Zero Waste Fashion: Designing for No Scraps: New Concepts
The Rise of Circularity in the Textile Industry
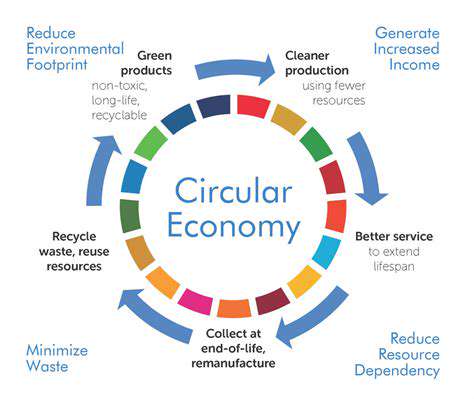
Circular Economy Principles in Textiles
The textile industry, historically known for its linear take-make-dispose model, is undergoing a significant transformation towards circularity. This shift emphasizes the importance of resource efficiency, waste reduction, and the creation of closed-loop systems. Implementing circularity principles requires a fundamental change in mindset and practice, moving away from single-use garments and towards designs that prioritize durability, recyclability, and repairability. This new approach aims to minimize environmental impact and maximize the value derived from textile resources throughout their lifecycle.
A key component of this transition is the adoption of innovative materials and technologies. This includes exploring sustainable alternatives to conventional fibers, such as recycled polyester and organic cotton, and developing advanced textile treatments that enhance durability and repairability. Companies are also focusing on extending the lifespan of garments through innovative designs and repair services.
Challenges and Opportunities in Circular Textiles
Despite the growing interest in circularity, the textile industry faces significant challenges in achieving this ambitious goal. These challenges include the complexity of material recycling, the need for infrastructure to support textile collection and sorting, and the development of standardized recycling processes. The lack of consistent consumer awareness and engagement also presents a hurdle in creating a truly circular system.
However, these challenges also present exciting opportunities. Investing in research and development of advanced recycling technologies could unlock new possibilities for transforming textile waste into valuable resources. Furthermore, the increasing consumer demand for sustainable products creates a compelling market for businesses embracing circularity, driving innovation and economic growth.
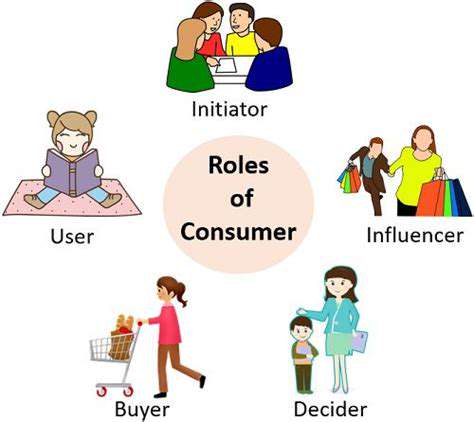
The Role of Consumers in Driving Circularity
Consumers play a crucial role in driving the textile industry towards a circular future. By making conscious purchasing decisions, supporting brands committed to sustainability, and adopting responsible consumption habits, consumers can significantly influence industry practices. This includes prioritizing durable and repairable garments, choosing products made from recycled materials, and opting for services that extend the lifespan of existing clothing.
Understanding the environmental impact of their clothing choices is key for consumers. By educating themselves on the lifecycle of textiles, consumers can make more informed decisions and contribute to a more sustainable fashion system. Supporting brands that embrace circularity signals a demand for responsible practices.
Technological Advancements and Innovations
Technological advancements are crucial to the successful implementation of circularity in textiles. Innovations in textile recycling, such as advanced sorting technologies and chemical recycling methods, are paving the way for efficient material recovery. The development of innovative dyeing and finishing processes that minimize chemical usage and water consumption is another critical area.
Digital technologies also play a significant role. Digital platforms can connect consumers with repair services, facilitate the sharing of clothing, and provide valuable data on textile consumption and waste. These tools can help streamline the circular process and create a more efficient system for managing textile resources.
