Sustainable Fashion: A Holistic Approach to a Better Industry
The Future of Sustainable Fashion: A Collective Effort

Circular Economy Principles in Sustainable Fashion
Sustainable fashion is increasingly focused on embracing circular economy principles, moving away from the traditional linear take-make-dispose model. This involves designing garments for durability, repairability, and recyclability. Implementing these principles requires a fundamental shift in the fashion industry, from a focus on fast production and consumption to one emphasizing longevity and resource efficiency. This approach can significantly reduce textile waste and minimize environmental impact.
By incorporating circularity into the design process, manufacturers can use recycled materials, design for disassembly and reuse, and create products with a longer lifespan. This reduces the demand for virgin resources, conserving raw materials and preventing the release of harmful chemicals into the environment.
Technological Advancements in Sustainable Textiles
Technological advancements are playing a crucial role in driving innovation within sustainable fashion. This includes the development of innovative materials like plant-based fabrics, bio-based polymers, and recycled fibers. These materials are often more sustainable than traditional options, requiring fewer resources and emitting lower amounts of greenhouse gases during production.
The use of 3D printing and other advanced manufacturing techniques is also transforming the industry. This allows for more customized and personalized designs, reduces textile waste, and enables the creation of intricate patterns and shapes that were previously impossible with traditional methods. These technologies open up new possibilities for sustainable and innovative design.
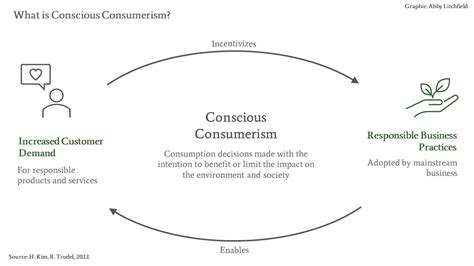
Consumer Demand and Ethical Production
Consumer demand for sustainable fashion is steadily increasing, driving brands to prioritize ethical and environmentally conscious practices. Consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental and social impacts of their purchasing decisions, leading to a greater emphasis on transparency and accountability from brands.
This growing consumer demand is pushing brands to adopt more ethical production practices, including fair wages, safe working conditions, and reduced labor exploitation. This shift is crucial for creating a truly sustainable and equitable fashion industry.
Transparency and Traceability in Supply Chains
Transparency and traceability are becoming increasingly important aspects of sustainable fashion. Consumers want to know where their clothes come from, how they are made, and the environmental and social impacts of their production. Brands are responding by implementing more transparent supply chains, allowing consumers to track the journey of their garments from raw material to finished product.
This increased transparency allows consumers to make informed purchasing decisions, hold brands accountable, and support ethical and sustainable practices. Traceability also allows for greater monitoring of environmental and social impact along the supply chain, promoting more responsible production and consumption.
The Role of Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in shaping the future of sustainable fashion. Governments can implement incentives for sustainable practices, such as tax breaks for companies using recycled materials or funding for research and development of sustainable textiles. This can encourage the adoption of sustainable practices throughout the industry.
Stronger regulations around textile waste and harmful chemicals can also significantly reduce the environmental impact of the industry. Government policies can create a supportive environment for sustainable fashion, driving innovation and encouraging a transition towards a more environmentally conscious industry.
The Evolution of Sustainable Fashion Retail
Sustainable fashion retail is evolving to meet the needs of conscious consumers, with a growing emphasis on online platforms, secondhand markets, and rental services. These platforms provide greater access to sustainable fashion options, enabling consumers to discover and purchase garments from eco-friendly brands. Sustainable fashion retail is also focusing on reducing waste through innovative approaches.
The rise of rental services and secondhand markets is transforming how people access and consume fashion. These models encourage circularity, reduce consumption, and minimize the environmental impact of the industry. This evolution is crucial to shifting the paradigm in the fashion industry.