looks and labels that resonate with your beliefs and tastes. Discovering eco-friendly alternatives that also mirror your distinctive fashion sensibility is absolutely achievable.
At its core, sustainable self-expression means synchronizing your clothing decisions with your convictions and participating in creating a more accountable, environmentally aware society. This deliberate selection process deepens our relationship with personal aesthetics while collectively advancing a greener tomorrow.
The Impact of Conscious Consumption
Deliberate purchasing behavior significantly influences the development of sustainable fashion systems. When buyers favor ethical and eco-conscious companies, they generate demand for responsible practices and motivate corporations to implement more environmentally sound and socially equitable methods. This cascade effect benefits the entire apparel ecosystem.
Through supporting sustainable enterprises and initiatives, consumers propel the industry toward a more ethical and ecologically balanced direction. Purchases become more than transactions—they're active participation in reshaping the sector's evolution.
Exploring Diverse Artistic Mediums: From Furniture to Fashion

Exploring Painting and Sculpture
Painting, an enduring creative tradition, enables artists to preserve emotions, scenery, and conceptual ideas on surfaces. Utilizing diverse brushes, pigments, and methods produces an extensive array of visual interpretations, from Impressionism's subtle touches to Abstract Expressionism's vigorous strokes. Commanding color dynamics, shape relationships, and spatial organization is paramount in painting, requiring profound medium expertise. Practitioners must account for lighting effects, chromatic interactions, and coherent visual storytelling.
Sculpture, another potent artistic vehicle, materializes three-dimensional expressions. From Hellenic representations of human perfection to modern assemblies questioning artistic conventions, sculptural works engage observers with spatial dimensions. Creators utilize numerous substances—marble, bronze, timber, metals, and repurposed items—each offering distinct textural and formal opportunities. Transforming raw materials into physical manifestations of concepts constitutes the essence of this creative practice. Meticulous attention to size relationships, compositional harmony, and equilibrium is vital for producing compelling sculptural works.
Delving into Photography and Digital Art
Photography, a more contemporary medium, has transformed visual storytelling. By immortalizing transient instants as concrete images, photographers employ illumination, framing, and vantage points to communicate stories and feelings. From spontaneous urban scenes documenting ordinary existence to carefully arranged character studies, this format provides boundless creative potential. The capacity to preserve and disseminate moments constitutes a formidable artistic instrument.
Digital art, an exponentially growing domain, spans immense innovative territory. From raster image alterations to sophisticated virtual paintings, digital creators harness software to produce astonishing, avant-garde artworks. Technological accessibility has equalized creative opportunities, permitting extensive stylistic experimentation. The merging of digital tools with artistic imagination has established groundbreaking expressive channels. This medium's progression demonstrates technology's creative potential.
Digital instruments facilitate exploration of sophisticated ideas and generation of meticulous imagery. Precise manipulation of hues, forms, and surfaces represents a major digital advantage. The capacity for rapid prototyping and revision enables extensive creative refinement.
Modern practitioners frequently blend multiple mediums, illustrating artistic discipline interconnectedness. Such stylistic synthesis yields original, provocative creative statements.
The Future of Creativity: Embracing the Circular Economy
Reimagining Waste as Resource
The circular economic framework radically alters our waste perception, transitioning from linear consumption to cyclical systems. This conceptual revolution requires viewing discards as valuable assets with transformation potential. Through prioritizing reuse, restoration, and reapplication, we can significantly decrease consumption's environmental impact, preserving resources and reducing landfill contributions.
This transformation demands collaborative action from manufacturers, consumers, and regulators. Enterprises must implement inventive product strategies emphasizing longevity, maintainability, and material recovery. Consumers contribute by selecting circular economy products, utilizing repair services, and undertaking inventive repurposing endeavors.
Upcycling: Transforming Trash into Treasure
Upcycling surpasses basic recycling, converting waste materials into novel, valuable items. This imaginative practice revitalizes objects otherwise destined for disposal, converting refuse into assets. Upcycling cultivates resourcefulness, motivating individuals to devise inventive waste solutions.
Potential applications are limitless. Worn apparel becomes fashionable carriers, scrap timber transforms into distinctive furnishings, and damaged electronics evolve into functional artworks. The creative scope extends beyond physical items to include concepts and theories, unveiling new expressive and problem-solving avenues.
The Economic Benefits of a Circular Economy
Implementing circular economic models yields substantial financial benefits. Waste reduction decreases material procurement and disposal expenses. Additionally, circular systems stimulate innovation, generating sustainable products, services, and sectors. This creates employment in repair, reuse, and upcycling fields, promoting sustainable economic development.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Upcycling
Technological advancements critically improve upcycling efficiency and quality. Additive manufacturing enables complex designs using recycled materials, permitting customized upcycled goods. Digital platforms connect upcycling participants, facilitating resource and knowledge sharing. This technological framework supports more effective upcycling networks.