The Business Case for Circularity: Beyond Sustainability: New Data
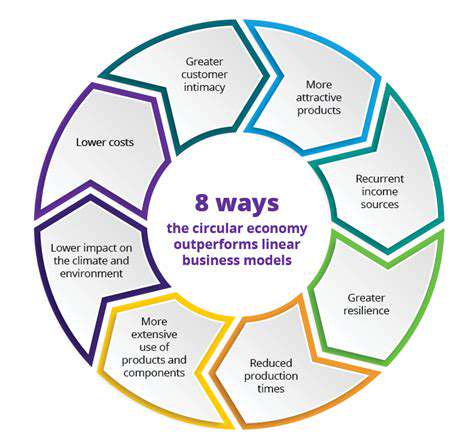
Quantifying the Financial Benefits of Circularity
Improved Resource Efficiency
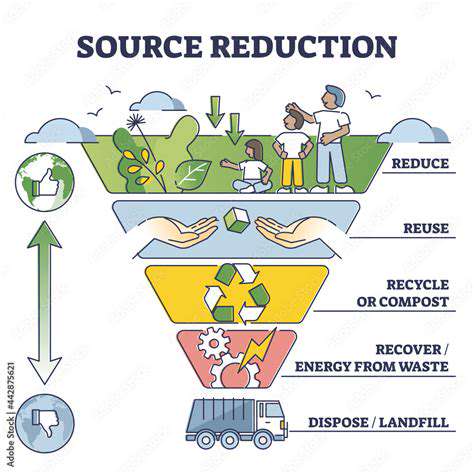
The transition from linear to circular systems creates dramatic efficiency gains. When materials stay in use through multiple lifecycles, procurement costs plummet while environmental impacts shrink. Consider plastic bottle manufacturing: comprehensive recycling programs can slash material expenses by 30% or more while reducing the operation's ecological footprint.
Reduced Waste Disposal Costs
Waste management expenses represent a major – and often unnecessary – cost center. Circular approaches attack this problem at its source by minimizing waste creation and maximizing reuse. Industries with traditionally high waste outputs (like packaging and electronics) can realize particularly dramatic savings, sometimes cutting disposal costs by half or more through smart redesign and recycling initiatives.
Enhanced Brand Reputation and Consumer Loyalty
Today's consumers increasingly vote with their wallets for sustainable brands. Companies demonstrating authentic circular commitments often enjoy stronger customer retention and premium pricing power. In many markets, sustainability has become the deciding factor in purchase decisions, making circular practices a powerful differentiator.
Increased Innovation and New Revenue Streams
Circular thinking sparks creative problem-solving that frequently leads to profitable innovations. Businesses developing novel uses for recycled materials or pioneering sustainable technologies often discover entirely new market segments with limited competition and strong growth potential.
Improved Supply Chain Resilience
In our volatile global economy, circular strategies provide crucial stability. By diversifying material sources and incorporating recycled inputs, companies buffer themselves against price spikes and supply disruptions. This resilience becomes increasingly valuable as resource scarcity and geopolitical tensions continue to challenge traditional supply chains.
The Role of Technology in Circularity Implementation
Technological Advancements in Waste Management
Modern waste management has been transformed by intelligent sorting systems that achieve unprecedented material recovery rates. These AI-driven solutions not only keep more waste out of landfills but also produce higher-quality recycled materials that command better market prices.
Circular Economy Models Powered by Technology
Digital platforms now connect producers and consumers in innovative sharing ecosystems. These technological solutions extend product lifespans dramatically while creating new business opportunities in the sharing economy.
Data Analytics for Resource Optimization
Advanced analytics turn waste streams into data streams, revealing patterns and opportunities invisible to traditional analysis. Smart bins and route optimization algorithms are just the beginning of this data revolution in resource management.
Sustainable Manufacturing and Product Design
3D printing represents a manufacturing revolution, enabling precise, on-demand production with minimal material waste. Combined with circular design principles emphasizing durability and recyclability, these technologies are reshaping how products enter the market.
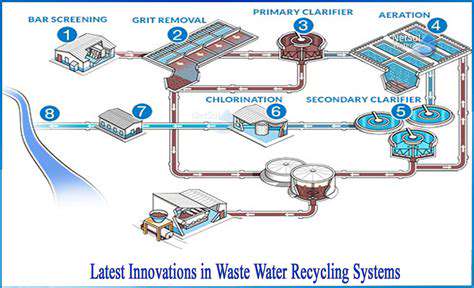
Enhanced Recycling Processes and Material Recovery
Today's material recovery facilities use everything from AI vision systems to advanced separators to achieve purity levels that were impossible a decade ago. These technological leaps make closed-loop systems increasingly practical and profitable.
Improved Tracking and Transparency
Blockchain and IoT solutions now provide unprecedented visibility into material flows. This transparency helps companies and consumers make better decisions while holding all supply chain participants accountable for their environmental impacts.
The Future of Circular Technology
Emerging bio-based materials and molecular recycling technologies promise to push circularity even further. These innovations will continue rewriting the rules of sustainable business, creating opportunities for those prepared to lead rather than follow.
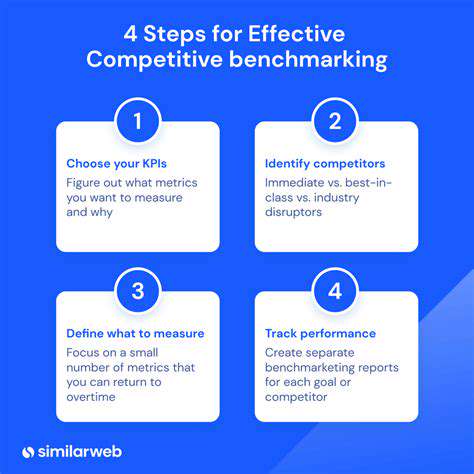
Measuring and Reporting on Circularity Performance
Defining Circularity Metrics
Effective measurement begins with clear, relevant metrics tailored to each business context. The most insightful KPIs track material flows throughout the entire value chain, from sourcing through end-of-life, creating a complete picture of circular performance.
Tracking Resource Consumption and Waste Generation
Granular tracking systems reveal exactly where resources enter and leave the system. This visibility uncovers hidden inefficiencies and opportunities that traditional accounting often misses.
Assessing Product Lifespan and Durability
Longevity metrics provide crucial insights into product design effectiveness. Companies excelling in this area often discover surprising revenue opportunities in repair services, refurbishment, and secondary markets.
Analyzing Material Recovery and Recycling Rates
Sophisticated material flow analysis helps companies identify which components and materials offer the best recovery potential, guiding smarter design and recycling investments.
Communicating Circularity Performance to Stakeholders
Transparent reporting builds trust while differentiating brands in competitive markets. The most effective communications highlight both business and environmental benefits, demonstrating how circular strategies create value for all stakeholders.