Investing in Circular Innovation: Opportunities for Sustainable Growth
Identifying Investment Opportunities in Circular Innovation
Understanding Circular Innovation
Circular innovation represents a paradigm shift in how we approach resource management and production. It moves away from the traditional take-make-dispose linear model, focusing instead on designing out waste, keeping products and materials in use, and regenerating natural systems. This approach not only reduces environmental impact but also creates new business opportunities and fosters economic growth by leveraging the inherent value in existing materials and products.
Identifying Key Drivers of Circularity
Several factors are driving the shift toward circular innovation. Increasing environmental awareness and stricter regulations are putting pressure on businesses to adopt more sustainable practices. Furthermore, the rising cost of raw materials and the growing scarcity of certain resources are incentivizing companies to explore alternative materials and production methods. Technological advancements also play a crucial role in enabling circular solutions, from advanced recycling processes to innovative product design.
Recognizing Potential Investment Areas
Investment opportunities in circular innovation are diverse and span across various sectors. From recycling and waste management technologies to the development of closed-loop supply chains, there are numerous avenues for investors to contribute to a more sustainable future. This includes funding research and development of new materials, processes, and technologies that enable circularity. Furthermore, investing in companies that are already implementing circular practices can be a powerful strategy for generating returns while promoting positive environmental impact.
Evaluating the Financial Viability of Circular Projects
Assessing the financial viability of circular projects requires a nuanced approach that goes beyond traditional profitability metrics. Investors need to consider the long-term value proposition of circular solutions, recognizing that environmental and social benefits can translate into substantial financial returns over time. This involves evaluating the potential cost savings from reduced resource consumption, the market potential for innovative products and services, and the future value of a strong brand reputation built on sustainability.
Analyzing Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Understanding current market trends and consumer preferences is crucial for identifying successful circular investment opportunities. Consumers are increasingly demanding sustainable products and services, and brands that demonstrate a commitment to circularity are often rewarded with higher sales and brand loyalty. Investors need to identify emerging trends, such as the growing demand for recycled materials, the rise of the sharing economy, and the growing popularity of eco-conscious products, to pinpoint high-potential investment opportunities.
Assessing Risk and Return Profiles in Circular Investments
Circular investments, while often promising, come with inherent risks. The novelty of some technologies, the uncertainty of future regulations, and the potential for market volatility can pose challenges. Therefore, a thorough risk assessment is crucial for investors. A comprehensive due diligence process should include evaluating the technical feasibility of the proposed solutions, understanding the competitive landscape, and assessing the potential for regulatory hurdles. Carefully balancing risk and return profiles is vital for successful circular investment strategies, ultimately focusing on projects with strong long-term potential and well-defined exit strategies.
The Role of Technology in Circular Innovation

The Evolution of Circular Economy Principles
Technological advancements are fundamentally reshaping the principles of the circular economy, enabling a paradigm shift from a linear take-make-dispose model to a more sustainable and resource-efficient approach. This evolution hinges on the ability of technology to optimize resource utilization, reduce waste, and promote the reuse and recycling of materials. This shift is crucial for mitigating the environmental impact of industrial processes and achieving global sustainability goals.
The circular economy concept itself is not new, but its practical application and widespread adoption have been significantly accelerated by technological innovation. Advanced materials science, coupled with sophisticated data analytics, allows for the design of products with enhanced durability and recyclability.
Technological Tools for Resource Recovery
Technological tools are increasingly vital in the recovery and reuse of valuable resources from waste streams. Advanced sorting technologies, such as automated optical and magnetic separators, are enabling more efficient and cost-effective recycling processes. These technologies can discern different materials with precision, leading to higher-quality recycled products and reducing the amount of material ending up in landfills.
Furthermore, innovative technologies like bioremediation and chemical recycling are emerging to handle complex or difficult-to-recycle materials. These processes offer promising solutions for effectively dealing with persistent pollutants and waste streams, promoting resource recovery and minimizing environmental damage.
