The Future of Fashion Production: Sustainable and Smart: New Visions
The Rise of Circularity in Fashion Manufacturing

Understanding the Circular Economy in Fashion
The fashion industry is notoriously unsustainable, with significant environmental impacts stemming from textile production, dyeing processes, and the sheer volume of discarded garments. The circular economy offers a paradigm shift, aiming to minimize waste and maximize resource utilization. This approach promotes a closed-loop system where materials are reused, repurposed, and recycled, ultimately reducing the industry's reliance on virgin resources and minimizing harmful emissions.
Circular fashion emphasizes design for durability, repairability, and recyclability. It fosters a shift in consumer behavior towards extending the lifecycle of garments and embracing clothing as a durable asset rather than a disposable commodity. This also includes promoting the use of sustainable materials and ethical manufacturing practices, reducing the environmental footprint at every stage.
Designing for Durability and Repurposing
Designing garments for longevity is crucial in the circular fashion model. This involves using high-quality, durable materials that resist wear and tear, facilitating repairs and extending the lifespan of garments. Embracing innovative design techniques and considering the entire lifecycle of a garment from initial design to end-of-life are essential aspects of this approach.
The concept of repurposing and upcycling is also key. Transforming old garments into new, unique pieces, or using them for different purposes, reduces textile waste and fosters creativity. This could include transforming old shirts into bags, or repurposing jackets into cushions, demonstrating the versatility of fabrics and the creative potential of repurposing.
Promoting Repair and Resale
Encouraging the repair and maintenance of clothing items is another vital aspect of the circular economy. Repair services and workshops can help extend the lifespan of garments, reducing the need for constant consumption. This not only minimizes waste but also fosters a sense of responsibility and care towards clothing items.
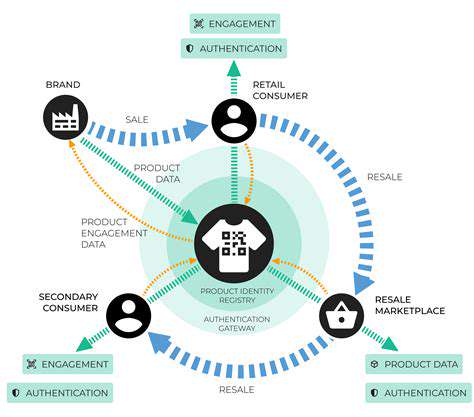
Resale platforms and secondhand markets play a significant role in promoting circularity. These platforms provide a market for pre-owned clothing, enabling consumers to access affordable and stylish garments while reducing textile waste. This helps to keep clothing in use longer and reduces the demand for new products.
The Role of Consumers in Circular Fashion
Consumers play a pivotal role in driving the circular fashion revolution. Adopting conscious consumption habits, such as prioritizing durable and repairable garments, choosing secondhand options, and engaging in repair services, are crucial steps in supporting a sustainable fashion system. By making informed choices, consumers can actively reduce their environmental impact and support brands committed to circular practices.
Sustainable Materials and Production Methods
Shifting towards the use of sustainable and recycled materials is essential for circular fashion. This includes incorporating innovative and eco-friendly materials derived from recycled fibers, organic cotton, and innovative bio-based alternatives. Such materials will reduce the environmental impact of the production processes and minimize the reliance on finite resources.
Furthermore, promoting ethical and transparent production methods is critical. This involves supporting manufacturers who prioritize fair labor practices, safe working conditions, and environmental responsibility. Transparency in supply chains is essential for ensuring that sustainability is maintained throughout the production process.
The Future of Circular Fashion
The future of circular fashion is bright, with increasing awareness and adoption of sustainable practices. This trend signifies a shift away from fast fashion's throwaway culture towards a more sustainable and responsible approach to clothing. Collaboration between designers, manufacturers, retailers, and consumers is essential for the successful implementation of circular principles in the fashion industry. The ongoing research and development of innovative technologies and processes will further accelerate progress in this area.
Smart Technologies Driving Efficiency and Transparency
Smart Materials and Processes
Innovative smart materials are revolutionizing the fashion industry, enabling more efficient and sustainable production processes. These materials often possess inherent properties like self-healing capabilities, improved durability, and enhanced responsiveness to environmental factors. This leads to reduced waste during manufacturing by minimizing material overuse and maximizing the lifespan of garments. For instance, fabrics developed with advanced self-cleaning properties require less frequent washing, significantly lowering water consumption and chemical use.
Furthermore, smart processes, such as 3D printing and automated cutting, are streamlining production. These technologies enable bespoke designs and customized products, reducing material waste and optimizing production timelines. This precision and customization are key to improving efficiency and reducing the environmental impact of the entire production chain, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable future for the fashion industry.
Data-Driven Design and Supply Chains
Integrating data analytics into the design and supply chain processes of the fashion industry is leading to greater transparency and efficiency. By tracking materials, production stages, and consumer preferences, brands can gain valuable insights into their operations and identify areas for improvement. This data-driven approach allows for more informed decision-making, leading to better resource allocation and reduced waste throughout the entire lifecycle of a garment.
Furthermore, utilizing data analytics in supply chain management enables brands to better understand their sourcing strategies and identify potential risks. This enhanced visibility and control help to ensure ethical and sustainable sourcing practices, building trust with consumers who increasingly prioritize transparency and ethical production.
Enhanced Customer Experience and Personalization
Smart technologies are transforming the customer experience in the fashion industry, allowing for greater personalization and seamless interaction. Digital platforms and augmented reality applications allow customers to virtually try on clothes, explore different styles, and receive personalized recommendations based on their preferences. This personalized approach enhances customer satisfaction and fosters stronger brand loyalty.
Sustainable Practices and Traceability
Smart technologies are driving the adoption of sustainable practices throughout the fashion industry. From using sensors to track materials and monitor environmental conditions in factories to utilizing blockchain technology to ensure product authenticity and traceability, brands are leveraging these tools to create more sustainable and transparent supply chains. These innovative approaches demonstrate a commitment to ethical and environmental responsibility, ultimately building consumer trust and fostering a more sustainable fashion ecosystem. By implementing these technologies, brands are able to demonstrate accountability at every stage of production, from raw material sourcing to final delivery.