Living Wages: New Strategies for Fair Compensation
Understanding the Concept of a Living Wage
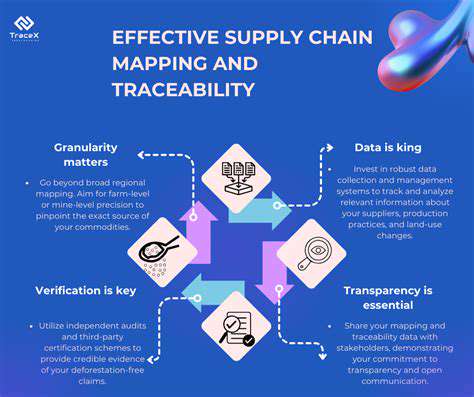
A living wage isn't simply a number; it's a crucial concept that reflects the minimum income necessary for individuals and families to afford basic necessities in a specific geographic area. This includes housing costs, food, transportation, healthcare, childcare, and other essential expenses. Calculating a living wage requires a thorough understanding of local economic realities, considering factors like housing market fluctuations, inflation rates, and the cost of essential services. This nuanced approach ensures the wage reflects the true financial needs of residents within that community.
Defining a living wage goes beyond simply meeting basic needs; it strives to provide a foundation for a modest but sustainable standard of living. This means allowing individuals to participate fully in their communities, save for the future, and potentially pursue personal and professional development without constant financial strain. A living wage empowers individuals to contribute to the economy and fosters a healthier, more equitable society.
Addressing the Diverse Needs of Different Communities
One crucial aspect of defining a living wage is recognizing the diversity within communities. Different communities face varying economic pressures and resource availability. For example, rural areas often have lower housing costs compared to urban centers, but transportation expenses may be disproportionately higher. Similarly, families with children have different financial needs than single individuals. Therefore, a one-size-fits-all living wage approach is inadequate; tailored calculations are essential to ensure that a living wage truly meets the needs of each specific community.
Furthermore, factors like the availability of affordable childcare, healthcare access, and local tax burdens must be considered. A community with a high cost of childcare will need a higher living wage than a community where these services are more affordable. This meticulous analysis ensures that the living wage accurately reflects the unique challenges and opportunities faced by residents in diverse communities.
Recognizing these disparities allows for the development of living wage frameworks that are appropriate and equitable for each region. This tailored approach fosters a more inclusive and supportive environment for all community members.
Implementing and Enforcing Living Wage Policies
Implementing a living wage policy requires a multi-faceted approach. It's not just about setting a number; it involves establishing clear guidelines for calculation, transparency in the process, and ongoing evaluation to ensure the living wage remains relevant. Partnerships between local governments, businesses, and community organizations are essential to build a supportive framework that addresses the practical implications of implementing a living wage policy. This includes considering the potential impact on businesses and exploring possible solutions to mitigate any negative effects.
Enforcing the policy requires a robust system of monitoring and accountability. Effective enforcement mechanisms will help guarantee that employers are adhering to the living wage standards. Furthermore, ongoing dialogue and feedback mechanisms with community members are crucial to ensure the policy's effectiveness and address any emerging concerns or challenges.
Finally, investing in resources to educate both employers and employees about the living wage is critical. This can help bridge the gap between theoretical understanding and practical application, fostering a more equitable and sustainable labor market.
Implementing Living Wage Policies: A Multi-faceted Approach
Understanding the Concept of a Living Wage
A living wage is a minimum wage that ensures workers can afford the basic necessities of life in a given location. This includes housing, food, transportation, healthcare, and other essential expenses. It's crucial to consider the specific cost of living in different areas when determining a fair living wage, as these costs vary significantly based on geographical location and economic conditions.
Establishing a living wage requires a comprehensive understanding of local economic realities and a commitment to ensuring a basic standard of living for workers. It's not simply about a numerical figure; it's about the impact that wage has on worker's quality of life and their ability to participate fully in their community.
Calculating a Living Wage
Calculating a living wage is a complex process, often involving detailed analyses of local cost of living data. This includes examining the prices of essential goods and services like housing, food, transportation, and childcare. Experts typically use a variety of methodologies to estimate the minimum wage needed to meet these expenses.
The Impact of Living Wage Policies on Workers
Living wage policies can have a significant positive impact on workers' financial well-being. Workers earning a living wage can reduce their reliance on public assistance programs and achieve greater financial stability. This can lead to improved health, reduced stress, and increased participation in the community.
Improved financial stability can also free up workers' time for other activities, like pursuing further education or engaging in hobbies, contributing to personal and professional growth.
The Economic Effects of Living Wage Policies
Living wage policies can stimulate local economies by increasing consumer spending. When workers have more disposable income, they are more likely to spend it in their local communities, boosting businesses and creating jobs. This can lead to a positive feedback loop that benefits the entire community.
Considerations for Small Businesses
Implementing a living wage can present challenges for small businesses, particularly those with limited profit margins. However, strategies exist to help small businesses adapt to these changes, such as exploring cost-saving measures and exploring opportunities for increased efficiency.
It's important to recognize that a living wage can positively impact small businesses in the long term by attracting and retaining skilled employees.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
One potential challenge related to living wage policies is the potential impact on businesses' operating costs. However, some solutions may include exploring opportunities for increased efficiency, exploring alternative revenue streams, and/or exploring opportunities for public-private partnerships to support business adaptation.
The Role of Government in Implementing Living Wage Policies
Governments play a crucial role in establishing and enforcing living wage policies. This involves conducting research to determine the appropriate living wage for their area, implementing policies to support businesses, and ensuring compliance. Government support is essential for successful implementation and effective management of living wage initiatives.
By providing resources and guidance, governments can help businesses navigate the transition to a living wage system and ensure a fair and equitable economy for all.

The Role of Public-Private Partnerships in Ensuring Fair Compensation

Public-Private Partnerships: A Catalyst for Development
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) represent a collaborative approach to development projects, leveraging the expertise and resources of both the public and private sectors. These partnerships often involve the transfer of risk and responsibility, allowing for the efficient allocation of capital and resources. By combining the strengths of each sector, PPPs can deliver innovative solutions to complex challenges, fostering economic growth and social progress.
A key benefit of PPPs is the potential for increased efficiency in project implementation. Private sector partners often possess specialized knowledge and experience in project management, construction, and operations, leading to streamlined processes and potentially lower costs compared to solely public sector initiatives.
Identifying Suitable Projects for PPPs
Not all projects are suitable for PPPs. Careful consideration must be given to the specific project's characteristics and the potential benefits and risks. Projects with significant private sector expertise, clear financial projections, and well-defined public sector roles are more likely to succeed.
Careful evaluation of the potential risks and rewards is essential. Thorough due diligence is needed to assess the feasibility and viability of the project, mitigating potential financial and operational challenges. Risk assessment should include market analysis, financial modeling, and legal and regulatory considerations.
Financial Structures and Agreements
The financial structures of PPPs can vary considerably, depending on the specific project and the needs of the partners. These structures often involve complex agreements outlining the responsibilities, obligations, and financial arrangements between the public and private entities.
Clearly defined contracts and agreements are crucial for managing expectations and resolving potential disputes. These agreements should include comprehensive provisions for risk allocation, performance standards, and dispute resolution mechanisms. Transparent and well-structured agreements foster trust and cooperation between the partners.
Risk Allocation and Management
One of the key aspects of PPPs involves the allocation and management of risks. Identifying and assessing potential risks is critical to ensure the sustainability and success of the project. This process often involves the transfer of certain risks from the public sector to the private sector, or vice-versa, based on the specific expertise and capacity of each partner.
Understanding the implications of risk allocation is vital, ensuring that both parties are adequately prepared for potential challenges. Comprehensive risk management plans, including contingency strategies, should be developed and implemented to minimize the impact of unforeseen circumstances.
Performance Monitoring and Evaluation
Ongoing performance monitoring and evaluation are essential components of successful PPPs. Regular assessment of project progress against agreed-upon benchmarks and performance indicators is vital for ensuring the project delivers its intended outcomes. This includes tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and making adjustments as needed.
Rigorous evaluation processes are needed to assess the effectiveness of the partnership and identify areas for improvement. This allows for the refinement of strategies and the optimization of project outcomes. Lessons learned from the experience can be valuable for future PPP initiatives.
Building Trust and Collaboration
Successful PPPs rely heavily on strong relationships and mutual trust between the public and private sectors. Effective communication channels and collaborative working environments are crucial for achieving shared goals and resolving conflicts.
Open communication and transparency are vital to fostering trust and collaboration. Regular meetings, clear reporting mechanisms, and accessible information can help ensure that both parties are aligned and working towards the same objectives. This collaborative approach fosters a culture of shared responsibility and mutual respect.