Transparency and Traceability in Ethical Sourcing
Understanding the Concept
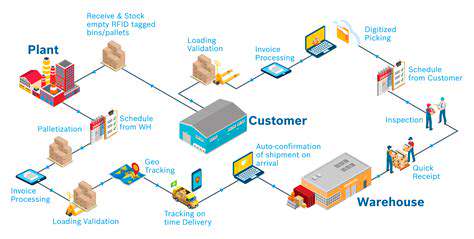
Product traceability represents a detailed historical record of an item's entire lifecycle. From initial materials to final delivery, this comprehensive tracking serves multiple industries. When quality issues arise, traceability systems enable rapid pinpointing of problems, minimizing disruptions. Meticulous documentation creates an audit trail that enhances both compliance and consumer confidence.
Benefits of Implementing Traceability
Quality control improves dramatically with proper tracking mechanisms. Identifying defects at their source prevents widespread issues, saving both time and resources. Regulatory requirements become easier to meet when every production phase remains documented. The ability to quickly trace problems also reduces operational downtime significantly.
Key Components of a Traceability System
Effective systems require centralized data repositories with robust search capabilities. Comprehensive records must capture every transformation and transfer, creating an unbroken chain of custody. Seamless information sharing between departments ensures the entire organization benefits from traceability data.
Applications Across Industries
Pharmaceutical firms rely on traceability to guarantee drug safety. Manufacturers use it to monitor component quality throughout assembly lines. Food producers particularly benefit from rapid recall capabilities, protecting both consumers and brand reputation. These applications demonstrate traceability's universal value across sectors.
Building Transparency into Your Supply Chain
Understanding the Importance of Transparency
Modern consumers increasingly demand visibility into product origins, making supply chain transparency essential rather than optional. Ethical considerations now encompass environmental impact and labor conditions alongside traditional business metrics. True transparency requires active partnership with suppliers and verifiable tracking systems.
Implementing Traceability Systems
Robust tracking mechanisms allow businesses to monitor materials from source to store shelf. When implemented effectively, these systems enable quick response to quality or ethical concerns, limiting negative consequences.
Fostering Ethical Practices Throughout the Chain
Transparent operations verify fair wages and safe working conditions at every production stage. Regular supplier audits and open communication demonstrate genuine commitment to ethical standards, differentiating brands in competitive markets.
Measuring and Monitoring Progress
Quantifiable metrics prove transparency initiatives' effectiveness. Tracking supplier compliance rates and consumer engagement with ethical information helps refine strategies. Data-driven adjustments ensure programs remain relevant as expectations evolve.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Transparency and Traceability
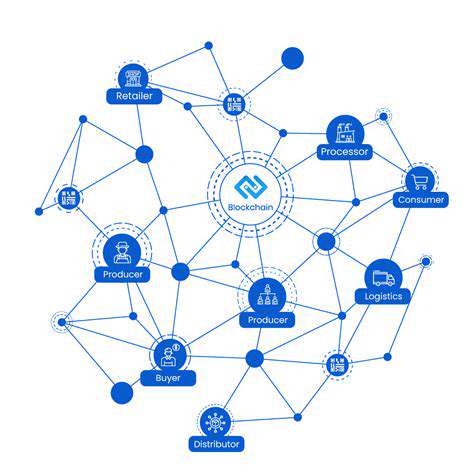
The Automation of Tasks
Modern tools handle repetitive processes with precision, freeing human creativity. Automated systems dramatically reduce errors while accelerating production, creating efficiencies across operations. These advancements also streamline administrative functions, cutting costs.
Improved Communication and Collaboration
Digital platforms dissolve geographical barriers between teams. Real-time information sharing fosters unexpected innovations as diverse perspectives converge. Cloud-based systems ensure everyone accesses current data simultaneously.
Enhanced Data Analysis and Insights
Advanced analytics transform raw information into strategic assets. Visualization tools reveal patterns that inform smarter decisions, helping organizations stay ahead of market shifts. This data-driven approach creates competitive advantages.
Increased Accessibility and Inclusivity
Technological solutions empower individuals with different abilities. Assistive technologies create equal opportunities for participation, enriching organizational diversity. Remote access tools also expand educational and professional possibilities.
The Importance of Cybersecurity and Data Protection
As reliance on digital systems grows, so do security requirements. Robust protections maintain stakeholder trust in transparency initiatives, safeguarding sensitive information. Continuous updates counter evolving cyber threats effectively.
Measuring and Monitoring Progress: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Choosing the Right KPIs
Effective measurement begins with carefully selected indicators that reflect strategic priorities. Practical data collection methods ensure consistent tracking. Alignment across stakeholders guarantees everyone focuses on shared objectives.
Tracking and Analyzing KPI Data
Regular reviews uncover meaningful trends in performance metrics. Visualization tools help teams quickly grasp complex information, enabling timely adjustments. Documented analysis creates accountability for improvement efforts.
Implementing and Maintaining Monitoring Systems
Dedicated oversight ensures measurement systems remain accurate. Periodic reviews adapt tools to changing needs, keeping metrics relevant. Well-maintained systems provide the insights needed for sustained success.