From Raw Materials to Retail: New Ethical Traceability Tools
Beyond the Digital Ledger: Expanding Traceability's Reach
Traditional blockchain applications often focus narrowly on digital transactions, but comprehensive traceability demands a broader perspective. An effective system must encompass every step of the supply chain, from raw material extraction to final delivery. Detailed record-keeping and open communication at each phase create a transparent narrative of a product's journey. This complete visibility builds consumer confidence by clearly showing the origins and path of purchased goods.
This approach requires moving beyond purely digital solutions to integrate physical tracking methods. The goal is establishing a cohesive network where all relevant data connects seamlessly, providing stakeholders with a full picture of the product's lifecycle - whether following agricultural produce from field to table or manufactured goods from workshop to customer.
Leveraging IoT for Real-Time Insights
The Internet of Things revolutionizes supply chain monitoring through continuous data collection. Strategically placed sensors track crucial variables like temperature fluctuations, moisture levels, and geographic location throughout the transportation process. These devices enable immediate detection of potential problems, allowing for swift corrective action before issues escalate.
Integrating IoT technology into logistics systems helps companies maintain optimal conditions for perishable goods. This proactive monitoring significantly decreases product loss while improving quality consistency. The instantaneous data flow also enhances supply chain flexibility, enabling rapid responses to unexpected disruptions.
Enhancing Data Integrity Through Secure Data Management
Maintaining trustworthy traceability records requires robust data protection measures. Secure databases, advanced encryption methods, and strict access controls prevent unauthorized information alteration. Digital verification techniques and comprehensive audit logs create immutable records of product movements and handling conditions.
The system must not only gather information but also ensure its long-term security and availability. Reliable data preservation is fundamental for maintaining stakeholder confidence and verifying supply chain claims made to consumers and regulators.
Collaboration and Standardization: Key to Success
Effective traceability systems depend on cooperation across all supply chain participants. From initial producers to final retailers, consistent data sharing is essential. Adopting universal formatting standards enables smooth information exchange between different technological platforms used by various partners.
Building strong partnerships and establishing clear communication protocols are vital for system-wide adoption. This collaborative framework ensures traceability becomes an integrated supply chain feature rather than an isolated function, strengthening overall transparency and accountability.
Beyond the Product: Traceability's Impact on Sustainability and Ethics
Modern traceability solutions serve purposes beyond simple origin tracking. They provide tools for monitoring environmental stewardship and social responsibility throughout production networks. Detailed tracking enables assessment of ecological impacts, verification of humane labor practices, and identification of potential safety concerns.
By connecting production details with consumer information, traceability empowers buyers to make values-based purchasing decisions. This transparency creates market incentives for ethical business practices, potentially driving industry-wide improvements in sustainability and social responsibility.
Virtual spaces blending augmented and virtual realities are creating unprecedented digital environments. These platforms extend far beyond gaming, developing into sophisticated ecosystems with unique economic models and social dynamics. Understanding these foundational elements proves critical for developing governance frameworks capable of evolving with technological progress while addressing novel challenges.
Improving Sustainability and Reducing Environmental Impact
Sustainable Sourcing of Raw Materials
Environmental stewardship begins with responsible material procurement. Leading companies prioritize vendors demonstrating commitment to ecological preservation and fair labor standards. This includes sustainable forestry practices, water conservation measures, and verified worker protections. Ongoing supplier evaluation ensures continued adherence to these principles throughout business relationships.
Material traceability systems provide the transparency needed to verify sustainable sourcing claims. Detailed origin documentation allows companies and consumers alike to assess the true environmental and social costs embedded within products, fostering accountability across supply networks.
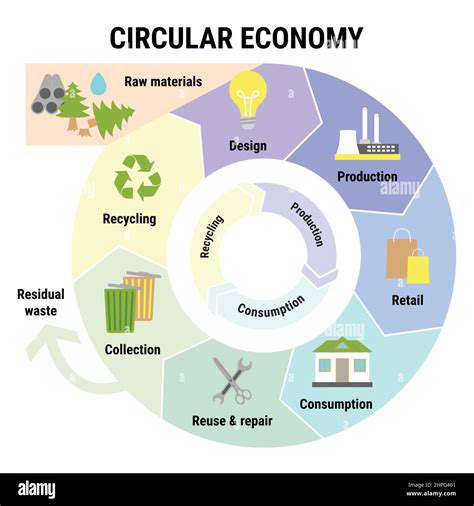
Reducing Waste and Optimizing Processes
Waste minimization strategies should permeate all production phases. Effective approaches include material efficiency improvements, manufacturing process refinements, and comprehensive recycling programs. True waste reduction considers the complete product lifecycle - from initial design through to ultimate disposal.
Applying lean manufacturing principles helps identify resource optimization opportunities. This systematic approach simultaneously reduces environmental impact while improving operational performance, creating both ecological and economic benefits.
Innovative Manufacturing Techniques
Advancements in production technology offer significant sustainability improvements. Companies investing in alternative materials, renewable energy integration, and cleaner processes often achieve long-term environmental and financial gains. Research and development in sustainable manufacturing requires substantial commitment but delivers meaningful returns.
Material innovation plays a crucial role, with many firms transitioning to recycled content or plant-based alternatives. These substitutions decrease dependence on environmentally damaging resources while maintaining product quality standards.
Responsible Packaging and Transportation
Shipping and packaging decisions significantly influence product sustainability. Environmentally conscious packaging strategies emphasize material reduction, renewable resources, and shipping efficiency. Prioritizing reusable container systems and easily recycled materials supports circular economy principles.
Transportation network optimization reduces fuel consumption and associated emissions. Tactics include shipment consolidation, modal efficiency improvements, and adoption of alternative fuel vehicles - all contributing to smaller carbon footprints.
Product Design for End-of-Life Management
Sustainable design principles incorporate end-of-life considerations from initial concept stages. Products should facilitate disassembly, component reuse, and material recovery. Thoughtful material selection and construction techniques can dramatically improve recyclability rates.
Durable design extends product lifespans, reducing replacement frequency and associated resource consumption. Building longevity into products represents one of the most effective waste prevention strategies, significantly decreasing environmental impacts over time.