Reverse Supply Chains: The Engine of Circular Fashion: New Innovations
Circular Fashion: A Paradigm Shift
The current linear fashion model, characterized by take-make-dispose, is unsustainable. Vast quantities of textile waste end up in landfills, contributing significantly to environmental pollution. The circular fashion revolution proposes a fundamental shift in mindset, moving away from a disposable culture towards one that prioritizes resource efficiency and prolongs the lifecycle of garments. This paradigm shift necessitates a complete reimagining of how we design, produce, consume, and dispose of clothing, embracing concepts like repair, reuse, and recycling.
Central to this revolution is the understanding that clothing, like other resources, should not be considered disposable. Instead, we must view fabrics and garments as valuable materials capable of being repurposed and reused. This approach extends beyond individual consumers to encompass the entire supply chain, demanding a commitment from designers, manufacturers, retailers, and consumers to collaboratively participate in the circular fashion economy.
Reverse Supply Chains: A Critical Component
Reverse supply chains are a critical component of the circular fashion revolution. These systems meticulously track and manage the flow of textiles and garments from the end of their lifecycle back to the beginning, enabling reuse, repair, or recycling. This intricate process involves establishing robust collection systems, sorting facilities, and processing plants capable of handling various textile types, ensuring that valuable materials are not lost to landfill but are instead returned to the production cycle.
Effectively implementing reverse supply chains requires collaboration across the entire fashion industry. Manufacturers must design products with recyclability and repairability in mind. Retailers need to establish convenient collection points for used garments. And consumers must be informed and motivated to participate in the process. By integrating reverse supply chains into the overall fashion system, we create a closed-loop system that minimizes waste, conserves resources, and promotes a truly sustainable future for the industry.
The development of robust reverse supply chains is not just about environmental responsibility; it also presents significant economic opportunities. The recovery and reprocessing of textiles can create new jobs, reduce reliance on virgin resources, and unlock cost savings throughout the supply chain. This highlights the interconnectedness of environmental sustainability and economic viability in the context of the circular fashion revolution.
By embracing reverse supply chains, the fashion industry can transition from a linear model that generates significant waste to a circular model that maximizes resource utilization and minimizes environmental impact.
This holistic approach to reverse logistics, encompassing design for disassembly, optimized material recovery processes, and robust consumer engagement, is crucial for the success of the circular fashion revolution.
Innovative Technologies Driving Reverse Supply Chains

Emerging AI-Powered Solutions
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various industries, and its impact on retail is particularly significant. AI-powered chatbots are revolutionizing customer service, providing instant support and personalized recommendations. These bots can handle a multitude of inquiries, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues. Furthermore, AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of customer data to predict trends and optimize inventory management, minimizing waste and maximizing profitability.
Advanced Data Analytics for Personalized Experiences
Advanced data analytics are enabling retailers to understand customer behavior in unprecedented detail. By analyzing purchase history, browsing patterns, and demographics, retailers can tailor their offerings and marketing campaigns to individual preferences. This personalized approach fosters stronger customer relationships and drives higher conversion rates. This data-driven insight allows for dynamic pricing strategies, personalized product recommendations, and targeted promotions that resonate with individual customers.
Augmented Reality (AR) for Enhanced Shopping Experiences
Augmented reality (AR) is poised to revolutionize the way consumers interact with products before purchasing. Retailers are leveraging AR to allow customers to virtually try on clothes, visualize furniture in their homes, or experience products in a realistic setting. This technology enhances the shopping experience, reducing uncertainty and increasing customer satisfaction. Through interactive experiences, AR fosters a more engaging and immersive shopping environment, ultimately leading to higher purchase rates and brand loyalty.
The Internet of Things (IoT) for Seamless Operations
The Internet of Things (IoT) is connecting various aspects of the retail environment, creating a more efficient and responsive system. IoT-enabled devices can monitor inventory levels, track product movement within the store, and optimize store layouts, streamlining operations and reducing waste. This connectivity facilitates real-time data analysis, enabling retailers to make data-driven decisions and improve their supply chain efficiency. Furthermore, IoT devices can enhance the in-store experience for customers, such as providing real-time product information or personalized recommendations.
Blockchain Technology for Enhanced Security and Transparency
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent platform for managing transactions and supply chains. Its decentralized nature enhances security and reduces the risk of fraud. By providing a secure and auditable record of transactions, blockchain technology strengthens trust with customers. This technology enables retailers to track products from origin to consumer, ensuring product authenticity and ethical sourcing. This transparency builds consumer confidence and fosters trust in the brand.
Building Robust Collection and Sorting Infrastructure
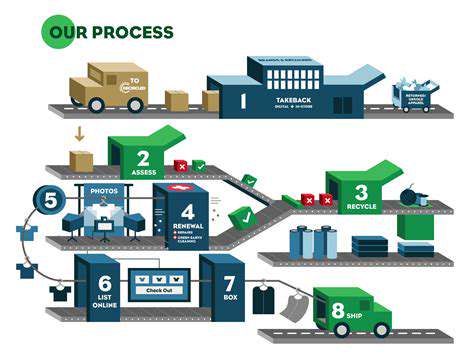
Data Ingestion Strategies
A robust collection strategy hinges on efficient data ingestion methods. Careful consideration must be given to the source and format of the data, ensuring compatibility with the intended storage and analysis systems. This includes handling potential data inconsistencies and errors during the ingestion process, which can significantly impact downstream analysis. Data validation steps are crucial for ensuring high-quality data from the outset.
