Measuring Circularity: Metrics for a Sustainable Fashion Future
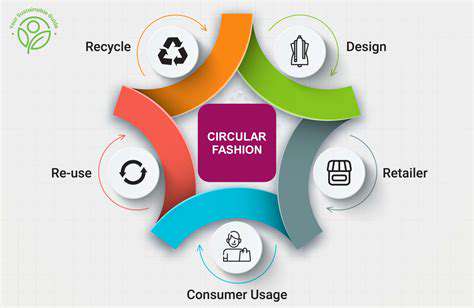
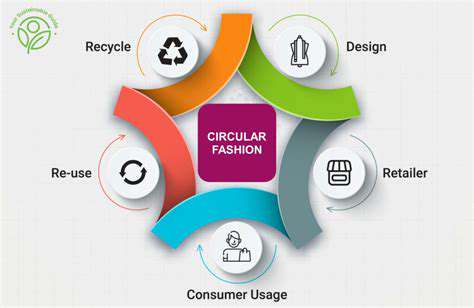
Material Circularity: From Cradle to Cradle
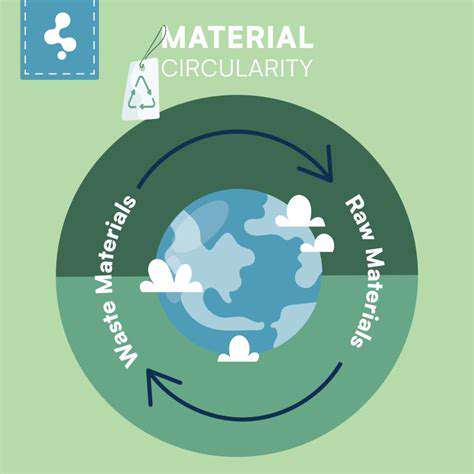
Material Circularity: A Fundamental Shift
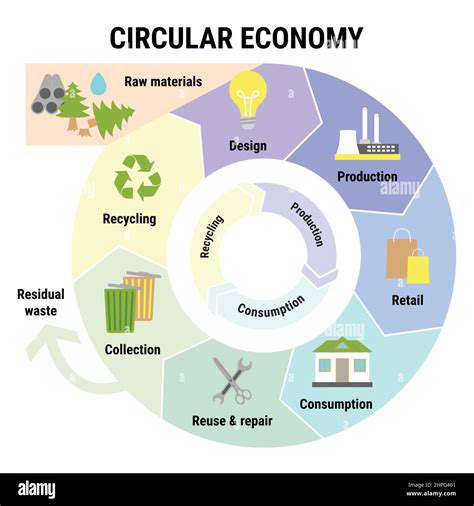
Material circularity represents a paradigm shift in our approach to resource management, moving away from a linear take-make-dispose model to a more sustainable and regenerative system. This shift necessitates a fundamental rethinking of production processes and consumption patterns, emphasizing the importance of resource efficiency and waste reduction. It's about designing products and systems that can be reused, repaired, or recycled at the end of their life cycle, minimizing the environmental impact and maximizing resource utilization.
The core principle of material circularity is to keep materials in use for as long as possible. This involves designing products for durability, repairability, and recyclability. By employing these principles, we can dramatically reduce the need for virgin materials and the associated environmental costs.
The Importance of Design for Disassembly
Designing products with disassembly in mind is crucial for material circularity. This approach considers the entire lifecycle of a product, from its initial design to its eventual end-of-life stage, aiming to maximize the potential for material recovery and reuse. This means using readily separable components, standardized interfaces, and materials that can be easily separated during the disassembly process.
Enhanced Recycling Technologies
Developing and implementing advanced recycling technologies is essential for material circularity. These technologies can effectively process complex materials and mixtures, recovering valuable components and reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills. Advanced technologies are key to unlocking the full potential of material circularity by recovering valuable resources from previously unusable materials.
This includes the development of technologies for plastics, electronic waste, and other complex materials that have proven challenging to recycle in the past. Innovative approaches are crucial to achieving greater efficiency in resource recovery.
