Sustainable Packaging from Recycled Ocean Plastic: New Approaches
Designing Sustainable Packaging from Recycled Ocean Plastic
Exploring the Problem of Ocean Plastic Pollution
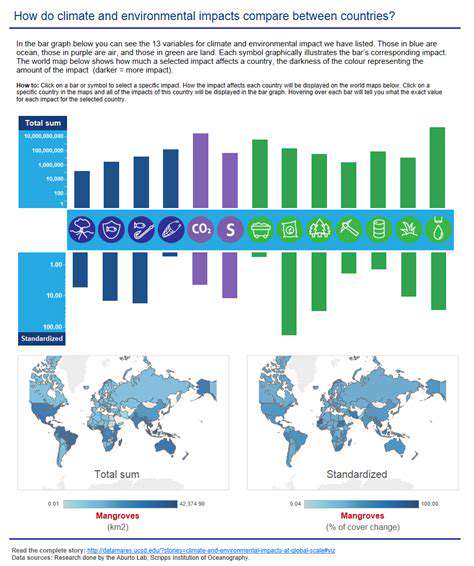
The global problem of plastic pollution, particularly in our oceans, is a significant environmental crisis. Millions of tons of plastic waste end up in marine ecosystems annually, harming marine life, disrupting ecosystems, and impacting human health. This overwhelming amount of plastic debris poses a serious threat to biodiversity and the delicate balance of marine environments, leading to long-term consequences. Understanding the scale and severity of this pollution is crucial for developing effective solutions.
The persistent nature of plastic, its slow degradation, and the sheer volume of plastic entering our oceans create a complex and multifaceted challenge. Addressing this issue requires a multi-pronged approach that includes reducing plastic consumption, improving waste management systems, and developing innovative technologies for plastic recycling and waste reduction. This is not just a scientific or environmental problem; it's a societal one that demands collective action.
The Potential of Recycled Ocean Plastic
Recycled ocean plastic offers a compelling opportunity to address the plastic pollution crisis and create a more sustainable future. By repurposing this discarded material, we can reduce reliance on virgin plastic production, lessen our environmental impact, and create valuable new products. The process of collecting, cleaning, and processing ocean plastic into usable materials requires careful consideration of the environmental footprint of each step, but the potential benefits are enormous.
The key to successfully utilizing recycled ocean plastic lies in developing efficient and cost-effective recycling processes that can effectively separate various plastic types and handle the inherent contamination often found in ocean-collected plastic. This will require technological advancements and collaborations between researchers, industry professionals, and communities to establish robust recycling infrastructure.
Designing Innovative Packaging Solutions
Designing sustainable packaging from recycled ocean plastic necessitates a shift in our thinking beyond traditional packaging materials. Innovative approaches to product design are crucial for creating attractive, functional, and environmentally responsible packaging solutions. This includes exploring alternative materials, such as bio-plastics or composites, that can be blended with recycled ocean plastic to enhance its properties and suitability for specific packaging applications.
The design process should prioritize minimizing material usage, maximizing recyclability, and ensuring the longevity and durability of the packaging. It's essential to consider factors like the product's transportation needs, consumer experience, and the entire lifecycle of the package from production to disposal.
The Economic and Social Benefits
Utilizing recycled ocean plastic for packaging has significant economic and social benefits. It stimulates innovation in the recycling sector, creating new jobs and business opportunities. Investments in recycling infrastructure and technology development contribute to economic growth and job creation, particularly in coastal communities often affected by plastic pollution.
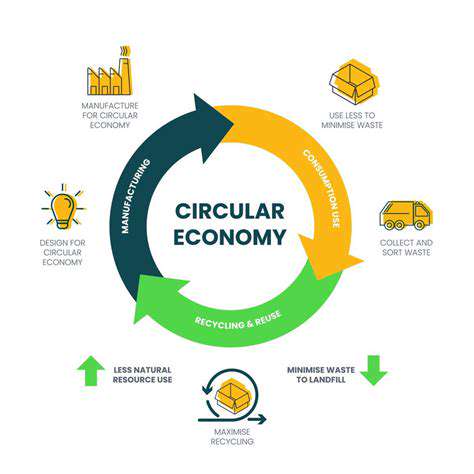
Furthermore, the use of recycled ocean plastic fosters a sense of social responsibility and environmental stewardship. It empowers communities to participate in tackling the plastic pollution crisis, raising awareness and encouraging collective action. This positive impact extends to supporting local economies and promoting a circular economy model.