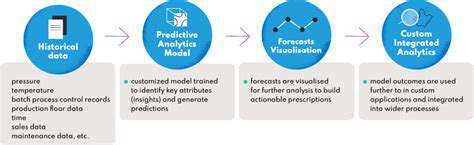
Data Analytics and Supply Chain Optimization
Data analytics plays a crucial role in optimizing circular supply chains. By tracking the flow of materials and products throughout the lifecycle, businesses can gain valuable insights into resource consumption, waste generation, and potential areas for improvement. This data-driven approach allows for the identification of inefficiencies and the implementation of strategies for enhanced resource utilization. This data-driven approach ensures that resources are used most effectively, minimizing waste and maximizing the value extracted from materials.
Furthermore, advanced data analytics can help predict and prevent material waste. By analyzing patterns and trends in consumption and production, businesses can proactively identify and address potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies in their supply chains. This preventative approach contributes to a more sustainable and resource-efficient system.
Enabling Technologies for Product Design and Manufacturing
Technology is transforming product design and manufacturing processes in the circular economy. The development of 3D printing and other additive manufacturing techniques allows for the creation of customized and complex parts with minimal material waste. This approach reduces the reliance on traditional methods that often result in excessive material usage and production of scrap.
Furthermore, the integration of digital twins in the design process enables virtual testing and optimization of product designs, enhancing product durability and recyclability. This iterative approach to design leads to products that are more sustainable and less impactful on the environment.
Regenerative real estate moves beyond simply minimizing environmental impact to actively restoring and enhancing the health of our planet and communities. This paradigm shift demands a fundamental rethinking of how we design, build, and operate our buildings, embracing principles of sustainability, resilience, and community well-being. Instead of simply aiming for zero negative impact, regenerative approaches actively seek to create positive change, fostering biodiversity, improving air and water quality, and supporting local economies.
Measuring and Evaluating Impact: Beyond Financial Returns

Defining Impact Measurement
Impact measurement is a crucial component of any successful initiative, whether it's a social enterprise, a non-profit organization, or a corporate social responsibility program. It involves systematically collecting and analyzing data to understand the effects of a project or program on its intended beneficiaries and the wider community. This process goes beyond simply tracking outputs; it delves into the outcomes and ultimately, the long-term impact.
A key element of impact measurement is clearly defining the intended impact beforehand. This ensures that the data collected is relevant and allows for a meaningful evaluation of the program's success in achieving its objectives. This definition should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Identifying Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Choosing appropriate KPIs is essential for accurately measuring impact. These indicators should directly reflect the program's goals and objectives. For example, if the goal is to improve literacy rates, KPIs might include the number of students who have achieved proficiency in reading, the number of books read by students, and the improvement in test scores. By focusing on these specific KPIs, the impact evaluation becomes more targeted and effective.
It's important to consider both quantitative and qualitative data when identifying KPIs. Quantitative data provides numerical metrics, while qualitative data offers insights into the experiences and perspectives of beneficiaries. Combining both types of data provides a more comprehensive understanding of the program's impact.
Data Collection and Analysis Methods
A crucial aspect of impact measurement is the systematic collection of data. This often involves surveys, interviews, focus groups, and observations, and the method selected should align with the specific program and its goals. Careful planning and execution of data collection are essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data. The chosen methods must be appropriate and reliable to ensure the quality of the results.
Analyzing the collected data is equally important. Data analysis should identify trends, patterns, and correlations that provide insights into the program's effectiveness. Sophisticated statistical methods may be required to ensure the data is correctly interpreted and used to inform future decisions.
Benchmarking and Comparison
Benchmarking against similar programs or initiatives is a valuable tool for evaluating impact. Comparing performance allows for the identification of best practices and areas for improvement within a program. By benchmarking, organizations can identify what works well in other similar programs and adopt or adapt those strategies.
Comparing the impact of different interventions or approaches is crucial to understanding which methods are most effective. This comparison allows for informed decision-making regarding resource allocation and program design.
Reporting and Communication of Findings
Finally, communicating the findings of impact measurement is essential for transparency and accountability. Clear and concise reports that effectively communicate the results are vital for stakeholders. These reports should not only highlight successes but also identify areas where improvements are needed.
Sharing the findings with key stakeholders, including beneficiaries, funders, and partners, is essential for fostering collaboration and ensuring that the lessons learned are applied to future initiatives.