Sustainable Fashion and the Rise of Conscious Consumers

Sustainable Materials: The Fabric of the Future
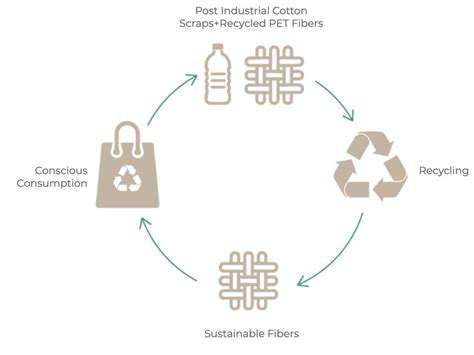
The fashion industry is increasingly recognizing the need for sustainable materials, moving away from traditional, resource-intensive fabrics like cotton and polyester. This shift is driven by growing awareness of the environmental impact of fast fashion and the desire for more ethical production methods. Innovative materials like recycled fibers, organic cotton, and plant-based alternatives are gaining popularity, offering a path toward a more environmentally friendly future for fashion.
These sustainable materials often boast superior performance characteristics, such as increased durability and breathability, alongside reduced water usage and carbon emissions throughout their lifecycle. This makes them not only environmentally sound but potentially more cost-effective in the long run by minimizing waste and reducing reliance on finite resources.
Circular Fashion Models: Reimagining the Cycle
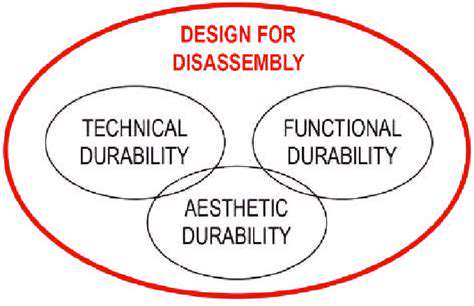
Circular fashion models are gaining traction, focusing on reducing textile waste and promoting the reuse and recycling of clothing and fabrics. These models aim to create a closed-loop system where garments are designed for disassembly and repurposing, minimizing the need for new material production. This approach is crucial for mitigating the environmental impact of the fashion industry's linear take-make-dispose model.
Transparency and Traceability: Building Trust
Consumers are demanding greater transparency and traceability in the fashion supply chain. This translates to knowing the origin of the materials, the working conditions of the laborers, and the environmental impact of the entire production process. Detailed information about each stage, from raw material sourcing to final product delivery, is paramount for fostering consumer confidence and promoting ethical practices.
Open communication and readily available data on these aspects will be vital for building trust and fostering a more sustainable fashion industry. Brands that prioritize transparency are more likely to attract conscious consumers and build lasting customer loyalty.
Technology's Role in Sustainable Fashion
Technological advancements are playing a significant role in driving innovation within the sustainable fashion sector. From 3D printing of garments to developing more efficient dyeing processes, technology is enabling the creation of sustainable materials and production methods.
Using technology to minimize waste and optimize resource utilization is crucial for a more sustainable future in the fashion industry. This includes utilizing digital tools for design, pattern making, and even virtual fashion shows to reduce the environmental footprint of the fashion industry.
Ethical Labor Practices: Fair Treatment for All
The fashion industry must prioritize ethical labor practices throughout the supply chain. This involves ensuring fair wages, safe working conditions, and respect for human rights for all workers involved in the production of clothing and accessories.
Promoting fair labor practices is not just a moral imperative but also a key driver of long-term sustainability. This includes supporting initiatives that empower workers and ensure they receive fair compensation for their labor. Ultimately, ethical labor practices are essential for creating a truly sustainable and equitable fashion system.
Consumer Responsibility: Conscious Choices
Consumers play a vital role in driving the shift toward sustainable fashion. By making conscious choices, such as opting for durable and well-made garments, supporting ethical brands, and reducing consumption, individuals can significantly impact the industry.
Consumers can support sustainable fashion by prioritizing quality over quantity and choosing brands that prioritize ethical and environmental concerns. By making informed decisions, consumers can create a demand for sustainable practices, ultimately influencing the industry to adopt more responsible and environmentally conscious methods.
The Future of Fashion Events: Adapting to Sustainability
Fashion events, from runway shows to trade fairs, can play a critical role in promoting sustainable fashion practices. Events can showcase innovative sustainable materials, highlight ethical brands, and foster dialogue about sustainable solutions.
By incorporating sustainability into fashion events, the industry can raise awareness and inspire change. This includes promoting eco-friendly initiatives within the event itself, such as using recycled materials and reducing waste, and encouraging a broader conversation about sustainable practices.