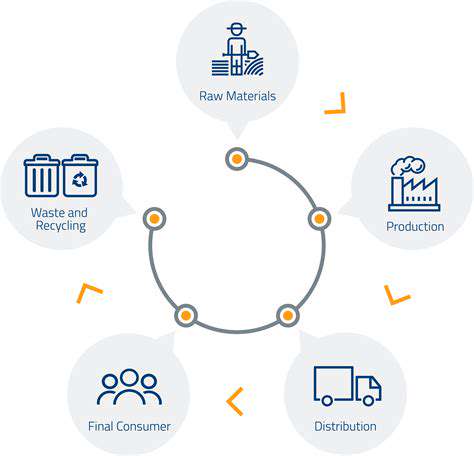
Understanding the Garment Worker's Journey: New Research
Working Conditions in Garment Factories
Garment factories often operate in challenging environments, with long working hours and demanding production schedules. Workers may be subjected to intense pressure to meet quotas, leading to stressful and potentially unsafe conditions. This pressure can manifest in physical strain, as workers are frequently required to perform repetitive tasks for extended periods, contributing to musculoskeletal disorders. Maintaining a clean and hygienic work environment is crucial, but these conditions can sometimes be compromised due to high production demands.
The layout and design of the factory floor can also play a significant role in worker well-being. Poorly designed spaces, insufficient ventilation, and inadequate access to rest areas can contribute to fatigue and reduced productivity. Moreover, the lack of proper safety equipment and training can expose workers to hazards that could lead to injuries or illnesses. Understanding these conditions is critical to improving the overall working experience and promoting the well-being of garment factory workers.
Health Hazards Associated with Garment Production
The garment industry presents a range of health hazards, often stemming from exposure to various chemicals used in textile production. These chemicals, including dyes, solvents, and finishing agents, can cause respiratory problems, skin irritations, and long-term health issues. Exposure to these substances can be particularly acute for workers who lack proper personal protective equipment (PPE) or training on safe handling procedures. Addressing these hazards requires comprehensive safety protocols and regular health screenings for employees.
Beyond chemical exposure, the repetitive nature of many garment tasks can lead to musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs). These issues, such as carpal tunnel syndrome and back pain, can significantly impact workers' quality of life and ability to perform their jobs. Ergonomic considerations, such as proper workstation design and the provision of adjustable equipment, are vital to mitigating these risks and preventing long-term health problems. Implementing proactive measures for addressing these health issues is crucial for a productive and healthy workforce.
Impact of Working Conditions on Worker Wellbeing
The cumulative effect of challenging working conditions, combined with the potential health hazards, can significantly impact the overall wellbeing of Garment workers. Stress, fatigue, and the risk of injury or illness can lead to reduced productivity, increased absenteeism, and diminished job satisfaction. Creating a supportive and safe work environment is crucial for fostering employee morale and encouraging a sense of belonging within the workplace. This also includes offering opportunities for rest breaks, and providing access to resources such as counseling services.
The mental health of garment workers is also a critical consideration. The pressure to meet production targets, coupled with potential exposure to harmful substances, can induce stress and anxiety. This can further exacerbate existing mental health conditions or lead to new ones. Employers have a responsibility to address these concerns by creating a work environment that prioritizes employee well-being and provides access to mental health support.
Addressing the Issues: Strategies for Improvement
Improving working conditions and mitigating health hazards in the garment industry requires a multifaceted approach. This includes implementing strict safety regulations, providing comprehensive training on safe handling procedures, and ensuring the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). Investing in ergonomic workstations and promoting proper lifting techniques are critical to reducing the risk of musculoskeletal disorders. Regular health screenings and access to healthcare are essential to detect and address potential health problems early on. Open communication channels and employee feedback mechanisms are also crucial to creating a supportive work environment.
