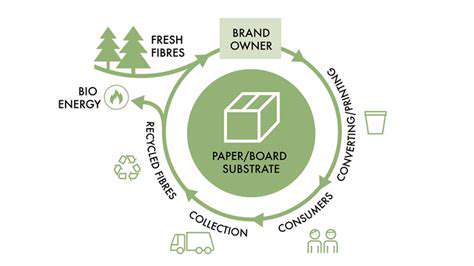
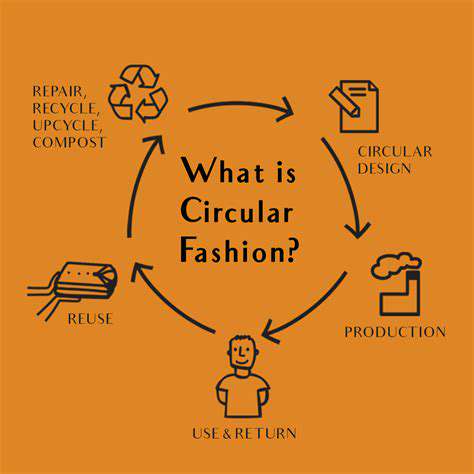
Sustainable Fashion and the Circular Economy: A Perfect Match
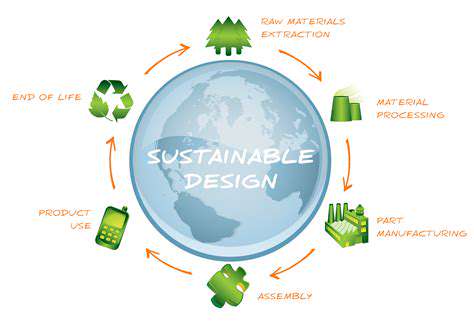
The Core Principles of a Circular Economy
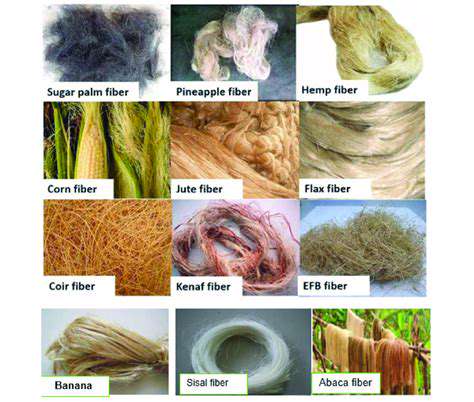
Traditional linear take-make-dispose models are being replaced by circular systems that emphasize resource efficiency. This transformative approach focuses on creating products designed for extended lifespans and eventual material recovery. By prioritizing durability and recyclability, we can establish closed-loop systems where materials remain in continuous use, dramatically reducing waste streams.
Central to this model is rethinking product lifecycles. Rather than disposable items, we're seeing innovative designs that facilitate repairs, upgrades, and multiple use cycles. This shift creates more resilient manufacturing systems that align with environmental limitations.
Economic Benefits of Transitioning to a Circular Economy
Businesses adopting circular principles discover significant cost advantages. Optimized resource use decreases reliance on virgin materials while creating new revenue streams from recycled components. These operational efficiencies translate directly to improved bottom lines while future-proofing against resource scarcity.
Innovative companies are developing competitive advantages through circular models. Repair services, refurbishment programs, and material recovery systems are spawning entirely new business sectors, driving economic diversification and employment opportunities in sustainability-focused fields.
Environmental Advantages of Circular Economy Practices
Circular systems offer profound ecological benefits by decoupling economic activity from resource depletion. This model reduces pressure on ecosystems by minimizing extraction, lowering emissions, and preventing pollution - critical factors in addressing climate change and biodiversity loss.
By dramatically decreasing demand for virgin materials, circular approaches alleviate the environmental damage caused by mining, drilling, and deforestation. This preservation of natural systems supports long-term planetary health.
Social Implications and Stakeholder Engagement
Circular models promote equitable resource distribution and sustainable consumption patterns. These systems can improve living standards while reducing environmental burdens on vulnerable communities.
Successful implementation requires unprecedented collaboration between manufacturers, policymakers, and consumers. Joint efforts in policy development, infrastructure investment, and consumer education are essential for systemic change. This collective approach ensures circular principles become mainstream practice.
Designing for Durability and Longevity: Key to Sustainability
Material Selection
Durable products begin with intelligent material choices. Engineers must evaluate materials for structural integrity, environmental resistance, and fatigue characteristics. Comprehensive testing ensures selections withstand intended use conditions without premature failure.