Consumer Responsibility in the Circular Economy
Consumers play a vital role in fostering material circularity. By making conscious choices about the products they buy, consumers can influence manufacturers and drive demand for more sustainable and circular products. This includes prioritizing durable, repairable products and supporting businesses committed to circular practices. Consumers can also actively participate in recycling programs and adopt a more mindful approach to consumption, reducing their overall environmental footprint.
Economic Benefits of Material Circularity
Implementing material circularity strategies offers numerous economic benefits. Reducing waste and maximizing resource utilization can lead to cost savings for businesses through lower material input costs and reduced disposal expenses. Creating a circular economy can also foster innovation and the development of new industries focused on resource recovery and reuse. This creates new job opportunities and fosters a more sustainable and resilient economy.
Policy Support for Circularity
Government policies play a critical role in promoting material circularity. Regulations and incentives can encourage businesses to adopt circular practices and consumers to make more sustainable choices. Policies that support the development and implementation of advanced recycling technologies, and incentivize reuse and repair, are crucial for achieving significant progress.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Achieving material circularity requires collaboration across various sectors. Partnerships between governments, businesses, and research institutions can facilitate the development and implementation of innovative solutions. This collaborative approach can leverage the expertise and resources of different stakeholders, accelerating the transition to a circular economy. Promoting knowledge sharing and collaboration between stakeholders is a key factor in driving the successful implementation of material circularity initiatives.
Consumer Behavior and Consumption Patterns: Driving Circularity from the Bottom Up
Understanding the Consumer Mindset
Consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of their purchasing decisions, leading to a shift in priorities. This awareness isn't just a fleeting trend; it's a fundamental shift in how consumers perceive value. They're no longer solely focused on the price tag or immediate gratification; they're considering the entire lifecycle of a product, from its origin to its eventual disposal.
This growing consciousness is driving a demand for more sustainable and ethical products. Consumers are actively seeking out brands that align with their values, preferring those that prioritize environmental responsibility and social equity. This shift in consumer mindset is the bedrock of circularity from the ground up, shaping the market and influencing business practices.
The Rise of Conscious Consumption
The concept of conscious consumption is gaining traction, influencing purchasing decisions in profound ways. Consumers are actively choosing products with a reduced environmental footprint, opting for reusable items over disposable ones, and prioritizing brands committed to sustainable practices. This conscious consumerism is a significant force in driving the circular economy.
Consumers are increasingly demanding transparency from brands about their supply chains and manufacturing processes. This emphasis on transparency empowers them to make informed choices and hold companies accountable for their environmental and social impacts.
The Impact of Social Media and Influencer Marketing
Social media platforms and influencer marketing have become powerful tools in shaping consumer behavior. Influencers, often highly engaged with their followers, can effectively promote sustainable products and lifestyles. This reach can significantly impact consumer choices, driving demand for environmentally friendly options.
Social media also allows consumers to connect and share information about their experiences with sustainable products. This peer-to-peer interaction fosters a sense of community and encourages a wider adoption of circular practices.
The Role of Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in shaping consumer behavior and influencing consumption patterns. Incentives for sustainable practices, such as tax breaks for eco-friendly products, can encourage consumers to make more environmentally conscious choices. Regulations regarding waste management and product labeling also contribute to fostering a circular economy.
The Significance of Product Design and Packaging
Product design and packaging are critical factors in influencing consumer behavior and encouraging circularity. Products designed for durability, repairability, and recyclability are more likely to be chosen by conscious consumers. Innovative packaging solutions that minimize waste and maximize recyclability can also significantly impact consumption patterns.
The Importance of Education and Awareness Campaigns
Education and awareness campaigns play a vital role in educating consumers about the benefits of circularity and the impact of their consumption habits. Providing clear information about the lifecycle of products, the environmental implications of choices, and the benefits of circular solutions empowers consumers to make more sustainable decisions.
The Future of Circularity Driven by Consumer Demand
The future of circularity is intrinsically linked to consumer demand and the willingness of businesses to adapt. As consumer awareness continues to grow, businesses that embrace circular models and cater to this demand will thrive in the long run. The shift towards a circular economy is not just an environmental imperative; it's a consumer-driven movement.
This dynamic interplay between evolving consumer preferences, innovative business strategies, and supportive policies will pave the way for a more sustainable and resilient future.