From Value Chain to Value Loop: The Circular Advantage in Fashion: New Insights
Understanding the Linear Economy's Limitations
The traditional linear take-make-dispose model of the economy has proven unsustainable. This model, prevalent for decades, relies on extracting vast quantities of raw materials, transforming them into products, and ultimately discarding them as waste. This approach generates significant environmental damage, depletes natural resources, and creates a constant stream of pollution. The sheer volume of waste produced by this system is unsustainable and poses a grave threat to the planet's future.
The limitations of this model become increasingly apparent as resources dwindle and environmental concerns escalate. This linear approach fails to account for the finite nature of our resources and the escalating environmental costs associated with waste disposal and pollution.
The Circular Economy: A Regenerative Approach
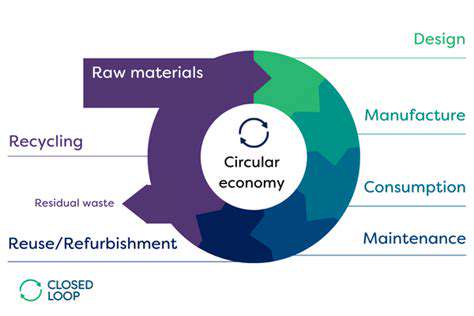
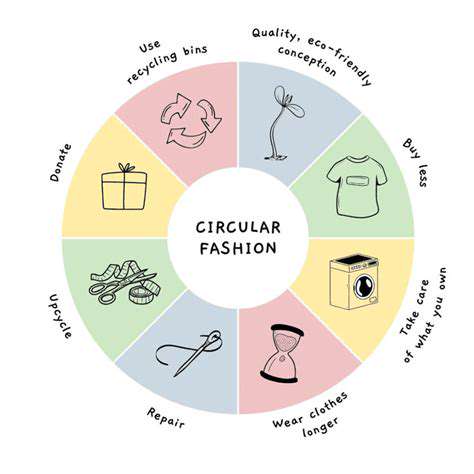
The circular economy presents a compelling alternative, advocating for a regenerative approach that prioritizes resource efficiency and minimizes waste. It aims to decouple economic growth from the consumption of finite resources. This is achieved by designing out waste and pollution, keeping products and materials in use, and regenerating natural systems.
This paradigm shift emphasizes the importance of designing products with a lifecycle in mind, considering aspects like durability, repairability, and recyclability.
Designing for Durability and Repairability
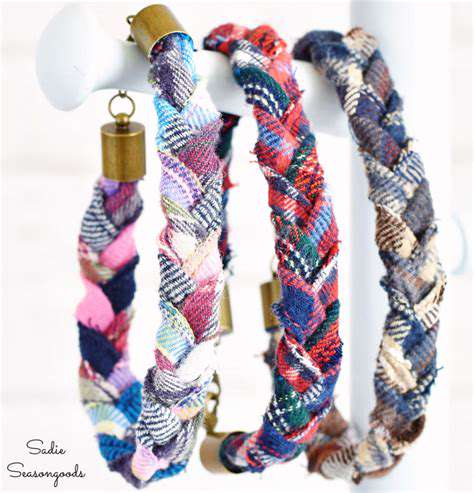
A key tenet of the circular economy is designing products for durability and repairability. This involves creating products that are built to last, using high-quality materials, and employing designs that facilitate easy repair and maintenance. Products designed for disassembly and reuse allow for a significant reduction in waste and resource consumption.
Implementing Closed-Loop Systems
Closed-loop systems are central to the circular economy. These systems aim to minimize waste by reintroducing materials back into the production process. This involves implementing recycling and reuse programs, as well as developing innovative technologies for material recovery and processing. This approach reduces the need for virgin materials and minimizes the environmental impact of manufacturing.
The Role of Innovation and Technology
Innovation plays a crucial role in driving the circular economy. New technologies and approaches are necessary to make the transition to a circular model possible. These innovations could include advancements in material science, recycling technologies, and closed-loop manufacturing processes. Investing in research and development is paramount for advancing these crucial innovations.
Value Creation Beyond Product Lifecycles
The circular economy fosters a shift in value creation beyond the traditional product lifecycle. It recognizes the value embedded in products throughout their entire lifespan and emphasizes the importance of extending their useful life. This approach fosters a more sustainable and equitable model of economic activity.
Stakeholder Collaboration for Systemic Change
Transitioning to a circular economy requires collaborative efforts across various stakeholders, including businesses, governments, and consumers. Collaboration among these groups is essential to establish policies, regulations, and incentives that support the shift toward a circular economy. This cooperative approach is crucial for fostering a systemic change necessary for a more sustainable future.
User consent is a fundamental principle in data privacy and security, acting as a crucial safeguard for individuals' personal information. It establishes a clear framework for how organizations collect, use, and share data, ensuring transparency and accountability. Understanding the legal and ethical implications of user consent is paramount for any organization handling personal data. It's not just a legal requirement; it's a demonstration of respect for individual autonomy and a commitment to data protection.
The Role of Technology and Innovation in Circularity

The Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have fundamentally reshaped various facets of our lives, driving innovation across industries. From communication to healthcare, the integration of technology has led to increased efficiency, productivity, and accessibility. The ability to connect with people globally, access vast amounts of information, and perform complex tasks with ease has revolutionized the way we live and work. This transformation has not only improved quality of life but has also created new opportunities for individuals and businesses alike.
Furthermore, technological progress has spurred innovation in diverse fields, leading to the development of groundbreaking solutions to complex problems. The convergence of different technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics, has yielded unprecedented opportunities for progress in areas like medicine, agriculture, and environmental conservation. This constant evolution necessitates continuous learning and adaptation to remain competitive and capitalize on the opportunities that emerge from these advancements.
Driving Innovation Through Technological Integration
Innovation is not merely about developing new technologies; it's also about effectively integrating them into existing systems and processes. This integration requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses not only technological expertise but also a deep understanding of the specific needs and challenges faced by different industries and individuals. This integration is crucial for maximizing the benefits of technological advancements and ensuring their seamless implementation.
Effective integration of technology often involves collaboration between various stakeholders, including researchers, developers, engineers, and end-users. This collaboration fosters a shared understanding of the potential applications of technology, encourages the development of innovative solutions, and ultimately drives progress and positive change. By fostering a culture of innovation and collaboration, organizations can leverage the power of technology to achieve significant breakthroughs and gain a competitive edge.
The Future of Technology and Innovation
Looking ahead, the future of technology and innovation appears promising, with exciting possibilities emerging across various sectors. The continued development of artificial intelligence, automation, and biotechnology holds the potential to revolutionize healthcare, transportation, and communication, among other crucial areas. These advancements promise to solve complex problems, improve efficiency, and ultimately enhance the quality of life for a multitude of individuals and communities.
However, with these advancements comes the need for careful consideration of the ethical implications and potential societal impacts. The integration of technology must be approached responsibly, with a focus on equity, accessibility, and sustainability. Addressing these concerns proactively is paramount to ensuring that technological progress benefits all members of society.