Different data sources necessitate different ingestion techniques. Structured data from databases might be loaded directly using SQL queries, while unstructured data from social media or logs might require specialized parsing and transformation tools. Understanding the nuances of each data source is paramount for effective ingestion and avoiding data loss or corruption.
Data Storage and Management
Choosing the right storage solution is critical. Selecting a scalable and reliable system that can accommodate future data growth is essential for long-term sustainability. Consider factors such as data volume, velocity, and variety when selecting a storage solution. Cloud-based solutions often offer significant advantages in terms of scalability and cost-effectiveness.
Implementing robust data management practices is just as important as selecting the right storage. This includes establishing clear metadata standards, implementing version control, and defining access control policies. These practices ensure data integrity, usability, and compliance with relevant regulations.
Sorting Algorithms and Performance
The efficiency of sorting algorithms directly impacts the overall performance of the collection process. Choosing the appropriate algorithm for the specific dataset and use case is crucial for optimizing speed and resource utilization. Understanding the characteristics of the data, such as size and distribution, will help determine the most suitable sorting algorithm.
Sorting algorithms, such as quicksort and mergesort, have different performance characteristics. Analyzing the time and space complexity of various algorithms is essential to choose the most efficient option. This analysis should account for potential edge cases and data anomalies to prevent unexpected performance bottlenecks.
Quality Control and Validation
Implementing rigorous quality control measures throughout the collection and sorting process is essential. This involves validating data integrity, consistency, and accuracy at various stages, from ingestion to final output. Regular audits and checks help identify and correct errors early on, minimizing downstream issues and ensuring data reliability.
Establishing clear data quality standards and metrics is critical for monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of the collection and sorting process. Monitoring these metrics and implementing corrective actions when necessary ensures ongoing data quality and compliance with business requirements. This proactive approach reduces the risk of unexpected issues and maintains data trustworthiness.
Data Security and Privacy
Robust collection and sorting processes must prioritize data security and privacy. Implementing appropriate security measures, such as encryption and access controls, is critical to protecting sensitive data. Data encryption safeguards confidentiality and integrity, preventing unauthorized access and breaches.
Adhering to relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA, is crucial. Implementing mechanisms for anonymization and pseudonymization can help protect sensitive information while still enabling analysis. This ensures compliance with legal requirements and builds trust with data subjects.
The Future of Reverse Supply Chains in Fashion: A Closed-Loop System
The Growing Importance of Circularity
The fashion industry is facing increasing pressure to adopt more sustainable practices, and reverse supply chains are a crucial component of this transition. Circular fashion models, which prioritize the reuse, repair, and recycling of garments, are becoming increasingly important. This shift towards a more circular economy is driven by consumer demand for ethical and environmentally conscious brands, as well as by the rising costs of raw materials and the growing awareness of the environmental impact of fast fashion.
Challenges and Opportunities in Reverse Logistics
Implementing effective reverse supply chains in fashion presents unique challenges. Logistics must be optimized to ensure that returned garments are collected efficiently and effectively, and that the sorting and processing of these items is streamlined. There are also significant opportunities for innovation in this area, such as the development of new technologies and processes for recycling and repurposing textiles. A successful reverse supply chain can significantly reduce waste and promote a more sustainable future for the industry.
Technology's Role in Enhancing Reverse Supply Chains
Technology plays a vital role in streamlining the reverse supply chain process. From sophisticated tracking systems that monitor the movement of returned items to automated sorting and processing technologies, technological advancements are making reverse logistics more efficient and cost-effective. This includes AI-powered systems that can analyze the condition of garments and recommend the best course of action for their repurposing or recycling.
The Impact on Brand Image and Consumer Perception
A strong reverse supply chain can significantly enhance a brand's image and consumer perception. Consumers are increasingly seeking out brands that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and ethical practices. By actively promoting their reverse supply chain initiatives, brands can build trust and loyalty with environmentally conscious consumers, attracting new customers and driving positive brand associations.
Economic Benefits of Closed-Loop Systems
Adopting closed-loop systems in fashion reverse supply chains can lead to substantial economic benefits. By reusing, repairing, and recycling garments, brands can reduce waste, lower material costs, and create new revenue streams through the sale of refurbished or repurposed items. This can translate to significant cost savings and greater profitability for businesses that embrace circularity.
Consumer Engagement and Education
A successful reverse supply chain hinges on consumer engagement and education. Consumers need to understand the importance of returning garments and the various options available for their repurposing or recycling. Brands can foster this understanding through clear communication, transparent processes, and user-friendly return programs. Educating consumers about the benefits of circular fashion will be critical to the success of closed-loop systems in the future.