Ultimately, a commitment from all stakeholders – including factory owners, workers, and government agencies – is necessary to foster a system where worker well-being and safety are paramount. This involves ongoing monitoring, evaluation, and adaptation of safety protocols to ensure compliance with the highest standards of worker protection.
Artificial intelligence (AI) presents a fascinating opportunity to revolutionize support systems for neurodivergent individuals. By understanding the unique cognitive processes and challenges faced by those with conditions like autism, ADHD, and dyslexia, AI can be tailored to create personalized learning environments, assistive technologies, and even tools to improve social communication. The potential for AI to make a meaningful impact on the lives of neurodivergent individuals is immense, offering a path towards greater inclusion and empowerment.
Empowering Garment Workers: The Path Forward
Understanding the Challenges
Garment workers, often overlooked in the global supply chain, face a multitude of challenges, from low wages and unsafe working conditions to limited access to education and healthcare. These issues often intersect, creating a complex web of systemic problems that hinder their ability to thrive and build a better future. Understanding these challenges is crucial for any effort to empower these workers and promote fair labor practices.
The lack of fair compensation frequently leads to a cycle of poverty. Workers may struggle to afford basic necessities, impacting their health and well-being, and limiting their opportunities for personal and professional development. This cycle can be particularly detrimental to families, impacting the overall quality of life for entire communities.
The Importance of Fair Wages
Fair wages are fundamental to empowering garment workers. A living wage, one that allows workers to meet their basic needs and participate fully in society, is essential. This includes considering not only the cost of living in the specific location but also the size of families and the additional expenses associated with raising children. Adequate compensation ensures workers can contribute to their communities while also improving their quality of life.
Improving Working Conditions
Unsafe working conditions are a pervasive issue in many garment factories. This includes inadequate safety measures, excessive workloads, and potential exposure to harmful chemicals and materials. Protecting workers' health and safety is paramount. Addressing these concerns through the implementation of strong safety regulations and worker protections will lead to a more sustainable and humane work environment.
Promoting Education and Skills Development
Empowering garment workers also involves providing opportunities for education and skill development. Training programs that equip workers with new skills can help them advance their careers and increase their earning potential. These programs can encompass a wide range of topics, from basic literacy and numeracy to specialized skills related to specific garment production processes. This knowledge empowers workers to adapt to evolving industries and potentially transition into other roles within the industry.
Addressing the Need for Healthcare Access
Access to quality healthcare is essential for the well-being of garment workers and their families. Providing affordable and accessible healthcare services can significantly improve their overall health and productivity. This includes preventative care, treatment for injuries and illnesses, and access to mental health services. A healthy workforce is a productive workforce.
Encouraging Worker Organization and Representation
Worker organization and representation are critical in advocating for fair labor practices. Allowing workers to form unions and collectively bargain for better wages, benefits, and working conditions is vital. Strong unions can act as a voice for the workers, ensuring their rights are protected and their concerns are addressed. Collective action can significantly improve the lives of garment workers.
Sustainable Practices and Ethical Sourcing
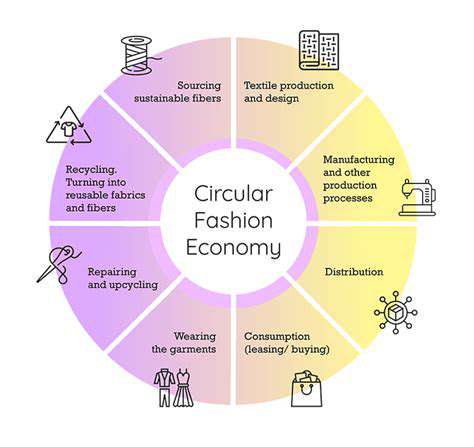
Encouraging sustainable practices and ethical sourcing throughout the garment supply chain is essential. This involves promoting environmentally friendly production methods, reducing waste, and ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly. By incorporating sustainability into the business model, companies can create a positive impact on the environment and contribute to a more equitable and just global supply chain. This approach benefits both the workers and the planet.