Challenges and Future Considerations
Despite the potential benefits, the use of recycled ocean plastic faces several challenges. The collection, sorting, and processing of ocean-collected plastic can be complex and expensive, requiring significant investment in infrastructure and technology. Ensuring the quality and purity of recycled plastic is crucial to maintain its integrity and prevent contamination of the final product.
Future considerations include promoting consumer awareness about the benefits of sustainable packaging, encouraging responsible waste management practices, and developing policies that incentivize the use of recycled materials. Collaboration between governments, businesses, and individuals is paramount for the successful implementation of sustainable packaging solutions that effectively address the global plastic pollution crisis.
The Future of Sustainable Packaging: Challenges and Opportunities
Technological Advancements in Sustainable Packaging
The future of sustainable packaging hinges significantly on technological advancements. Innovations in materials science are crucial, offering the potential for creating packaging from renewable resources like plant-based polymers and bio-plastics. These materials not only reduce reliance on fossil fuels but also often possess superior biodegradability and compostability compared to traditional petroleum-based plastics. Furthermore, advancements in 3D printing and other additive manufacturing techniques promise customized packaging solutions, minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency.
Simultaneously, there's a growing emphasis on developing packaging that's both sustainable and functional. This includes exploring materials that offer enhanced barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and light, ensuring product freshness and safety while maintaining environmental consciousness. Research into biodegradable coatings and composite materials is also vital in this pursuit.
Consumer Demand and Shifting Preferences
Consumer preferences are increasingly driving the demand for sustainable packaging solutions. Consumers are becoming more aware of the environmental impact of their choices and are actively seeking out brands that prioritize sustainability. This growing awareness is translating into a demand for transparent and traceable supply chains, allowing consumers to understand the origin and environmental impact of the packaging they purchase. Companies that embrace sustainable practices are likely to gain a competitive edge and build brand loyalty in the future.
Moreover, the desire for aesthetically pleasing and functional sustainable packaging is driving innovation. Consumers are increasingly attracted to packaging that not only protects the product but also contributes to a positive brand image. This includes packaging designs that highlight the sustainability credentials of the product and resonate with the values of environmentally conscious consumers.
Regulatory Frameworks and Policies
Government regulations and policies play a critical role in shaping the future of sustainable packaging. Policies promoting the use of recycled content, banning specific plastics, and incentivizing the development of sustainable alternatives are essential drivers for change. Clearer regulations on packaging waste management and extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes can significantly influence the industry's adoption of sustainable practices.
Economic Incentives and Market Drivers
Economic incentives and market forces are powerful catalysts for the transition towards sustainable packaging. Government subsidies, tax breaks, and other financial incentives for companies adopting sustainable practices can accelerate the shift. Furthermore, the growing demand for sustainable packaging from retailers and consumers is generating a market pull, motivating businesses to invest in sustainable solutions. This market-driven approach will further propel the development and adoption of sustainable packaging options.
Collaboration and Partnerships
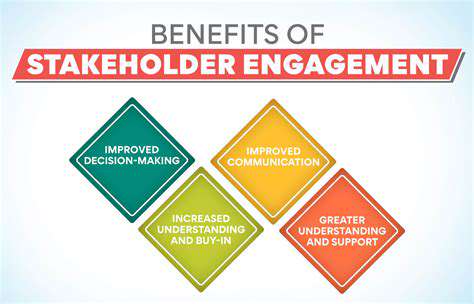
Collaboration and partnerships between various stakeholders are crucial for driving progress in sustainable packaging. This includes partnerships between businesses, research institutions, NGOs, and government agencies. Shared knowledge, resources, and expertise can accelerate innovation and the development of effective solutions. Collaboration also fosters transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain, promoting a more sustainable and responsible approach to packaging.
Open communication and coordinated efforts between these diverse groups will be essential to navigating the complexities and challenges of developing and implementing sustainable packaging solutions on a large scale.