Investing in Humanity: The New Returns of Ethical Sourcing
Ethical Considerations in Business
Navigating today's intricate business environment demands more than just financial acumen—it requires a steadfast commitment to ethical principles. Organizations that embed ethics into their core operations frequently enjoy heightened brand credibility and enduring customer relationships, which directly contribute to sustained profitability. The ethical decision-making matrix spans diverse domains: equitable labor policies, ecological stewardship, transparent supplier networks, and beyond. A robust ethical framework ensures companies thrive economically while honoring their societal obligations.
When businesses demonstrate ethical integrity, they cultivate trust across all stakeholder groups—from employees and consumers to investors and local communities. This trust manifests as improved workplace dynamics, stronger customer connections, and enhanced organizational stability. Instilling an ethical culture isn't about temporary initiatives; it's a continuous journey requiring unwavering dedication from every leadership tier.
The Consequences of Ethical Lapses
Ethical violations can trigger catastrophic outcomes for businesses. A solitary ethical misstep may permanently tarnish a company's standing, eroding consumer confidence beyond repair. Such breakdowns in trust frequently precipitate customer boycotts, damaging media exposure, and dwindling investment interest. The financial fallout can be severe, jeopardizing both immediate earnings and future viability.
Beyond financial implications, unethical conduct often invites legal consequences including regulatory penalties, civil litigation, and potentially criminal proceedings. The reputational harm alone can paralyze a company's operations, diminishing market position and overall competitiveness.
Cultivating an Ethical Organizational Culture
Developing an ethical corporate culture necessitates a comprehensive, forward-looking strategy. This begins with formulating explicit ethical standards and behavioral codes that are thoroughly disseminated throughout the workforce. These guidelines should address multifaceted issues ranging from conflict resolution to sustainable operations. Complementing these standards with regular ethics training ensures employees internalize these principles in their daily work.
Executive leadership carries particular responsibility in modeling ethical conduct. Senior management must personify ethical values, champion principled decision-making, and guarantee ethical considerations inform all strategic choices. Additionally, implementing confidential reporting mechanisms for ethical concerns promotes organizational transparency and accountability.
Ethical Business in the Global Marketplace
As global interconnectivity intensifies, ethical business practices grow increasingly vital. Modern consumers actively evaluate the moral dimensions of their buying decisions, preferentially supporting companies that mirror their ethical convictions. This consumer awakening presents substantial opportunities for ethically-driven enterprises.
The evolution of ethical business will likely emphasize unprecedented transparency and answerability. Corporations must openly disclose operational practices and accept responsibility for their societal and environmental impacts. This transformation requires moving beyond pure profit motives to embrace a balanced perspective that prioritizes stakeholder welfare alongside financial results.
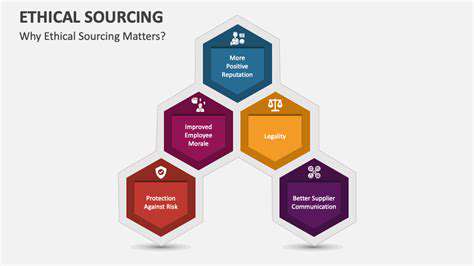
The Tangible Benefits of Ethical Sourcing
Brand Reputation Enhancement
Ethical sourcing has transitioned from optional to essential for corporate reputation management. Today's consumers critically examine the societal and ecological ramifications of their purchases, actively patronizing brands that demonstrate ethical commitments. Visible dedication to responsible sourcing significantly elevates brand perception, attracting value-driven customers who prioritize integrity. This enhanced reputation fosters greater consumer trust, repeat business, and ultimately, improved financial performance.
Ethically-conscious buyers frequently become brand advocates, generating organic marketing through positive referrals. This goodwill extends beyond immediate transactions, strengthening long-term brand equity and insulating companies against future reputational challenges.
