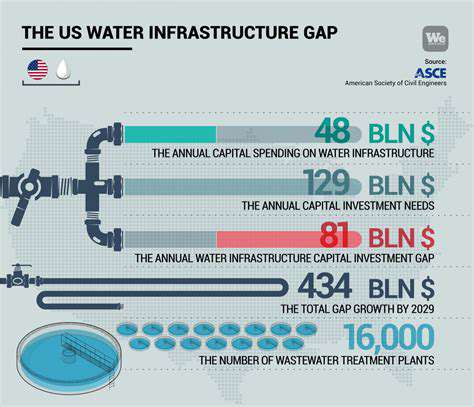
Circular Economy Principles Applied to Fashion Design
Bio-based polymers, derived from renewable resources like plants and agricultural waste, are a key component of the regenerative materials movement. These materials offer a compelling alternative to petroleum-based plastics, significantly reducing reliance on fossil fuels and associated environmental impacts. Their inherent biodegradability and compostability are crucial factors in minimizing plastic waste and promoting a circular economy.
The Role of Nanotechnology in Regenerative Materials
Nanotechnology plays a pivotal role in the development of regenerative materials by enabling the creation of materials with enhanced properties and functionalities. By manipulating materials at the nanoscale, scientists can create novel structures with improved strength, durability, and biocompatibility. This allows for the development of materials with tailored properties for specific applications.
Nanomaterials can also be designed to promote self-healing properties in materials, leading to longer lifespans and reduced waste generation throughout the product lifecycle.
Regenerative Materials in Construction
The construction industry is a significant consumer of materials, and regenerative materials offer a promising avenue for sustainable building practices. Materials like bio-cement, derived from agricultural byproducts, can replace traditional cement, reducing the industry's carbon footprint and promoting environmental stewardship. These alternatives are not only environmentally friendly but also often exhibit comparable or even superior performance characteristics.
Advancements in Textile Manufacturing
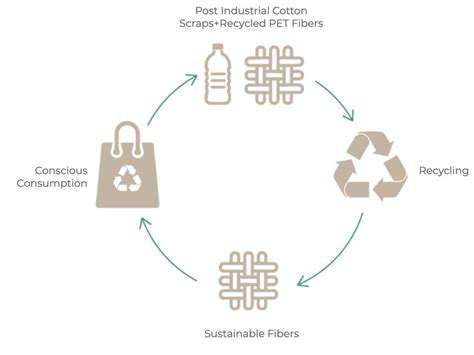
Regenerative materials are also transforming textile manufacturing, leading to the development of sustainable fibers and fabrics. Innovations in bio-based fibers, such as those derived from mushrooms or algae, are offering a sustainable alternative to conventional cotton and synthetic fabrics. This shift towards biodegradable and compostable textiles is crucial for reducing the environmental impact of the fashion industry.
The Future of Regenerative Materials
The field of regenerative materials is rapidly evolving, with continuous advancements in material science and engineering. Ongoing research and development promise even more sustainable and efficient solutions in the future, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in terms of environmental responsibility and resource efficiency. This includes further exploration of novel bio-based materials and the development of advanced manufacturing processes.
As awareness of environmental issues grows, the demand for regenerative materials is expected to surge, driving further innovation and adoption across various industries.
The shift towards hybrid learning models signifies a significant paradigm shift in education, moving away from the traditional, solely in-person or solely online formats. This flexibility allows for a more personalized learning experience, catering to diverse student needs and preferences. Students can now access educational resources and interact with teachers and peers in ways that were previously unimaginable.
Encouraging Consumer Engagement and Collaboration
Fostering a Culture of Circularity
Encouraging consumer engagement in a circular economy requires shifting consumer mindsets from a linear take-make-dispose model to a more sustainable repair, reuse, recycle approach. This involves educating consumers about the environmental and economic benefits of circularity, highlighting the value of products designed for longevity and repairability. Companies can play a vital role in this transformation by prominently featuring circular economy principles in their marketing strategies, showcasing how their products are designed for durability and repairability. Ultimately, a shift towards a circular economy requires a collective effort, with consumers, businesses, and governments working together to adopt sustainable practices.
Empowering Consumers Through Transparency and Choice
Transparency is key to empowering consumers in the circular economy. Providing clear information about product lifecycles, materials used, and repair options empowers consumers to make informed choices aligned with circular principles. Consumers need to understand the environmental and social impact of their purchasing decisions. This includes detailed labeling of products that highlight their recyclability, repairability, and potential for reuse. Furthermore, offering consumers a variety of repair services and access to repair manuals can significantly increase the lifespan of products.
Giving consumers a clear understanding of the lifecycle of a product, from raw material extraction to disposal, allows them to make informed choices. Providing detailed information about the environmental and social impacts of a product's creation, use, and eventual disposal allows consumers to make purchasing decisions that align with their values.
Promoting Collaboration Between Businesses and Consumers
Encouraging collaboration between businesses and consumers is crucial for the successful implementation of circular economy principles. Businesses can incentivize consumer participation through initiatives like take-back programs for products, offering repair services, or promoting product sharing platforms. Consumers can actively participate by choosing products with a focus on durability and repairability, supporting businesses that prioritize sustainability, and engaging in peer-to-peer sharing networks. These collaborative efforts can create a virtuous cycle of sustainability, driving innovation and fostering a shared responsibility for environmental stewardship.
Driving Innovation and Design for Circularity
Circular economy principles demand a paradigm shift in product design. Businesses need to move away from a linear model that prioritizes disposability and towards a circular model that prioritizes durability, repairability, and recyclability. This innovative approach will require businesses to design products with a longer lifespan in mind, using recycled materials, and creating products that can be easily disassembled and reused or recycled. By investing in research and development focused on circular design, businesses will not only reduce their environmental footprint but also create new economic opportunities in the circular economy. Such innovation can lead to the development of entirely new markets and business models based on sustainability principles.