The Global Challenge of Textile Waste
Understanding the lifecycle of a garment is crucial to appreciating the environmental impact of textile waste. The extraction of raw materials, the production processes, the transportation of goods across continents, the use of the garment by the consumer, and ultimately, its disposal all contribute to the overall environmental footprint. Each stage presents opportunities for improvements in sustainability and responsible practices.
Waste Generation and Disposal Methods
The sheer volume of textile waste generated globally is staggering. From discarded garments in landfills to textile scraps and remnants, the disposal of this waste often leads to environmental contamination. Traditional methods of disposal, such as landfilling, release harmful greenhouse gases and pose significant risks to soil and water quality. The need for innovative and sustainable disposal methods is paramount.
The Impact on Water Resources
Textile manufacturing is a water-intensive industry. The dyeing and finishing processes often involve the use of harmful chemicals that contaminate water sources, posing risks to human health and aquatic life. The depletion of freshwater resources, particularly in regions where water is already scarce, is a serious concern exacerbated by unsustainable textile practices.
Efficient water management strategies and the adoption of eco-friendly dyes and finishing agents are crucial to mitigating the impact on water resources.
Microplastic Pollution and its Consequences
The breakdown of synthetic fibers during washing and wear releases microplastics into the environment. These tiny particles contaminate water bodies, affecting marine life and potentially entering the human food chain. The long-term consequences of microplastic pollution are still being researched, but the potential for harm to ecosystems and human health is substantial.
Consumer Behavior and its Role in Waste Reduction
Consumers play a vital role in reducing textile waste. Sustainable consumption patterns, such as opting for durable and high-quality garments, extending the lifespan of clothing through repair and repurposing, and choosing eco-friendly brands are all crucial steps in mitigating the environmental impact of the textile industry. Educating consumers about the environmental consequences of their choices can drive positive change.
Innovative Solutions and Technological Advancements
The textile industry is increasingly exploring innovative solutions to reduce waste and minimize its environmental impact. From developing biodegradable fibers to implementing closed-loop systems for textile recycling, technological advancements are paving the way for more sustainable practices. Investing in research and development of these technologies is critical to achieving significant progress in combating textile waste.
Innovative Solutions for a Sustainable Future
Innovative Solutions for Textile Waste Reduction
The global textile industry faces a significant challenge in managing the vast amount of waste it generates. Innovative solutions are crucial for mitigating this environmental impact and ensuring a more sustainable future. These solutions must address the entire lifecycle of textiles, from design and production to consumption and disposal.
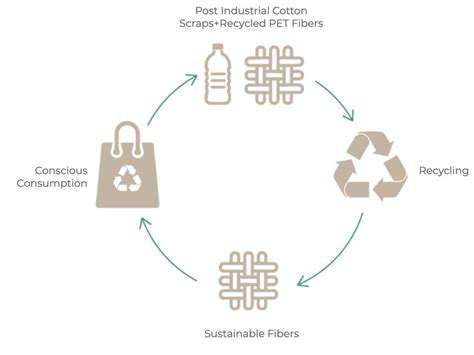
Adopting circular economy principles, emphasizing reuse and recycling, and promoting the development of biodegradable materials are critical steps towards minimizing textile waste. This requires a collaborative effort across the entire supply chain, from designers and manufacturers to retailers and consumers.
Designing for Durability and Longevity
Designing textiles for durability and longevity is a key aspect of minimizing waste. By incorporating durable materials and implementing robust manufacturing processes, we can extend the lifespan of garments and reduce the frequency of replacements. This approach not only decreases waste but also fosters a more conscious consumption pattern.
Promoting Sustainable Materials
The exploration and adoption of sustainable materials are essential for a more environmentally friendly textile industry. Bio-based fabrics, recycled materials, and innovative approaches to textile production are crucial for reducing the reliance on traditional, often resource-intensive, methods. This includes exploring the potential of innovative materials like mushroom leather or seaweed-based fibers.
Improving Recycling and Upcycling Techniques
Improving recycling and upcycling techniques is vital for transforming textile waste into valuable resources. Developing advanced recycling technologies that can effectively break down and repurpose textile materials into new products is paramount. This includes exploring innovative methods for textile recycling, such as chemical recycling, which can break down complex materials into their constituent parts, and innovative upcycling techniques.
Encouraging Consumer Responsibility
Consumer behavior plays a significant role in textile waste reduction. Educating consumers about the environmental impact of their choices and promoting responsible consumption patterns are critical steps in fostering a more sustainable textile industry. Encouraging consumers to prioritize durable, high-quality garments and to repair or reuse existing items can significantly reduce textile waste.
Implementing Extended Producer Responsibility
Implementing extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes is essential for holding manufacturers accountable for the end-of-life management of their products. This approach requires producers to take responsibility for the collection and recycling of their textiles, fostering a more sustainable and circular textile economy. EPR schemes can incentivize the development of more sustainable materials and manufacturing processes.
Government Regulations and Incentives
Government regulations and incentives can play a crucial role in driving the adoption of sustainable practices in the textile industry. Implementing policies that encourage the use of sustainable materials, promote textile recycling, and penalize unsustainable practices are vital for achieving significant progress. Financial incentives, tax breaks, and stricter regulations can accelerate the transition towards a more sustainable textile industry, influencing both producers and consumers.