The Power of Consumer Activism in Driving Ethical Change
Beyond the Transaction: The Ripple Effect of Consumer Choices
Consumer choices extend far beyond the immediate purchase. The products we buy, the brands we support, and the companies we patronize all contribute to a larger societal impact. This extends to environmental sustainability, labor practices, and ethical sourcing. Understanding this ripple effect is crucial to appreciating the power of collective action, where individual consumer decisions, when combined, can create significant change.
Building a Movement: The Power of Consumer Advocacy
Consumer activism isn't just about complaining; it's about building a movement. By organizing, educating, and advocating for change, consumers can influence corporate practices and drive positive societal shifts. This can take the form of boycotts, product reviews, social media campaigns, or even direct engagement with businesses. The key is recognizing the collective strength of a unified voice.
The Ethical Consumption Landscape: Navigating Values and Choices
Today's consumers are increasingly aware of ethical considerations. From fair trade practices to sustainable materials, consumers are actively seeking out brands and products aligned with their values. This growing awareness creates a dynamic ethical consumption landscape, where businesses must adapt to meet consumer expectations for transparency and accountability. It's a landscape ripe for positive change.
From Boycotts to Buycotts: Amplifying Consumer Power
Consumer activism manifests in various forms, from boycotts designed to penalize unethical practices to buycotts that reward socially responsible companies. These actions, whether individual or collective, can significantly impact a company's bottom line and its overall approach to business. The power lies in the ability to choose, to reward good practices, and to punish those that fall short.
The Role of Transparency and Accountability: Driving Change Through Information
Transparency is vital in fostering consumer trust. Businesses that openly communicate their practices, sourcing, and environmental impact build credibility and encourage responsible consumer choices. Accountability, in turn, allows consumers to hold companies responsible for their actions, creating a dynamic feedback loop that can lead to improvements across the board. This flow of information is crucial in empowering collective action.
The Future of Consumer Activism: Harnessing Technology and Innovation
Technology plays an increasingly significant role in consumer activism, enabling broader reach and faster mobilization. Social media platforms, online petitions, and collaborative tools allow consumers to connect, organize, and amplify their voices. This digital evolution is transforming how consumers engage with brands and driving a new era of consumer-led change. The future of activism is intertwined with the evolution of technology itself.
Session recordings provide a valuable window into how users interact with your website or application. By observing their actions, clicks, and navigation patterns, you can gain a deeper understanding of their experience. These recordings are crucial for identifying pain points, areas of confusion, and opportunities for improvement, ultimately leading to a more intuitive and user-friendly design. Session recordings are a critical aspect of user experience research, allowing businesses to see firsthand how users navigate their digital platforms.
The Role of Transparency and Accountability
Transparency in Supply Chains
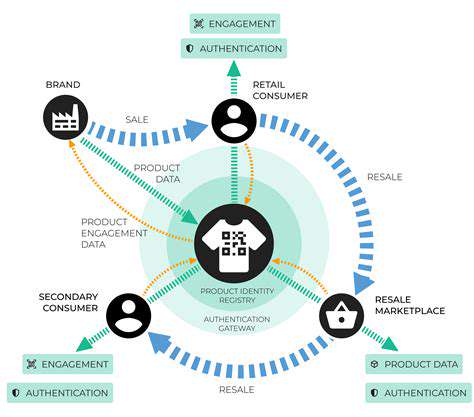
Transparency in supply chains is crucial for fostering consumer trust and empowering informed decision-making. Consumers increasingly demand visibility into the origin of their products, the labor practices used in production, and the environmental impact throughout the entire lifecycle. This demand for transparency is driving companies to adopt more sustainable and ethical sourcing practices, leading to a ripple effect of positive change throughout the industry. A lack of transparency, conversely, can fuel consumer distrust and ultimately harm a company's reputation.
Detailed information about the suppliers, manufacturing processes, and materials used in a product can dramatically increase consumer confidence. This allows consumers to align their purchasing decisions with their values, leading to more responsible consumption patterns.
Accountability for Business Practices
Accountability is intrinsically linked to transparency. When businesses are transparent about their operations, they become more accountable for their actions. Consumers can hold companies responsible for their environmental impact, labor practices, and ethical sourcing decisions. This accountability is essential for fostering a more sustainable and ethical marketplace, where businesses are incentivized to operate responsibly.
Consumer Activism and Ethical Sourcing
Consumer activism plays a critical role in driving ethical sourcing practices. By demanding transparency and accountability, consumers can pressure businesses to adopt more sustainable and ethical practices. This can range from boycotts of products made with unethical labor to advocating for fair trade practices. Consumer activism can also involve supporting businesses that demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing and environmental responsibility.
The Power of Collective Action
Consumer activism is most effective when it's a collective effort. By uniting around shared values and concerns, consumers can amplify their voices and exert significant pressure on businesses. This collective action can lead to meaningful changes in corporate practices, pushing companies to become more responsible and responsive to consumer demands.
Social media and online platforms have become powerful tools for organizing and mobilizing consumer activism. Consumers can easily connect with like-minded individuals, share information, and coordinate actions to drive change.
Impact on Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Consumer activism significantly impacts corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives. Companies are increasingly recognizing that ethical and sustainable practices are not just good for the environment and society but also good for business. Pressure from consumers often compels companies to adopt CSR strategies, leading to improvements in environmental protection, worker safety, and community development. This shift in corporate priorities is crucial for building a more sustainable and equitable future.
Driving Positive Change Through Purchasing Decisions
Ultimately, the power of consumer activism lies in the individual purchasing decisions of consumers. By consciously choosing products and services from companies that align with their values, consumers can send a strong message to the marketplace. This conscious consumerism can create a powerful demand for ethical and sustainable products, leading to systemic change within the industry. By supporting businesses with strong ethical standards, consumers are directly contributing to a more responsible and sustainable marketplace.
Measuring Success and Future Trends
Defining Success Metrics
Success in any endeavor is multifaceted and requires careful consideration of the specific goals. Defining clear, measurable metrics is crucial for tracking progress and ensuring alignment with overall objectives. These metrics should be specific, quantifiable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For instance, a successful marketing campaign might be measured by increased website traffic, lead generation, or conversion rates over a predetermined period.
Different industries and organizations will have varying metrics for success. A non-profit might measure success in terms of beneficiaries reached or funds raised, while a for-profit business may focus on revenue growth, profit margins, and market share. