From Linear Consumption to Circular Systems in Fashion: New Transformations
Linearity's Environmental Impact: A Faulty Model
The linear model, a cornerstone of the fast fashion industry, operates on a straightforward principle: design, produce, sell, and discard. This approach, while seemingly efficient in terms of rapid turnover, creates a significant environmental burden. The sheer volume of garments produced and discarded annually, driven by the relentless pursuit of trends and short-lived styles, translates into massive amounts of textile waste, which often ends up in landfills or polluting ecosystems. This relentless cycle of consumption and disposal is fundamentally unsustainable, placing a tremendous strain on natural resources and contributing to climate change. The linear model fails to account for the intricate web of environmental consequences stemming from its simplistic approach.
Furthermore, the linear model often overlooks the hidden costs embedded within the production process. From the extraction of raw materials, like cotton and synthetic fibers, to the energy-intensive manufacturing processes and the transportation of finished goods, each step in the production chain leaves a significant environmental footprint. These hidden costs, rarely factored into the price of clothing, ultimately contribute to the unsustainable nature of the fast fashion industry. Understanding and addressing these hidden costs is crucial in transitioning to a more environmentally conscious approach.
The Need for Circularity: A Sustainable Alternative
A more sustainable approach to fashion necessitates a shift away from the linear model and towards a circular economy. This circular model focuses on reducing waste, reusing materials, and recycling products, creating a closed-loop system where resources are continually cycled and minimized environmental impact. By embracing circularity, designers and manufacturers can significantly reduce their environmental footprint, promoting a more sustainable and responsible approach to clothing production and consumption.
Implementing circularity in fast fashion requires a multifaceted strategy. This includes promoting the use of recycled and sustainable materials, designing garments for durability and longevity, incentivizing repair and reuse, and developing robust recycling programs. These strategies can help create a system where resources are valued and waste is minimized, ultimately contributing to a healthier planet. Such a shift in approach, while challenging, is vital for the future of the fashion industry and its environmental impact.
Implementing circularity in fast fashion is not just about reducing waste; it's about fundamentally changing the industry's mindset. By embracing sustainable practices at every stage, from design to disposal, the industry can create a more ethical and environmentally responsible system. This shift requires collaboration between designers, manufacturers, retailers, and consumers, fostering a collective commitment to a more sustainable future.
The transition to a circular economy will require significant investments in research and development, infrastructure, and education. However, the long-term benefits, both environmental and economic, are undeniable. By adopting a circular approach, the fast fashion industry can move away from its unsustainable practices and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Ultimately, a move toward circularity is not just an environmental imperative; it's a crucial step toward building a more equitable and resilient fashion industry. This shift necessitates a fundamental reassessment of values, prioritizing durability, sustainability, and ethical production over fleeting trends and disposable fashion.
Innovative Solutions: Design, Technology, and Consumer Behaviour
Innovative Design for Sustainable Consumption
Innovative design plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable consumption patterns. By incorporating environmentally conscious principles into the design process, manufacturers can create products that are durable, repairable, and easily recyclable. This shift in design thinking moves beyond the traditional planned obsolescence model, encouraging a longer lifespan for products and reducing the demand for frequent replacements. Companies that embrace this approach not only contribute to a more sustainable future but also often find that this design ethos resonates with environmentally conscious consumers, leading to increased brand loyalty and market share.
Technological Advancements in Product Lifecycles
Technological advancements are revolutionizing the entire product lifecycle. From 3D printing enabling customized and on-demand production to smart technologies embedded in products that extend their useful life, and new methods of recycling and material recovery, the possibilities are vast. These advancements allow manufacturers to optimize resource use, reduce waste, and create more efficient production processes. Furthermore, these technologies provide valuable data about product usage and maintenance, leading to a deeper understanding of consumer needs and desires, which can then be incorporated into future product development cycles.
Understanding Consumer Behavior for Sustainable Choices
Understanding consumer behavior is vital to promoting sustainable consumption. Research into consumer motivations and decision-making processes can reveal the factors that influence sustainable choices. This knowledge can then be used to develop targeted marketing campaigns, product design strategies, and educational initiatives that encourage consumers to adopt more eco-friendly practices. By understanding the psychological drivers behind consumption, businesses can develop products and services that appeal to consumers' values and desires, facilitating a shift towards sustainable consumption habits.
The Role of Education and Awareness in Sustainable Consumption
Education and awareness play a critical role in fostering sustainable consumption. Raising public awareness about the environmental impact of consumption choices and providing individuals with the knowledge and tools to make more sustainable decisions are essential steps. Educational campaigns can highlight the benefits of sustainable practices, from reducing waste to choosing energy-efficient products. This education empowers consumers to actively participate in the transition towards a more sustainable future and encourages businesses to adopt responsible practices.
Encouraging Circular Economies and Product Longevity
The concept of a circular economy, where products are designed for reuse, repair, and recycling, is gaining significant traction. Companies are increasingly focusing on designing products with durability and repairability in mind, extending their lifespan and reducing waste. This requires a fundamental shift in manufacturing processes and consumer attitudes, but it offers significant environmental and economic benefits. Promoting product longevity through innovative design and repair services can significantly reduce the demand for new products and the associated environmental impact.
The Importance of Sustainable Packaging and Logistics
Sustainable packaging and logistics are crucial components of a comprehensive approach to sustainable consumption. Minimizing packaging materials, using recycled content, and optimizing transportation routes are all important steps in reducing the environmental footprint of products. Innovative packaging designs that prioritize recyclability and reduce waste are key to ensuring that products reach consumers with a minimal environmental impact. Efficient logistics systems that minimize transportation distances and use sustainable modes of transport further contribute to this important goal.
Incentivizing Sustainable Consumer Choices
Incentivizing sustainable consumer choices is crucial to driving widespread adoption. Government policies, such as tax incentives for eco-friendly products or extended producer responsibility schemes, can encourage businesses and consumers to make sustainable choices. Businesses can also offer financial incentives and rewards for customers who opt for sustainable options, creating a positive feedback loop that reinforces sustainable consumption patterns. These incentives create a market-driven approach to sustainability, motivating both companies and consumers to embrace eco-friendly practices.
The Role of Technology in Driving Circularity
The Shift from Linear to Circular Consumption
The traditional linear economic model, characterized by take-make-dispose, has placed immense strain on our planet's resources. This model fosters a culture of consumption where products are used, discarded, and replaced, generating significant waste and environmental damage. Transitioning to a circular economy requires a fundamental shift in mindset, moving away from the finite resources paradigm and towards a model that prioritizes reuse, repair, and recycling.
This transition is not just about environmental sustainability; it also presents significant economic opportunities. By reimagining the value chain and integrating technology, businesses can unlock new revenue streams, reduce operational costs, and enhance their brand reputation. This shift from linear to circular consumption is a crucial step in creating a more sustainable future for all.
The Power of Technology in Material Recovery
Advanced technologies are playing a critical role in improving material recovery processes. From sophisticated sorting technologies that can identify and separate different types of materials in waste streams to innovative recycling methods that recover valuable materials from complex mixtures, technology is enabling the extraction of valuable resources from waste and reducing the need for virgin materials. This efficiency in resource recovery is a key driver of circularity.
For example, sophisticated sensors and AI-powered image recognition systems are now being used to automate the sorting process, achieving higher purity rates and reducing labor costs. This advancement allows for more efficient and cost-effective recovery of valuable materials, contributing significantly to a circular economy.
Digital Platforms for Product Lifecycle Management
Digital platforms are revolutionizing product lifecycle management, enabling companies to track products throughout their entire lifespan. This data-driven approach allows for better understanding of product usage patterns, identifying potential for reuse or repair, and optimizing material selection for recyclability. Data analytics are essential for creating product designs that are more easily disassembled, repaired, and recycled.
These platforms provide a centralized repository of information about products, from their design specifications to their end-of-life disposal instructions. This detailed information empowers businesses to make more informed decisions about product design, material sourcing, and manufacturing processes, all contributing to a more circular approach.
Innovations in 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
3D printing and additive manufacturing are transforming the way products are designed and produced. These technologies allow for the creation of customized parts and products on demand, reducing waste associated with mass production. This capability is especially beneficial for producing parts for repair or repurposing existing products, extending their lifespan.
This technology also enables the creation of products with intricate geometries and complex functionalities, pushing the boundaries of design and enabling more efficient use of materials. The possibility of creating spare parts on demand or designing products for easy disassembly and component replacement further supports a circular economy model.
Smart Packaging and Material Science Advancements
Smart packaging, incorporating sensors and other technologies, can monitor product freshness, track location, and even provide information about the product's origin and composition. This real-time data allows for more efficient logistics and reduces food waste. The use of biodegradable and compostable packaging materials further supports a circular economy model.
Advances in material science are leading to the development of new materials with enhanced recyclability and biodegradability. These materials are designed to be easily separated and recycled, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing the reuse of valuable resources. The focus on designing for disassembly and creating products that are fully recyclable is a critical aspect of this innovation.
The Role of Collaboration and Policy in Fostering Circularity
The transition to a circular economy requires collaboration among various stakeholders, including governments, businesses, and consumers. Government policies that incentivize circular practices, such as extended producer responsibility schemes and tax breaks for sustainable materials, can significantly accelerate this transition. Public awareness campaigns that educate consumers about the benefits of circularity are also essential.
Collaboration between businesses and research institutions is vital for developing and implementing new technologies and processes. Sharing knowledge and resources fosters innovation and accelerates the adoption of circular practices. This multifaceted approach, combining technology, policy, and social awareness, is crucial for achieving true circularity.
The Future of Fashion: A Sustainable and Circular Ecosystem
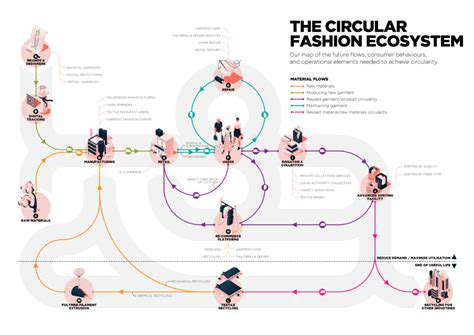
The Rise of Sustainable Materials
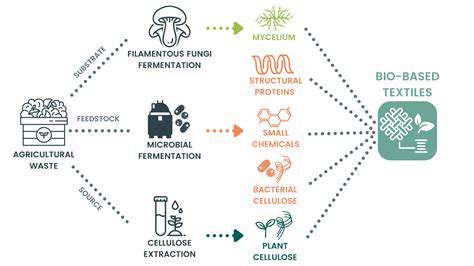
The fashion industry is undergoing a significant transformation, with a growing emphasis on sustainability. Consumers are increasingly demanding ethical and environmentally conscious choices, leading designers and brands to explore innovative and eco-friendly materials. This shift is crucial for minimizing the industry's environmental footprint and promoting responsible practices throughout the supply chain. From recycled fabrics like organic cotton and Tencel to innovative plant-based alternatives, the availability of sustainable materials is expanding rapidly.
The use of innovative materials like mycelium and mushroom leather is gaining traction. These materials offer a compelling alternative to traditional leather, providing a sustainable and cruelty-free option. Moreover, the development of advanced technologies in textile production is paving the way for more efficient and environmentally friendly processes.
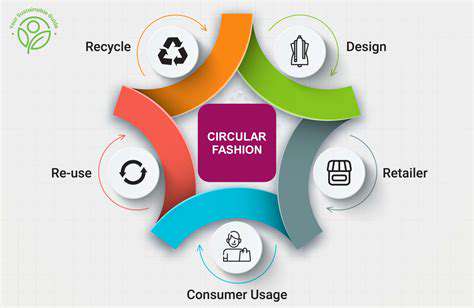
Circular Fashion Models
Circular fashion models are gaining significant momentum, encouraging a shift away from the traditional take-make-dispose linear approach. This involves strategies to reduce waste, promote reuse, and encourage the repair and repurposing of garments. These models are essential for minimizing textile waste and extending the lifespan of clothing items.
Companies are exploring various strategies, including innovative rental programs, clothing swaps, and upcycling initiatives. These models not only benefit the environment but also create new business opportunities and foster a greater sense of community amongst consumers.
Technological Advancements in Design and Production
Technological advancements are revolutionizing the fashion industry, enabling greater efficiency and sustainability in design and production. Digital design tools allow for more precise and environmentally conscious pattern making, reducing material waste. 3D printing is emerging as a powerful tool for creating customized and personalized garments, further minimizing overproduction.
Furthermore, advanced technologies in textile dyeing and finishing are reducing water and chemical consumption. These innovations are driving greater efficiency and reducing the overall environmental impact of fashion production.
Ethical Labor Practices and Supply Chains
Ethical labor practices are becoming increasingly important in the fashion industry. Consumers are demanding transparency and accountability from brands regarding the working conditions of their suppliers. This includes fair wages, safe working environments, and respect for human rights throughout the entire supply chain.
Brands are now incorporating traceability and transparency into their operations. This involves carefully documenting the origin of materials, the production processes, and the labor conditions involved. These efforts are essential to fostering trust and ensuring that fashion production is conducted in a socially responsible manner.
The Role of Consumers in Shaping the Future
Consumers play a pivotal role in shaping the future of fashion. Their conscious choices and demands for sustainable and ethical products are driving the industry's transition. Consumers are increasingly demanding transparency and accountability from brands regarding their environmental and social impact. By supporting brands that prioritize sustainability and ethical practices, consumers can significantly influence the direction of the fashion industry.
The rise of conscious consumerism is fostering a shift in the industry's approach to production, design, and consumption. Consumers are taking an active role in promoting sustainable practices, ultimately driving the industry towards a more environmentally and socially responsible future.