The Impact on Sustainability and the Fashion Industry
The Environmental Footprint of Fast Fashion
Fast fashion, with its relentless cycle of trends and disposability, leaves a significant environmental footprint. The industry's reliance on cheap, often unsustainable materials, coupled with the sheer volume of production and disposal, contributes to pollution of water sources, deforestation, and greenhouse gas emissions. This massive impact on the environment necessitates a fundamental shift in the fashion industry's practices, and zero-waste strategies are a crucial part of that change.
The extraction of raw materials, the manufacturing processes, and the transportation of garments all contribute to a substantial ecological burden. This burden, often externalized and invisible to consumers, highlights the importance of considering the entire lifecycle of a garment when evaluating its environmental impact.
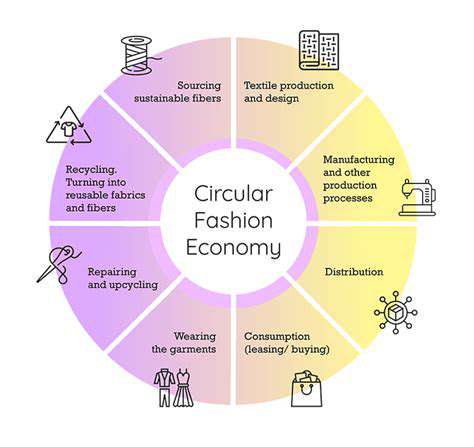
Circular Economy Principles in Fashion
Zero-waste fashion aligns perfectly with the principles of a circular economy. This model emphasizes reducing waste, reusing materials, and recycling garments to create a closed-loop system. By embracing these principles, the fashion industry can move away from the linear take-make-dispose model and towards a more sustainable and resilient approach.
Circular fashion encourages the use of recycled and renewable materials, the repair and repurposing of existing garments, and the development of innovative technologies for material recovery and reuse. This approach minimizes waste and maximizes the lifespan of fashion items.
Innovative Material Choices for Zero Waste
A crucial element of zero-waste fashion is the selection of sustainable materials. This includes using recycled fabrics, organic cotton, innovative plant-based fibers, and upcycled materials. These alternatives reduce the need for virgin resources and minimize the environmental impact associated with traditional textile production.
The exploration of new materials and innovative techniques for fabric creation is vital to the development of a truly sustainable fashion industry. This includes researching and developing bio-based materials and exploring ways to use less water and energy in production processes.
Design Strategies for Minimal Waste
Zero-waste design principles demand a shift in the way garments are conceived and produced. This involves meticulous pattern cutting, innovative construction techniques, and the use of less fabric. Designers can minimize waste by focusing on simple silhouettes, adaptable garments, and designs that maximize the use of fabric scraps.
The Role of Technology in Reducing Waste
Technological advancements play a critical role in achieving zero-waste fashion goals. Computer-aided design (CAD) software, for example, can optimize pattern cutting, minimizing fabric waste. 3D printing and other innovative technologies can enable customized production, further reducing the need for excess fabric.
The use of cutting-edge technology is essential to streamline production processes and identify areas where waste can be minimized. Further research and development in this area are crucial for the future of zero-waste fashion.
Consumer Responsibility and Sustainable Consumption
Consumers play a vital role in fostering a zero-waste fashion movement. Making conscious purchasing decisions, prioritizing quality over quantity, and supporting brands committed to sustainable practices are crucial steps. Investing in well-made garments that can last longer contributes to reducing textile waste.
Consumers can also embrace the concept of repairing and repurposing clothes, thereby extending their lifespan. By changing their consumption habits, consumers can have a significant impact on the fashion industry's environmental footprint.
The Future of Sustainable Fashion
Zero-waste fashion represents a significant paradigm shift in the fashion industry, moving away from the unsustainable practices of the past. The transition towards a more sustainable future requires collaboration between designers, manufacturers, retailers, and consumers. The future of fashion lies in a collective commitment to reducing waste and embracing innovative solutions.
By integrating zero-waste principles across the entire supply chain, from design to disposal, the industry can create a more environmentally responsible and socially equitable fashion system. This transition will require ongoing innovation, collaboration, and a shared commitment to sustainability.