Sustainable Fashion: A Blueprint for a Better Future

Transparency and traceability are crucial components of any effective supply chain management system. They allow businesses to understand the origin and movement of goods, materials, and information throughout the entire process. This understanding is essential for building trust with customers and stakeholders, as well as for identifying and mitigating risks.
By implementing transparent and traceable systems, organizations can gain a more comprehensive view of their operations. This enables them to make more informed decisions about inventory management, production scheduling, and quality control. Improved visibility into the supply chain often leads to optimized processes and reduced costs.
Enhanced accountability is a key benefit of transparency and traceability. When every step of the supply chain is documented and verifiable, it becomes easier to identify responsible parties for any issues or discrepancies that may arise. This accountability is vital for maintaining ethical standards and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Furthermore, this detailed record-keeping allows for quicker and more effective resolution of problems. Tracing the flow of materials and information swiftly pinpoints the source of errors, enabling faster response and recovery.
Traceability systems can significantly improve customer confidence. Consumers are increasingly demanding greater transparency in the products they buy. Knowing the origins of ingredients, the manufacturing processes, and the ethical treatment of workers throughout the supply chain builds consumer trust and loyalty.
A crucial aspect of transparency is the ability to track products throughout their lifecycle. This includes detailed records of raw material sourcing, manufacturing processes, distribution channels, and final destination. This comprehensive record-keeping allows businesses to identify potential risks and address them proactively.
Implementing technology solutions for data management and tracking is vital for establishing effective transparency and traceability systems. These solutions can automate data collection, storage, and analysis, streamlining operations and reducing the risk of errors. Advanced technologies like blockchain can further enhance security and immutability, ensuring the integrity of the data.
Supply chain transparency and traceability are not just beneficial for internal operations; they also foster stronger relationships with business partners. By providing clear visibility into the entire process, businesses can collaborate more effectively and build trust with suppliers, distributors, and retailers. This collaborative approach often leads to innovation and improved efficiency throughout the entire network.
The benefits of transparency and traceability extend beyond financial gains. They contribute to a more sustainable and responsible supply chain. By understanding the environmental impact of each stage of production, businesses can make informed decisions to minimize their ecological footprint. Furthermore, ethical considerations, such as worker safety and fair labor practices, are easier to monitor and address with transparent systems.
A positive and supportive learning environment is crucial for fostering engagement and motivation. Students are more likely to participate actively and embrace new challenges when they feel safe, respected, and valued. Creating this environment involves actively listening to students, addressing their concerns, and celebrating their successes. This fosters a sense of belonging and encourages a growth mindset. It also reduces anxiety and promotes a more conducive atmosphere for learning.

Embracing Innovation and Technological Advancements
Sustainable Materials: A Foundation for Change
The quest for sustainable fashion hinges on the adoption of innovative and eco-friendly materials. Moving beyond traditional fabrics like cotton and polyester, designers and manufacturers are exploring a wide range of sustainable alternatives, including organic cotton, recycled fabrics, and innovative plant-based materials like Tencel and Piñatex. These materials often boast superior environmental profiles, requiring less water and pesticides in their production, and reducing the overall carbon footprint compared to conventional options. This shift towards sustainable materials is a crucial first step in dismantling the unsustainable practices inherent in traditional textile production.
Furthermore, the development and utilization of innovative techniques for processing these materials are crucial. These techniques often involve less energy-intensive methods and reduce the use of harmful chemicals, making the entire process more environmentally conscious. The focus is not just on finding new materials, but also on optimizing the existing ones and finding ways to create them with minimal environmental impact.
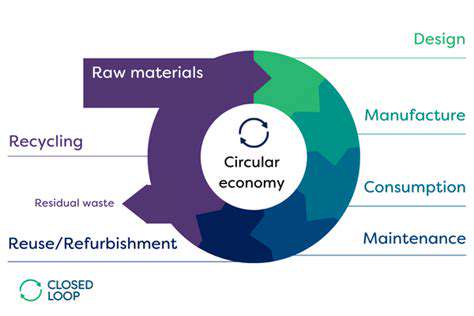
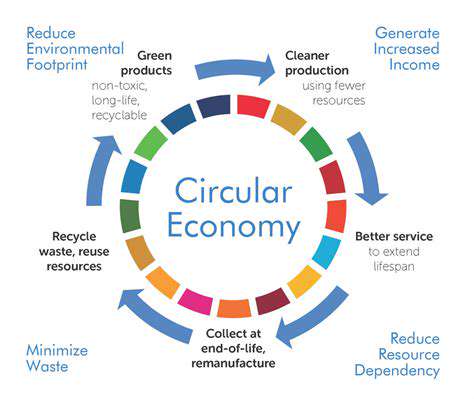
Circular Design Principles: Closing the Loop
Embracing circular design principles is paramount to achieving true sustainability in fashion. This involves designing garments for longevity, recyclability, and repairability. Garments should be designed with disassembly in mind, making it easier to recover and reuse materials at the end of their lifecycle. This approach reduces textile waste and minimizes the demand for new resources, effectively closing the loop and creating a more sustainable fashion system.
Ethical Production Practices: Fair Labor and Working Conditions
Sustainable fashion is not just about materials; it's also deeply intertwined with ethical production practices. Transparency and accountability are essential in ensuring fair labor practices throughout the supply chain. This involves fair wages, safe working conditions, and the elimination of exploitative labor practices. By prioritizing ethical considerations, we can support workers and communities involved in the fashion industry, promoting a more just and equitable system.
Companies committed to ethical production often implement rigorous monitoring and auditing systems to ensure compliance with labor standards. This commitment to worker rights and fair treatment creates a more sustainable and humane fashion industry, where everyone involved benefits from a more ethical and responsible approach.
Transparency and Traceability: Building Trust
In the quest for sustainable fashion, transparency and traceability are crucial for building consumer trust. Consumers need to know where their clothes come from, how they were made, and what impact their purchase has on the environment and communities. This information allows consumers to make informed decisions and support brands that prioritize sustainability and ethical practices.
Consumer Responsibility: Conscious Consumption
Sustainable fashion is not solely the responsibility of brands and manufacturers; consumers also play a vital role in driving change. Conscious consumption is key. This means being mindful of the environmental and social impact of our purchasing decisions. Choosing durable, well-made garments from reputable brands that prioritize sustainability is crucial. Consumers can also repair and reuse clothing whenever possible, extending its lifespan and reducing the demand for new products.
Sustainable Fashion Education and Advocacy: Fostering Change
Education and advocacy play a vital role in creating a sustainable fashion movement. Raising awareness about the environmental and social impacts of fast fashion is crucial for driving positive change. Educating consumers about sustainable materials, ethical production, and responsible consumption habits is essential to fostering a more sustainable fashion future. Advocating for policies and regulations that promote sustainability in the fashion industry can also create significant progress.