Blockchain for Circularity: Enhancing Traceability
Blockchain's Role in Enhancing Transparency
Blockchain technology, at its core, provides a transparent and immutable digital ledger. This inherent transparency is a significant advantage in various sectors, including supply chains. By recording every transaction on a shared, distributed database, blockchain creates a clear audit trail, eliminating ambiguity and fostering trust among stakeholders. This transparency can be particularly impactful in addressing issues of counterfeiting, product origin, and ethical sourcing.
This shared, accessible record, visible to all authorized parties, significantly reduces the potential for fraud and manipulation. The immutable nature of blockchain ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, preserving the integrity of the data and contributing to a more reliable and accountable system.
Decentralization: Powering Trust and Security
A key feature of blockchain is its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional systems where a single entity controls the data, blockchain distributes the ledger across a network of computers. This decentralized structure enhances security and reduces the risk of single points of failure. This distributed control model makes the system more resilient to attacks and corruption, as no single entity holds the entire database, bolstering trust in the system.
The decentralized control also empowers participants by giving them ownership and control over their data. This shared control model fosters a sense of trust and collaboration, which is crucial for building sustainable and efficient supply chains.
Traceability: Unveiling the Journey of Products
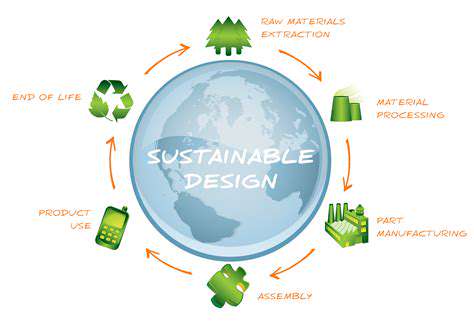
Blockchain's ability to record and track every step in a product's lifecycle provides unparalleled traceability. From raw material sourcing to manufacturing, distribution, and end-user consumption, each transaction is meticulously documented on the blockchain. This detailed record allows businesses and consumers to understand the complete journey of a product, fostering transparency and accountability.
Smart Contracts: Automating Processes for Efficiency
Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code, automate processes within the blockchain. These automated agreements reduce the need for intermediaries and streamline operations, leading to increased efficiency and reduced costs. The use of smart contracts can significantly improve efficiency in various stages of a circular economy, such as product return and reuse agreements.
Improving Ethical Sourcing and Labor Practices
Blockchain provides a robust platform for verifying ethical sourcing practices throughout a product's lifecycle. By tracking materials from their origin to the final product, businesses can ensure that they are sourced responsibly and ethically, complying with labor standards and environmental regulations. This enhanced visibility helps to eliminate exploitation and promote fair trade practices, critical elements of a circular economy.
Environmental Impact Transparency: Reduced Waste and Enhanced Sustainability
Blockchain can help track environmental impact throughout a product's lifecycle. Each step, from resource extraction to waste management, can be recorded. This data can be used to identify areas for improvement and promote more sustainable practices. By providing transparent and verifiable data on environmental impact, blockchain fosters greater accountability and encourages businesses to minimize their environmental footprint, contributing to a circular economy.
Supply Chain Resilience: Building a More Robust System
In today's complex and often unpredictable global supply chains, resilience is paramount. Blockchain's ability to provide transparency and traceability throughout the entire process helps businesses understand and respond to disruptions more effectively. By having a complete and auditable record of every stage, businesses can identify vulnerabilities and implement strategies to mitigate risks and disruptions, leading to a more robust supply chain that is better prepared for challenges.
Improving Transparency and Accountability

Improving Transparency in Financial Reporting
Transparency in financial reporting is crucial for maintaining investor confidence and ensuring the integrity of the market. Investors need clear and concise information to make informed decisions about where to allocate their capital. This transparency is not just about presenting numbers; it's about providing context and explanations to help stakeholders understand the underlying factors influencing financial performance. Robust disclosure policies and standardized accounting practices are essential components of achieving this transparency. Investors should be able to easily access and understand financial statements, without having to spend undue time and effort deciphering complex information.
Furthermore, proactive disclosure of potential risks and challenges is a key aspect of transparency. Companies that openly acknowledge potential difficulties, alongside their strategies for mitigating them, demonstrate a commitment to accountability. This approach fosters trust and encourages constructive dialogue with stakeholders. By providing a comprehensive view of the financial landscape, companies can build stronger relationships with investors and other stakeholders, ultimately improving their long-term value.
