Ethical Sourcing and the Pursuit of Decent Work: New Benchmarks
In today's interconnected global economy, the concept of ethical sourcing has evolved from a desirable practice to a crucial necessity for businesses seeking long-term sustainability and profitability. The complexities of global supply chains, often spanning multiple countries and involving numerous suppliers, create significant challenges in ensuring ethical treatment of workers, environmental protection, and fair labor practices. Companies neglecting these aspects risk reputational damage, legal repercussions, and diminished consumer trust, impacting their bottom line and long-term viability.
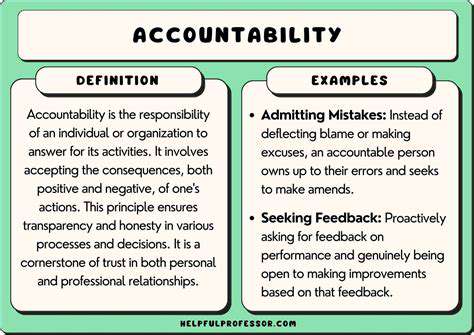
Transparency and accountability are paramount in ethical sourcing. Businesses must actively engage with their suppliers to understand their labor practices, environmental impact, and adherence to ethical standards. This includes implementing robust due diligence processes, conducting regular audits, and fostering open communication channels. Only through a thorough understanding of the entire supply chain can companies effectively identify and address potential ethical violations and build a truly sustainable and responsible system.
The Impact of Unethical Practices on Consumers and Communities
The consequences of unethical sourcing extend far beyond the immediate stakeholders of a company. Consumers are increasingly conscious of the ethical implications of their purchasing decisions, demanding greater transparency and accountability from brands. When companies engage in unethical sourcing practices, it can lead to a loss of consumer trust and loyalty, impacting sales and brand reputation. This erosion of trust can be particularly damaging in today's digital age, where negative reviews and social media campaigns can rapidly spread and significantly harm a company's image.
Furthermore, unethical practices often have a devastating impact on workers and communities in developing countries where many supply chains originate. Exploitation of labor, unsafe working conditions, and environmental degradation can lead to serious social and economic consequences. Companies that prioritize profit over ethical considerations contribute to a cycle of poverty and inequality, undermining the very communities they rely on for their products.
The Role of Technology and Innovation in Enhancing Ethical Sourcing
Technological advancements offer powerful tools for enhancing ethical sourcing practices. Digital platforms, data analytics, and blockchain technology can provide unprecedented transparency into the complex web of suppliers and production processes. Implementing these technologies can facilitate real-time monitoring of working conditions, environmental impacts, and labor standards, allowing companies to identify and address potential issues proactively. This increased visibility can also help build trust with consumers and stakeholders by showcasing the commitment to ethical practices.
Beyond monitoring, technology can also streamline the entire ethical sourcing process. Automated audits, improved communication channels, and data-driven decision-making can enhance efficiency and effectiveness. By embracing these innovative tools, companies can create more sustainable, transparent, and responsible supply chains that benefit both businesses and the communities they serve. This proactive approach to ethical sourcing is not only ethically sound but also strategically advantageous in the long run.

Implementing Ethical Sourcing Initiatives: A Holistic Approach
Understanding Ethical Sourcing Principles
Ethical sourcing isn't just a buzzword; it's a fundamental shift in how businesses operate, recognizing the interconnectedness of their supply chains with social and environmental well-being. It encompasses a range of principles, from fair wages and safe working conditions for laborers to responsible resource management and environmental protection. Understanding these principles is crucial for implementing effective initiatives that go beyond mere compliance and truly impact positive change throughout the entire supply chain, from raw material extraction to final product delivery.
A comprehensive understanding of ethical sourcing must include the recognition of diverse perspectives and needs. This involves a deep dive into the specific challenges and opportunities in different regions and industries, acknowledging the unique contexts that shape labor practices and environmental concerns. Understanding these nuances is essential for developing initiatives that are not only effective but also culturally sensitive and respectful of local traditions and customs.
Establishing Clear Ethical Sourcing Policies
Creating a robust ethical sourcing policy is paramount. This policy should be clearly articulated, encompassing specific standards for all aspects of the supply chain, from supplier selection to production processes. It needs to detail requirements for fair wages, safe working conditions, environmental responsibility, and the prohibition of child labor and forced labor. Moreover, the policy should outline clear procedures for monitoring compliance, investigating potential violations, and taking corrective actions.
Implementing Effective Monitoring and Evaluation Mechanisms
Ethical sourcing isn't a one-time project; it's an ongoing commitment. Implementing robust monitoring and evaluation mechanisms is critical to ensure that policies are being followed and that progress is being made. This involves regular audits of suppliers, assessments of working conditions, and data collection on environmental impacts. Regular reporting and feedback loops are crucial for identifying areas needing improvement and adapting strategies as necessary.
The evaluation process should also consider the impact on local communities. This means not just focusing on the immediate workers but also considering the wider economic and social effects of the sourcing practices. Evaluating the long-term sustainability of the initiatives is key to ensuring lasting positive change.
Building Strong Partnerships and Fostering Transparency
Collaboration is key to ethical sourcing success. Building strong partnerships with suppliers, NGOs, and community organizations is crucial for sharing best practices, fostering transparency, and collectively working towards common goals. Transparency in all aspects of the supply chain, from the origin of materials to the production process, allows for greater accountability and trust. This transparency fosters a collaborative environment where all stakeholders can participate actively in improving ethical sourcing practices.
Open communication and collaboration with stakeholders, including consumers and the wider public, are vital for achieving broader buy-in and for building a shared understanding of the importance of ethical sourcing. This can lead to increased consumer trust, brand loyalty, and a more sustainable future.