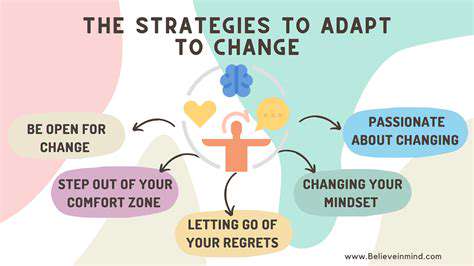
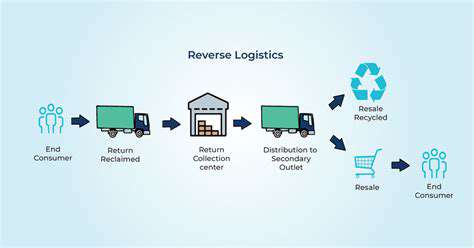
Reverse Supply Chains: The Engine of Circular Fashion
Understanding the Core Concepts
The linear model, a cornerstone of statistical analysis, posits a straightforward relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. This relationship is typically represented by a straight line, allowing for the prediction of the dependent variable's value based on the known values of the independent variables. Understanding this fundamental concept is crucial for interpreting and applying the model effectively. Essentially, the model seeks to identify the pattern of change in the dependent variable as the independent variables change.
Formally, a linear model assumes a linear association between variables. This means that a change in one variable leads to a proportional change in another. Understanding this fundamental assumption is critical to the model's validity and reliability. For example, a linear model might predict a company's revenue based on its marketing expenditure.
Exploring the Key Assumptions
Several critical assumptions underpin the reliability of linear models. One such assumption is the linearity of the relationship between the variables. Another critical assumption is the independence of the observations. This means that the values of one observation shouldn't influence the values of any other. Properly understanding and validating these assumptions is essential for accurate model interpretation and application.
The assumption of normally distributed errors is also vital. This means that the residuals, or the differences between the observed and predicted values, should follow a normal distribution. The presence of outliers can significantly affect the model's accuracy.
Delving into Model Estimation
Estimating the parameters of a linear model involves finding the best-fitting line that minimizes the sum of squared differences between the observed and predicted values. This process, known as ordinary least squares (OLS), is a common and efficient method for achieving this. This method is fundamental to the model's function. The goal is to find the line that most closely aligns with the observed data points.
Different techniques, like maximum likelihood estimation, can also be used depending on the specific characteristics of the data set.
Interpreting Model Coefficients
The coefficients of a linear model represent the change in the dependent variable for a one-unit change in the corresponding independent variable, holding all other variables constant. Understanding these coefficients is crucial for interpreting the model's implications. For example, a positive coefficient suggests a positive relationship between the variables, while a negative coefficient indicates an inverse relationship. The magnitude of the coefficient reflects the strength of the effect.
Proper interpretation involves considering the context and ensuring that the coefficients are statistically significant.
Assessing Model Fit
Assessing the goodness of fit of a linear model is paramount for determining its predictive power and reliability. Various metrics, including R-squared, can be used to evaluate how well the model explains the variance in the dependent variable. Understanding these metrics is important. A higher R-squared value generally indicates a better fit.
Addressing Limitations and Considerations
Linear models, despite their widespread use, have limitations. One key limitation is their assumption of a linear relationship between variables. Non-linear relationships may require alternative modeling approaches. Another consideration is the potential for multicollinearity, where independent variables are highly correlated, affecting the interpretation of individual coefficients. Carefully evaluating these limitations is essential for effective model application and interpretation.
Data quality and sample size also play crucial roles in the model's reliability and accuracy. Always scrutinize the data before applying a linear model.
Building Partnerships for Success: Collaboration in Circular Fashion

Cultivating Trust and Respect
Strong partnerships are built on a foundation of trust and respect. This involves actively listening to the perspectives of your potential partners, acknowledging their contributions, and valuing their expertise. Demonstrating genuine interest in their goals and challenges fosters a collaborative environment where everyone feels heard and respected. This mutual understanding is crucial for long-term success, paving the way for open communication and effective problem-solving.
Furthermore, transparency and honesty are essential components of building trust. Sharing information openly and honestly, even when it's challenging, creates a sense of security and reliability. It demonstrates a commitment to ethical conduct and fosters a deeper connection between partners. By prioritizing these values, you create a strong foundation for collaboration and shared success.
Defining Shared Goals and Objectives
A clear understanding of shared goals and objectives is fundamental to any successful partnership. This requires a collaborative process where all parties define their individual needs and aspirations, and then identify common ground and areas for mutual benefit. This alignment helps to ensure everyone is working towards the same vision and minimizes potential conflicts down the line.
