The Science of Upcycling: Transforming Waste into Value: New Discoveries
Materials derived from renewable biological sources like plants and algae present compelling alternatives to conventional petroleum-based plastics. Their sustainable nature, rooted in natural cycles, positions them as key players in upcycling initiatives. This production approach reduces dependence on finite resources while minimizing manufacturing's environmental impact. Moreover, these materials' versatility enables diverse applications, fostering innovation across multiple sectors.
Bio-based materials offer benefits beyond environmental considerations. Their biodegradable and compostable nature supports circular economic models that minimize waste and optimize resource use. This perfectly aligns with upcycling principles that transform waste into valuable products, decreasing landfill contributions while improving resource efficiency.
The Science Behind Bio-Based Polymers: A Deep Dive
Polymers sourced from natural materials like corn starch and sugarcane are revolutionizing plastics manufacturing. These alternatives match conventional plastic properties while significantly reducing carbon footprints. The conversion of biological resources into usable polymers involves sophisticated chemical and biological processes, demonstrating this approach's scientific complexity.
Comprehending bio-based polymers' molecular structure is key to understanding their unique attributes. Their biodegradability depends on specific molecular configurations and microbial interaction potential. Such detailed scientific understanding is vital for optimizing production and application.
Upcycling Techniques for Enhancing Bio-Based Materials
Upcycling bio-based materials extends beyond simple plastic substitution. Innovative methods enhance their properties and functionality. Combining bio-based polymers with traditional plastics creates composites with improved strength and durability, expanding application possibilities while maximizing material efficiency.
Emerging techniques like 3D printing with bio-based filaments create unprecedented design possibilities. These methods produce complex shapes and structures unachievable through conventional manufacturing, significantly broadening bio-based materials' upcycling potential.
The Economic Viability of Bio-Based Materials
Bio-based materials are becoming economically attractive due to growing demand for sustainable alternatives. Government incentives and subsidies stimulate innovation and cost reduction. These materials also create new market opportunities, generating economic benefits across industries.
Cost-effectiveness depends on factors like raw material availability, production efficiency, and manufacturing scale. Continuous research improves these aspects, making bio-based materials increasingly competitive.
Environmental Impact Assessment and Life Cycle Analysis
Evaluating bio-based materials' environmental impact is crucial. Life cycle assessments (LCAs) examine environmental footprints from production to disposal, identifying improvement opportunities and optimizing sustainability throughout the production chain.
Technological Advancements and Future Trends
Technological progress is rapidly shaping bio-based materials' future. Emerging processing and modification techniques enhance properties and expand applications. Developing more efficient polymers with superior performance remains a primary focus.
Integrating bio-based materials into existing industrial processes is gaining momentum, a critical step for widespread adoption of these sustainable alternatives.
Applications and Market Opportunities
Bio-based materials serve diverse industries including packaging, textiles, and construction. Their potential for innovative product development creates new business opportunities. The market is projected to grow substantially as consumers increasingly favor sustainable products.
Bio-based alternatives address environmental challenges associated with traditional manufacturing, a trend likely to continue as sustainability becomes a priority for consumers and businesses alike.
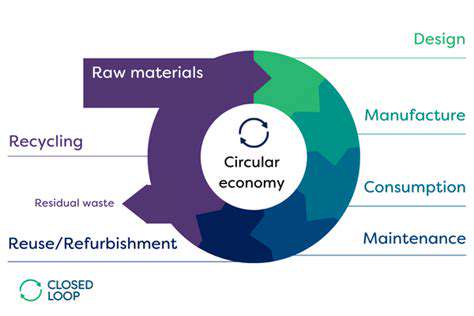
The Future of Upcycling: A Circular Economy Perspective
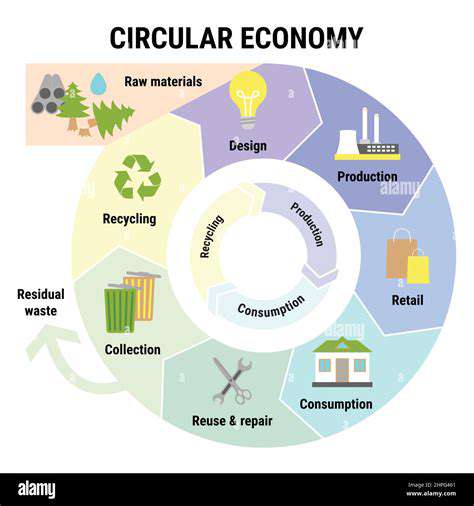
The Rise of Sustainable Practices
Upcycling is emerging as a cornerstone of circular economies, replacing traditional linear production models. Growing environmental awareness motivates consumers to seek products and services that minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency. This heightened consciousness drives innovation and encourages sustainable business practices.
The circular economy transition involves systemic changes. Companies are redesigning production processes to create longer-lasting products with reduced environmental impact—an essential strategy for combating climate change and conserving resources.
Innovative Design for Longevity
Future upcycling success hinges on creative design approaches. Designers are developing products that are easily repaired, repurposed, and adapted for multiple uses. This philosophy extends material lifespans and reduces resource extraction needs, shifting focus from disposable items to transformable products.
Technological Advancements in Material Science
Technological progress enables more effective upcycling. New material extraction and processing methods create sustainable products from previously unusable materials. These developments make upcycling more accessible and efficient, promoting wider adoption.
Researchers are discovering innovative ways to recycle and repurpose various materials, including new techniques for material breakdown and recombination that expand upcycling possibilities.
The Economic Benefits of Upcycling
Upcycling generates significant economic advantages by creating jobs and stimulating local economies. Investing in upcycling initiatives supports entrepreneurship and builds sustainable, resilient futures. Growing demand for upcycled products creates new business opportunities.
The Social Impact of Upcycling
Upcycling positively impacts society by empowering communities and fostering inclusion. It provides training and skill development, particularly in underserved areas, while encouraging creativity and innovation.
These programs offer vocational training and employment opportunities, improving lives and building community connections through collaborative efforts.
Upcycling in the Fashion Industry
While the fashion industry generates substantial waste, it also presents significant upcycling potential. Reinventing discarded textiles allows dramatic reductions in environmental impact. Brands are transforming old fabrics into new clothing, accessories, and home décor items, creating distinctive sustainable fashion solutions.
The Role of Education and Awareness
Cultivating an upcycling culture requires education and awareness. Teaching consumers about upcycling benefits and providing practical resources is essential for broad adoption. Highlighting waste's environmental consequences and upcycling's potential will inspire environmentally conscious consumption.
Educational initiatives including workshops and instructional materials promote understanding and appreciation of upcycling practices across communities.