Material compatibility across components is equally crucial. Understanding how different materials interact under stress prevents systemic weaknesses in final products.
Manufacturing Processes
Precision manufacturing techniques significantly impact product longevity. Advanced quality control systems detect microscopic defects that could lead to future failures. Specialized joining methods, from ultrasonic welding to structural adhesives, create more robust assemblies than conventional techniques.
Process optimization minimizes stress concentrations and material degradation during production. This attention to manufacturing details results in products that maintain integrity over extended periods.
Design for Maintenance
Thoughtful maintenance design extends product usefulness. Modular architectures with standardized interfaces allow component-level repairs instead of full replacements. Clear maintenance protocols and accessible service points empower users to preserve functionality.
Stress Analysis and Testing
Comprehensive testing protocols simulate years of use in accelerated conditions. Advanced simulations predict failure points before production begins, allowing designers to reinforce vulnerable areas. Real-world testing validates theoretical models, creating reliable performance data.
Long-term durability testing reveals how materials degrade over time. This information drives material selection and design improvements for enhanced lifecycle performance.
Environmental Considerations
Products must withstand their operating environments. Designs incorporate corrosion resistance, UV stabilization, and thermal management appropriate for intended use climates. These considerations prevent environmental factors from prematurely ending product lifecycles.
User Interface and Ergonomics
Intuitive designs reduce accidental damage from misuse. Clear operational feedback and comfortable interfaces encourage proper use, while protective features safeguard against common handling errors. These human factors significantly influence real-world durability.
Global interconnectedness enables unprecedented collaboration, with digital platforms and logistics networks creating a tightly woven economic fabric. Yet these connections demand nuanced understanding of cultural contexts and regulatory environments to ensure ethical and sustainable practices across borders.
Collaboration and Transparency: Essential Elements for Progress
Open Communication Fosters Trust
Authentic dialogue between designers, manufacturers, and consumers builds necessary trust for sustainability initiatives. Detailed disclosures about material origins and production conditions enable informed decision-making throughout the value chain.
Transparency transforms consumer relationships. When brands openly share their sustainability journey - including challenges - they create opportunities for constructive engagement rather than superficial marketing claims.
Collaboration Across the Supply Chain
Systemic change requires alignment across all production stages. Strategic partnerships with ethical suppliers create resilient networks committed to continuous improvement. Knowledge-sharing platforms help disseminate best practices industry-wide.
Transparency in Material Sourcing
Detailed material traceability provides visibility into environmental and social impacts. Blockchain technologies now enable immutable records of material journeys from source to final product, building consumer confidence in sustainability claims.
Consumer Engagement and Education
Informed consumers drive market transformation. Clear communication about sustainable alternatives and their impacts empowers purchasing decisions that align with environmental values. Interactive platforms make sustainability education engaging rather than preachy.
Accountability and Traceability
Robust tracking systems verify compliance with sustainability standards. Third-party certifications and regular audits ensure accountability, while transparent reporting demonstrates measurable progress toward environmental goals.
Empowering Local Communities
Circular systems create local economic opportunities. Supporting regional material recovery infrastructure and artisan partnerships builds community resilience while reducing transportation emissions.
Measuring and Reporting Progress
Quantifiable metrics track sustainability performance over time. Standardized reporting frameworks allow meaningful comparison between initiatives, driving industry-wide improvement through transparent benchmarking.
Consumer Engagement: Driving the Demand for Sustainable Fashion
Understanding Consumer Motivations
Modern shoppers balance aesthetic, ethical, and environmental considerations. Growing awareness of fashion's ecological impact drives demand for transparent supply chains and verifiable sustainability claims. Consumers increasingly view purchases as expressions of environmental values.
The fast fashion backlash demonstrates shifting priorities. Customers now seek quality over quantity, favoring versatile pieces with extended usability over disposable trends. This mindset creates opportunities for brands emphasizing durability and timeless design.
Strategies for Effective Engagement
Authentic storytelling resonates more than corporate sustainability reports. Brands that showcase real people behind their products and transparently share challenges build deeper consumer connections.
Community-driven initiatives create participation opportunities. Repair workshops, clothing swaps, and upcycling programs transform passive consumers into active sustainability partners. These experiences foster brand loyalty while advancing circular economy principles.
Gamification elements make sustainable choices rewarding. Reward programs for garment returns, recycling participation, or sustainable care practices incentivize ongoing engagement with minimal environmental impact.
Ultimately, meaningful engagement transforms shopping habits. By making sustainability accessible, enjoyable, and rewarding, brands can guide consumers toward more responsible consumption patterns that benefit both people and planet.