Collaborative Initiatives for Ethical Fashion Solutions: Shared Responsibility: New Partnerships

Sustainable Sourcing of Raw Materials
Sustainable materials require responsible sourcing from the outset. This means prioritizing suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental standards throughout their supply chain. Transparency and traceability are crucial to ensure that materials are genuinely sustainable and not simply marketed as such. This involves meticulously tracking the origin of materials, from the initial extraction to the final product, allowing for greater accountability and a reduction in environmental impact.
Careful consideration must be given to the environmental impact of the extraction process. Using materials that require minimal processing and have a low carbon footprint during extraction is essential. This can involve exploration of alternative extraction methods and materials that minimize deforestation and habitat disruption.
Manufacturing Processes and Energy Efficiency
Sustainable production goes beyond the raw materials. Efficient manufacturing processes are fundamental to minimizing waste and conserving energy. Implementing lean manufacturing principles, optimizing production layouts, and adopting advanced technologies for energy efficiency are crucial steps. This reduces the overall environmental footprint of the production line, from start to finish.
Utilizing renewable energy sources in the manufacturing process is another vital aspect. Switching to solar, wind, or hydroelectric power can dramatically reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease greenhouse gas emissions. This transition is not just environmentally beneficial; it also often translates into cost savings in the long run.
Waste Reduction and Recycling
Minimizing waste generation throughout the entire production cycle is paramount. This involves optimizing designs to reduce material usage, implementing closed-loop systems for recycling, and exploring innovative waste reduction technologies. By minimizing waste, we not only conserve resources but also lessen the burden on landfills and reduce pollution.
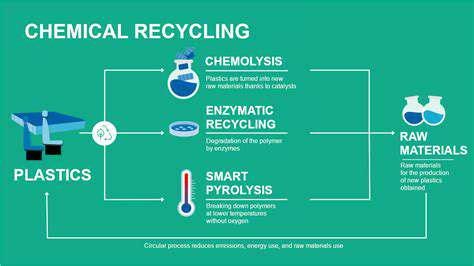
Recycling is a critical component of a sustainable production cycle. Developing and implementing effective recycling programs, both for the manufacturing process and for consumer products, ensures that materials are reused instead of being discarded. This not only conserves resources but also lowers the overall environmental impact.
Circular Economy Principles
Adopting circular economy principles is essential for creating a truly sustainable production model. These principles prioritize the reuse and recycling of materials, thereby minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency. This approach fosters a closed-loop system where products are designed for disassembly and reuse, rather than ending up in landfills.
Bio-Based and Biodegradable Materials
Exploring and utilizing bio-based and biodegradable materials represents a significant shift towards sustainability. These materials, derived from renewable resources like plants and agricultural byproducts, offer a viable alternative to traditional materials with reduced environmental impact. The use of these materials can drastically reduce the reliance on fossil fuels and decrease the demand for finite resources.
However, the full potential of bio-based materials needs careful consideration. Ensuring that the production of these materials does not lead to increased competition for arable land and negatively impact food production is critical. A thorough life-cycle assessment is necessary to evaluate the environmental performance of these materials.
Product Design for Durability and Longevity
Designing products for durability and longevity is crucial for reducing the overall environmental impact. Products that are built to last longer require fewer replacements, thus minimizing the demand for raw materials and reducing waste. Investing in robust designs and high-quality components is essential in achieving this goal.
Encouraging repairability and upgradeability of products is another aspect of durable design. This allows for extending the lifespan of products, reducing the need for new production and consumption.
Life Cycle Assessment and Impact Analysis
Implementing a comprehensive life cycle assessment (LCA) is essential to evaluate the environmental impact of a product or material from cradle to grave. This assessment considers all stages of the product's lifecycle, from raw material extraction to manufacturing, use, and disposal. LCA provides a holistic understanding of the environmental footprint of the product.
Conducting a thorough impact analysis is vital for identifying areas for improvement in the production process. Identifying critical environmental impacts and understanding their relationship to various stages of the product's life cycle allows for effective strategies to minimize the negative consequences.