The Power of Data in Driving Ethical Transparency and Accountability
Data Integrity and Accuracy
Maintaining precise and reliable data forms the foundation of trust-building. When information is repeatedly incorrect or inconsistent, it undermines confidence in any system dependent on it. This principle is non-negotiable for sustaining credibility and cultivating a favorable organizational reputation. Implementing thorough data verification processes and periodic evaluations helps identify and rectify mistakes, guaranteeing dependable results.
Establishing comprehensive data management protocols creates standardized approaches for information quality, accessibility, and application. These measures minimize opportunities for mistakes and discrepancies, resulting in more credible data. True data quality extends beyond mere accuracy; it must also consider currentness, thoroughness, and applicability to the situation at hand.
Data Accessibility and Sharing
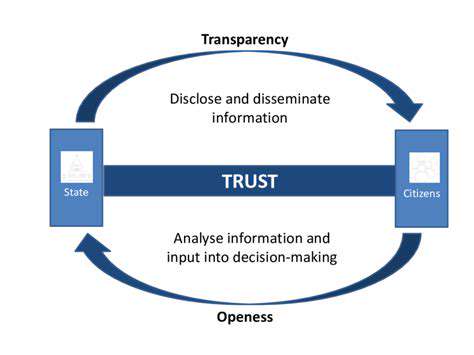
Making data available to appropriate parties serves as a significant trust-building mechanism. When stakeholders can observe how information informs decisions, it creates openness and enables proper evaluation. This visibility nurtures confidence, stimulating cooperation and responsibility across organizations.
Nevertheless, potential drawbacks of widespread data availability must be carefully weighed. These include safeguarding confidential details and guaranteeing proper handling of shared information. Clear guidelines regarding data access must strike an appropriate balance between transparency and necessary protections for security and personal privacy.
Data Explanation and Contextualization
Offering detailed interpretations and background information about data is crucial for proper comprehension and application. Information without proper framing often becomes useless or misunderstood. This proves particularly vital in technical fields where analytical results might support multiple conflicting conclusions. Comprehensive documentation that explains measurement parameters, research techniques, and inherent constraints enhances clarity and minimizes confusion.
Complete records should specify origins of information, gathering procedures, and possible distortions. Supplying relevant background helps users recognize constraints and potential effects on analytical outcomes.
Data Security and Privacy
Safeguarding confidential information remains fundamental for establishing and preserving trust. Protective measures are indispensable for preventing improper viewing, utilization, or distribution. Advanced encryption, permission-based access systems, and routine security assessments constitute essential elements of an effective data protection strategy.
Privacy concerns demand equal attention, necessitating adherence to applicable laws and standards. Open communication about information gathering protocols and policies proves crucial for gaining confidence from data providers.
Data Usage and Accountability
Explicit standards for information application are necessary to enforce responsibility and guarantee ethical handling. Revealing who can access data, how it's utilized, and what conclusions are drawn promotes confidence throughout the information ecosystem.
Creating procedures for periodic examinations helps sustain responsibility and correct potential misapplications. Those handling information should face consequences for improper actions, reinforcing integrity throughout the data lifecycle.

Promoting Data Literacy and Ethical Awareness
Promoting Data Literacy
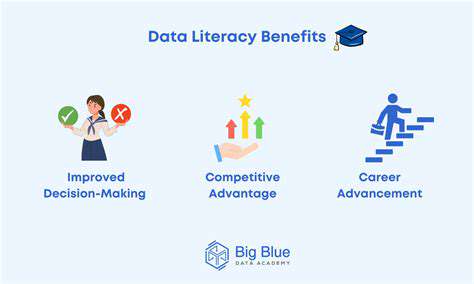
Understanding data has become essential in our information-centric environment. This extends beyond basic spreadsheet skills to developing analytical capabilities regarding information origins, constraints, and potential distortions. Data competence enables people to base choices on factual evidence rather than speculation or false premises. This evaluative capacity is indispensable for managing modern complexities and making prudent judgments across multiple disciplines.
Cultivating data proficiency requires diverse educational strategies. These include mastering core concepts like information classification, gathering techniques, and analytical approaches. Importantly, they must also encompass moral implications of data applications. Developing data skills isn't merely technical training; it's about establishing evidence-based thinking patterns. This proves particularly valuable in healthcare, social research, and commerce, where data insights drive meaningful progress.
Data-proficient individuals can recognize significant developments and irregularities in information. They can evaluate source reliability and convey findings to varied audiences. These interpretation skills benefit numerous professions, including media, academia, and strategic planning. Enhanced data understanding creates better-informed communities, more capable workers, and ultimately, a society guided by verifiable facts.
Ethical Considerations in Data Handling
Moral data practices are critical in our data-intensive era. Ethical data treatment involves more than avoiding damage; it requires building confidence, ensuring equity, and honoring personal boundaries throughout information collection and utilization. Data morality covers numerous principles, from protecting confidentiality to preventing prejudiced algorithmic outcomes.
Comprehending and following ethical standards is vital for maintaining public confidence and responsible data management. This involves transparent collection methods, proper consent procedures, and security against unauthorized usage. All parties must acknowledge their obligations when handling sensitive information.
Tackling challenges like computational prejudice, security violations, and potential data abuse demands coordinated efforts from legislators, technologists, and citizens. Encouraging ethical standards requires continuous learning, cooperation, and dedication to core values. By prioritizing responsible data culture, we can ensure information benefits society collectively.