Workforce Motivation and Stability
Ethical sourcing initiatives inspire employee dedication by connecting daily work to meaningful social impact. Workers take pride in organizations that champion human rights and environmental protection, resulting in heightened engagement and job satisfaction. Companies prioritizing ethical procurement cultivate workplace cultures grounded in moral principles, leading to improved retention rates and lower turnover expenses. The outcome is a more consistent, productive employee base.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Ethical sourcing provides natural protection against supply chain vulnerabilities and misconduct-related hazards. Through transparent supplier relationships, companies gain operational visibility that helps preempt potential issues. This vigilance minimizes exposure to damaging publicity, legal entanglements, and financial penalties stemming from unethical practices. Responsible sourcing establishes supply networks characterized by reliability and adaptability.
Operational Optimization
Ethical sourcing frequently yields unanticipated efficiency gains. Partnering with suppliers who uphold fair labor standards often reveals process improvements, waste reduction opportunities, and quality enhancements. Supply chains built on mutual trust and openness typically achieve long-term cost reductions, delivering competitive advantages in crowded markets.
Product Excellence and Advancement
Ethical procurement naturally emphasizes superior materials and craftsmanship, as suppliers maintain rigorous quality benchmarks. This focus spurs product innovation as companies collaborate with like-minded partners committed to excellence. The resulting quality improvements elevate customer satisfaction and brand perception.
Market Expansion Potential
Ethical credentials unlock access to new business opportunities and partnerships. Organizations recognized for principled practices attract investors, collaborators, and customers sharing similar values. This facilitates market diversification and alliances with sustainability-focused entities, driving business growth through ethical leadership.
Stakeholder Relationship Building
Ethical sourcing strengthens bonds with all organizational stakeholders—customers, employees, investors, and communities alike. Demonstrable commitment to ethical standards fosters openness and confidence, enabling more productive interactions and cooperative ventures that benefit all parties.

Investing in a Sustainable Future: A Long-Term Perspective

Environmental Stewardship Imperative
Sustainability investment has evolved from specialty concern to business necessity. The tangible effects of environmental neglect—from coastal flooding to climate volatility—demand immediate action. Sustainable strategies encompass both footprint reduction and climate adaptation, creating resilient systems for future generations. The renewable energy transition and green technology sector present remarkable innovation potential.
Environmental responsibility helps mitigate climate risks while preserving ecological health. Companies integrating sustainability into their DNA often attract eco-conscious consumers and investors, demonstrating forward-thinking leadership that builds market confidence.
Sustainable Economic Development
Environmental and economic objectives need not conflict. Numerous sustainability initiatives generate employment and spur technological breakthroughs. The clean energy sector exemplifies this synergy, creating jobs while reducing carbon emissions.
Sustainable infrastructure investments yield substantial economic returns over time. Reduced resource dependence and environmental protection translate to long-term cost efficiencies. Simultaneously, sustainability commitments enhance corporate reputation and market reach.
Equitable Sustainability Transition
True sustainability addresses social disparities, ensuring fair access to emerging opportunities. Sustainable development must prioritize vulnerable populations, distributing benefits equitably across society. The shift toward green economies requires careful consideration of social impacts to prevent exacerbating existing inequalities.
Fair employment conditions, resource accessibility, and inclusive community development constitute essential elements of comprehensive sustainability. The goal extends beyond environmental protection to creating opportunities for all demographic groups.
Technological Solutions for Sustainability
Technological innovation drives sustainable progress across sectors. Breakthroughs in energy storage, sustainable materials, and efficient systems accelerate our transition to cleaner operations. Dedicated research investment remains critical for developing next-generation environmental solutions.
Priority areas include renewable energy infrastructure, energy efficiency enhancements, and sustainable mobility systems. These advancements promise not only ecological benefits but also improved quality of life through smarter, cleaner technologies.
Policy Frameworks for Global Sustainability
Effective governance structures are indispensable for coordinated global sustainability efforts. International agreements establish collective targets and align multilateral action toward shared environmental goals. Well-designed regulations and incentives encourage widespread adoption of sustainable practices.
Policy focus areas span carbon pricing, renewable energy adoption, responsible resource management, and sustainable consumption patterns. Governments must balance support for green innovation with accountability measures, while international cooperation addresses planetary-scale challenges like climate change and biodiversity loss.