Clearly outlining the responsibilities, roles, and expectations of each partner is also critical. This avoids ambiguity and ensures that everyone understands their contributions and how they fit into the overall strategy. Establishing measurable milestones and timelines allows for progress monitoring and adjustments as needed, ensuring everyone stays on track and focused on achieving the desired outcomes.
Maintaining Open Communication and Feedback
Effective communication is the lifeblood of any successful partnership. Regular communication channels, whether formal or informal, are vital to keep everyone informed about progress, challenges, and opportunities. This includes actively seeking feedback from all partners to identify areas for improvement and ensure that everyone's voices are heard.
Open and honest communication channels allow for prompt resolution of conflicts and address any concerns that may arise. This fosters a culture of trust and collaboration, ultimately leading to more productive and satisfying partnerships. A willingness to actively listen to feedback and adapt strategies is key to navigating challenges and ensuring sustained success.
Establishing regular check-in meetings and utilizing various communication tools, such as project management software or shared document platforms, can greatly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of communication. Consistent communication fosters a sense of shared ownership and responsibility, which is crucial for the longevity of any successful partnership.
The Economic and Social Benefits of a Circular Fashion System
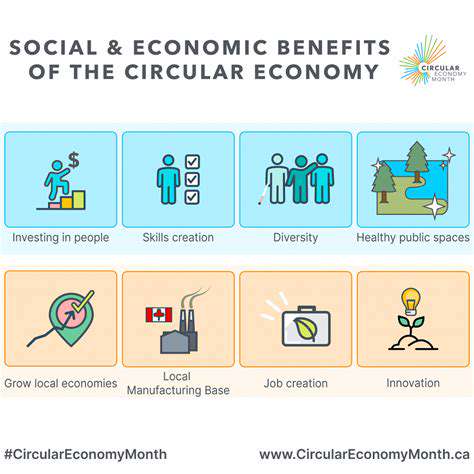
Economic Growth and Development
A thriving economy, fueled by sustainable growth, is essential for a better quality of life for all citizens. Economic development fosters job creation, leading to increased income and opportunities for individuals and families. This, in turn, strengthens communities and reduces poverty rates. Sustainable economic growth also allows for investment in essential infrastructure, such as schools, hospitals, and transportation networks, further enhancing the overall well-being of the population.
Furthermore, a robust economy attracts foreign investment, which can stimulate innovation and technological advancement, leading to even greater economic growth and development in the long run. This influx of capital can also improve productivity and create a more competitive market, benefiting businesses and consumers alike.
Improved Living Standards
Economic prosperity directly impacts living standards. Increased incomes allow people to afford better housing, nutritious food, and access to quality healthcare and education. These improvements in living standards contribute to a healthier and more productive population.
Access to quality education is particularly crucial. It equips individuals with the skills and knowledge needed to participate actively in the workforce and contribute to the overall economic success of the nation. This in turn, creates a positive feedback loop, where a higher quality of life leads to even greater economic prosperity.
Enhanced Social Cohesion
Economic and social benefits often intertwine. A robust economy can lead to greater social cohesion by fostering shared prosperity and reducing inequality. When people feel economically secure, they are more likely to engage in constructive social interactions and contribute to their communities.
Reduced Poverty and Inequality
Economic prosperity often translates into a reduction in poverty and inequality. When opportunities are available and income is more evenly distributed, fewer people fall below the poverty line. This can lead to a more stable and harmonious society, where individuals feel a sense of belonging and purpose.
Furthermore, reducing inequality can foster social mobility. Individuals from disadvantaged backgrounds can have increased opportunities to improve their socioeconomic standing, leading to a more equitable society.
Increased Access to Resources and Services
Economic growth typically correlates with increased access to resources and services. As economies expand, governments have more resources to invest in essential services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure. This is particularly crucial for underserved communities and regions.
Improved access to quality healthcare can lead to better health outcomes for the entire population, creating a healthier workforce and a more vibrant society. Access to quality education is vital for empowering individuals and building a skilled workforce.
Improved Health Outcomes
Economic well-being often translates into better health outcomes. When individuals have access to nutritious food, clean water, and healthcare, their health and well-being improve significantly. This can lead to a more productive and resilient population, contributing to further economic growth.
Sustainable Development and Environmental Protection
Economic growth should not come at the expense of the environment. Sustainable development strategies are crucial to ensure that economic progress is achieved in a way that protects natural resources and ecosystems for future generations. Investing in renewable energy sources and adopting environmentally friendly practices are essential for long-term sustainability.
Protecting the environment is not just about preserving nature; it's also about ensuring the long-term economic viability of our planet. Sustainable practices can create new industries, generate jobs, and lead to a healthier, more resilient future.