The Environmental Impact of Chemical Discharges from Fashion Production: New Data
The Toxic Cocktail: Identifying the Key Pollutants
Industrial Discharge and Runoff
Industrial facilities play a vital role in modern economies, but their operations often introduce dangerous substances into the environment through direct discharges and runoff. These contaminants infiltrate water systems, endangering aquatic ecosystems and potentially entering human food supplies. The pollutants include toxic heavy metals such as lead and mercury, along with organic solvents and acids that persist in ecosystems. This creates a self-perpetuating cycle of environmental harm that may require generations to reverse.
Chemical-laden runoff from manufacturing sites frequently pollutes rivers, lakes, and coastal regions. The contamination doesn't remain localized - it travels downstream, allowing toxins to accumulate in fish and other organisms. This bioaccumulation ultimately threatens human health when people consume tainted seafood.
Agricultural Practices and Pesticide Use
Modern farming methods depend heavily on pesticides and fertilizers to maximize crop production. However, these chemicals frequently seep into groundwater and surface water, compromising drinking water quality and damaging aquatic habitats. The problem extends beyond immediate contamination as agricultural runoff carries these pollutants into nearby waterways, affecting entire ecosystems.
Pesticide residues can linger in soil and water for years, disrupting soil microbiology and reducing biodiversity. The overapplication of these chemicals has led to resistant pest populations, forcing farmers to use increasingly potent formulations that amplify environmental damage.
Urban Runoff and Stormwater Drains
Cities generate massive amounts of polluted runoff containing contaminants from roads, construction sites, and residential areas. This toxic mixture of heavy metals, petroleum products, and other hazardous materials flows into storm drains, eventually reaching natural waterways. The consequences include degraded aquatic ecosystems and potential health risks for humans.
During heavy rainfall, urban runoff frequently overwhelms treatment facilities, resulting in partially treated wastewater being released. Improving urban infrastructure with better stormwater management systems represents a critical step toward solving this environmental challenge.
Plastic Pollution and its Consequences
Our reliance on plastic products has created an environmental crisis affecting both terrestrial and marine ecosystems. Plastic waste, ranging from visible debris to microscopic particles, accumulates in nature, endangering wildlife and entering food chains. Animals that ingest plastic suffer from malnutrition, internal damage, and other serious health effects.
Emerging research indicates plastic pollution may cause extensive ecological disruption. Plastic fragments absorb and concentrate toxic substances, multiplying their harmful effects and potentially threatening human health through contaminated seafood consumption.
Atmospheric Emissions and Air Quality
Industrial operations, transportation networks, and other human activities release numerous pollutants into the air we breathe. These emissions, including fine particulates and noxious gases, contribute to respiratory diseases and other health problems. Chronic exposure can lead to severe long-term health consequences.
Air pollution doesn't just affect human health - it also contributes to acid rain formation and climate change, altering weather patterns and damaging ecosystems worldwide. Addressing this complex issue requires technological innovation, policy reforms, and individual behavioral changes.

Sustainable Solutions and the Future of Fashion Production
Sustainable Agriculture Practices
Regenerative farming methods focus on meeting current needs without compromising future generations' ability to meet theirs. Techniques like crop diversification, biological pest control, and conservation tillage improve soil fertility, conserve water, and reduce chemical inputs. These approaches create more resilient agricultural systems that benefit both farmers and the environment.
Adopting these methods can lower production costs while increasing yields over time. Sustainable farming also supports greater biodiversity in agricultural landscapes, enhancing overall ecosystem health.
Renewable Energy Sources
Shifting to renewable energy represents our best hope for combating climate change and reducing fossil fuel dependence. Solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal technologies provide clean alternatives with minimal environmental impact. As these technologies become more affordable and efficient, they offer practical solutions for global energy needs.
The renewable energy sector also creates new employment opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance, supporting economic development alongside environmental protection.
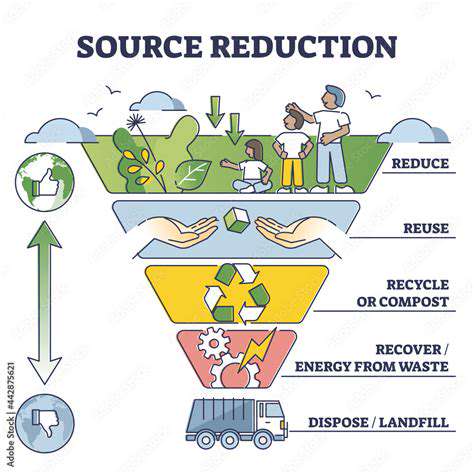
Waste Management and Recycling
Comprehensive waste management systems are essential for reducing environmental harm. Effective collection, sorting, and processing can dramatically decrease landfill waste while recovering valuable materials. This approach benefits ecosystems while generating economic activity in the recycling industry.
Developing advanced waste processing technologies and educating consumers about proper disposal methods are critical for building truly sustainable waste systems.
Efficient Resource Use
Sustainability requires optimizing resource utilization across all sectors. Water conservation in agriculture and industry, energy-efficient building design, and circular economy models all contribute to reduced environmental impact. These strategies not only protect natural resources but also deliver substantial financial savings.
Sustainable Transportation
Eco-friendly transportation solutions prioritize reduced emissions and energy efficiency. Expanding public transit networks, promoting cycling and walking infrastructure, and developing electric vehicles all contribute to cleaner air and healthier communities. Investing in sustainable transport infrastructure creates more accessible, environmentally responsible cities.
Urban Planning and Design
Sustainable city planning emphasizes environmental and human wellbeing. Incorporating green spaces, efficient infrastructure, and smart technologies creates more livable urban environments. These measures mitigate urban heat islands and improve air quality, benefiting public health while reducing ecological impacts.
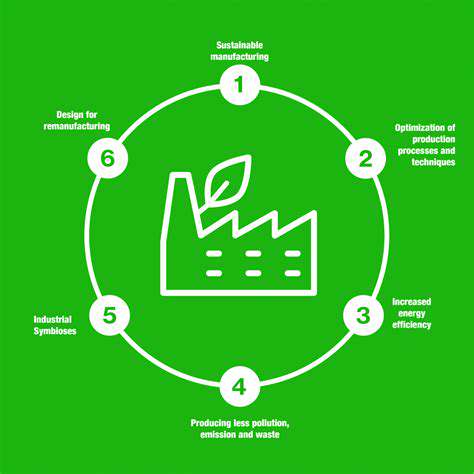
Sustainable Consumption and Production
Responsible consumption involves choosing durable, ethically produced goods and reducing overall material consumption. Prioritizing quality over quantity and supporting sustainable businesses are essential for creating a circular economy. Encouraging mindful purchasing decisions and sustainable manufacturing practices represents our best path toward environmental sustainability.