How Resale Platforms Are Reshaping the Fashion Industry: New Dynamics
The Rise of the Circular Economy in Fashion
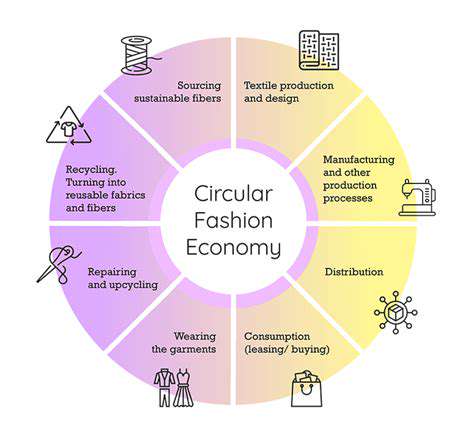
The Core Principles of Circularity
Moving beyond the traditional linear model of take-make-dispose, the circular economy focuses on maximizing resource efficiency and cutting waste. At its heart lies the design of products that last longer, can be easily repaired, and are fully recyclable. This transformative approach is essential for reducing the ecological footprint of consumption and production, paving the way for a greener tomorrow. By prioritizing the extended use of materials and minimizing waste generation, this model represents a fundamental shift in how we think about resources.
Economic Benefits of Circularity
Embracing circular economy principles unlocks substantial financial advantages. Companies that reduce waste and enhance resource efficiency can slash production costs while tapping into new revenue opportunities through material recovery. Circular strategies spur innovation and generate employment in sectors like recycling, product refurbishment, and sustainable design. Moreover, this transition builds economic resilience by decreasing reliance on scarce natural resources.
Environmental Impact of Linearity
Our current linear economic system - extract, produce, discard - has wreaked havoc on the planet's ecosystems. From pollution to habitat destruction and climate change, the environmental toll is undeniable. Mountains of waste from this system choke landfills and contaminate our air, waterways, and soil. The urgent need for systemic change has never been clearer as we face these mounting ecological crises.
Technological Advancements Driving Circularity
Cutting-edge technologies are accelerating the shift toward circular systems. Breakthroughs in material science, production techniques, and waste processing enable smarter product design and optimal resource utilization. These innovations facilitate closed-loop cycles where materials circulate continuously through reuse and recycling networks. Such systems create a virtuous circle that benefits both economic growth and environmental preservation.
Policy Support for Circular Initiatives
Governments wield significant influence in advancing circular economy adoption through strategic policymaking. Legislation that rewards reuse and recycling while penalizing wasteful practices can dramatically accelerate the transition. Financial incentives, supportive regulations, and penalties for linear practices create fertile ground for circular business models to thrive. Successful implementation demands collaboration across government agencies, corporations, and individual consumers.
Consumer Role in Circular Economy
Individual purchasing decisions collectively shape market demand and drive systemic change. Opting for durable, repairable goods instead of disposable items represents a powerful consumer choice. Supporting circular businesses and actively participating in reuse programs allows shoppers to directly contribute to sustainability efforts. These daily decisions gradually transform consumption patterns toward greater environmental responsibility.
Enhancing Transparency and Traceability in Fashion
Improving Supply Chain Visibility
Modern resale marketplaces are transforming fashion by illuminating previously opaque supply chains. Detailed disclosures about garment origins, materials, and manufacturing processes empower buyers to make values-aligned purchases. This transparency extends throughout a product's lifecycle, tracking its journey from initial production through subsequent owners and any modifications. Such comprehensive visibility helps consumers identify and support ethically responsible brands while avoiding problematic ones.
Advanced verification systems combat counterfeit goods and unethical labor practices by authenticating products and confirming ethical sourcing. These measures build consumer confidence while discouraging purchases that harm people or the planet. By documenting material origins and treatment processes, resale platforms enable shoppers to make informed choices that reflect their environmental and social values.
Promoting Sustainable Consumption Patterns
The growing popularity of secondhand fashion directly supports more sustainable consumption habits. Extending the lifespan of clothing reduces demand for new production, significantly lowering the textile industry's environmental impact. This shift conserves water resources, decreases pollution, and alleviates pressure on ecosystems. The economic benefits mirror the environmental advantages, as circular models minimize waste while creating new business opportunities.
Resale platforms encourage thoughtful purchasing by offering diverse pre-owned alternatives to fast fashion. This fosters appreciation for quality over quantity, helping consumers build distinctive wardrobes without supporting unsustainable production practices. The movement toward slower, more intentional fashion consumption represents a crucial step in industry transformation.
Facilitating Authenticated Resale and Reduced Waste
Trust forms the foundation of successful resale markets, leading platforms to implement rigorous authentication protocols. Partnerships with verification experts and advanced inspection processes protect buyers while legitimizing the secondhand market. These measures prevent counterfeit infiltration, creating safer trading environments for all participants.
The environmental benefits of resale are equally significant. By keeping garments in circulation longer, these platforms dramatically reduce textile waste - a major sustainability challenge for the fashion industry. This circular approach decreases demand for resource-intensive new production, conserving materials and reducing ecological damage. As awareness of fashion's environmental impact grows, resale platforms offer practical solutions for conscious consumers.
Challenges and Opportunities for the Future

Navigating the Complexities of Technological Advancement
Rapid technological evolution creates both obstacles and possibilities for businesses. Staying competitive requires agility in adopting innovations while managing associated risks through continuous learning and skills development. Emerging technologies frequently spawn entirely new markets and business paradigms, demanding organizational flexibility and creative thinking.
The accelerating pace of change necessitates ongoing workforce education to maintain relevant skillsets. Ethical considerations surrounding technologies like AI require careful attention to ensure responsible development and maintain public trust in these systems.
Addressing the Skills Gap and Talent Acquisition
The widening skills shortage presents a critical challenge across industries. Strategic recruitment and educational partnerships become essential for developing talent pipelines with future-ready capabilities. Comprehensive training programs and mentorship initiatives help bridge competency gaps, requiring sustained organizational commitment to workforce development.
Harnessing the Power of Innovation and Creativity
Forward-thinking organizations cultivate cultures that encourage experimentation and idea generation. Providing resources for innovation while accepting measured risk-taking enables breakthrough solutions to emerge. Regular evaluation of processes and willingness to adapt ensures companies remain responsive to shifting market dynamics.
Overcoming the Barriers to Digital Transformation
Transitioning to digital operations involves substantial investments in technology infrastructure and personnel training. A phased implementation approach helps organizations manage this complex transition while addressing resistance to change through clear communication and change management strategies.
In today's interconnected world, robust cybersecurity measures are non-negotiable for protecting sensitive data and maintaining operational integrity. Proactive security protocols mitigate risks that could otherwise damage reputation, finances, and customer relationships.
Exploring the Future of Work and Collaboration
Technological progress continues reshaping workplace dynamics, requiring adaptation to remote work models and digital collaboration tools. Ensuring equitable technology access supports inclusive participation in evolving work environments.
While automation and AI present efficiency gains, they also raise important questions about workforce impacts. Responsible implementation includes retraining initiatives and thoughtful consideration of the societal implications of these technologies.