Accountability in Corporate Governance
Accountability in corporate governance is paramount to building trust and maintaining ethical standards. Strong corporate governance structures are essential to ensure that companies are run in a responsible and transparent manner, benefiting all stakeholders. This involves establishing clear lines of responsibility, implementing robust internal controls, and ensuring that decision-making processes are aligned with the interests of all stakeholders. Effective corporate governance mechanisms also contribute to a more stable and predictable business environment, which fosters economic growth and stability.
Transparency in decision-making processes, coupled with clear communication channels, is vital for accountability. Stakeholders need to have access to information about how decisions are made, the rationale behind those decisions, and the potential consequences. This allows for informed scrutiny and feedback, ensuring that the actions of the organization align with the best interests of all involved.
Enhancing Stakeholder Engagement
Improving stakeholder engagement is critical for fostering a culture of transparency and accountability. Open communication channels and active listening are essential for understanding the concerns and needs of various stakeholders, including investors, employees, customers, and the wider community. Actively soliciting feedback and addressing concerns promptly demonstrates a commitment to transparency and builds trust. This kind of engagement can lead to invaluable insights that can inform business strategies and enhance decision-making. Building strong relationships with stakeholders through regular dialogue and transparency can help companies navigate challenges more effectively.
In addition, providing access to relevant information through accessible platforms, such as online portals or regular reports, can facilitate stakeholder engagement. This approach fosters a sense of shared responsibility and empowers stakeholders to actively participate in the company's success. By making information readily available and encouraging dialogue, companies can cultivate a culture of trust and collaboration that benefits all involved parties.
Unlocking Opportunities for Sustainable Material Management
Leveraging Blockchain for Transparency
Blockchain technology offers a robust solution for enhancing transparency throughout the lifecycle of materials. By creating a shared, immutable record of transactions, from sourcing raw materials to manufacturing, distribution, and end-of-life management, blockchain fosters trust and accountability among all stakeholders. This transparency allows for greater traceability, enabling businesses to identify and mitigate risks associated with supply chain complexities and ensure ethical sourcing practices are adhered to.
This enhanced visibility into the material's journey empowers consumers to make informed decisions about their purchases, supporting brands committed to sustainable practices. Ultimately, this transparency fosters a more collaborative and sustainable material management system.
Streamlining Material Flow Tracking
Blockchain's distributed ledger technology facilitates real-time tracking of materials, eliminating the need for disparate, often inaccurate, data silos. This streamlined tracking allows for efficient inventory management, reducing waste, and optimizing resource allocation across the entire supply chain. Precise tracking of materials throughout their journey enables businesses to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, leading to significant cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
Enabling Circular Economy Principles
A core tenet of the circular economy is the reuse and recycling of materials. Blockchain can empower this process by providing a secure platform for tracking recycled materials, verifying their quality, and ensuring that they are used in subsequent production processes. This closed-loop system reduces reliance on virgin resources and minimizes environmental impact, making the circular economy a tangible reality.
Promoting Ethical Sourcing and Labor Practices
Blockchain's inherent security and transparency can be instrumental in verifying ethical sourcing practices. By documenting the origin and journey of raw materials, blockchain systems can help identify and prevent exploitation of workers or environmental damage along the supply chain. This verification process builds consumer trust and encourages ethical sourcing practices across all industries.
Implementing blockchain in supply chains can create a more sustainable and equitable environment, which benefits businesses and communities alike by encouraging responsible and transparent practices.
Improving Waste Management and Recycling
Blockchain can revolutionize waste management and recycling processes by providing a secure platform for tracking materials from collection to processing. This system can accurately record the type and quantity of materials collected, enabling more effective sorting and recycling. This data can also inform policy decisions and resource allocation by revealing patterns and bottlenecks in the waste management system.
Facilitating Collaboration and Data Sharing
Blockchain facilitates seamless collaboration among various stakeholders in the material management system, including producers, consumers, recyclers, and governments. By fostering a shared platform for data exchange, blockchain enables a more coordinated and efficient approach to material management, leading to greater transparency and accountability. This improved collaboration empowers stakeholders to collectively address the challenges of sustainability and resource management.
Enhancing Product Lifecycle Management
Blockchain can effectively track products throughout their entire lifecycle, from design and manufacturing to use and end-of-life disposal. This comprehensive tracking system enables businesses to gain valuable insights into product performance, customer usage patterns, and material degradation. By understanding the full product lifecycle, businesses can refine design, optimize production processes, and improve resource efficiency.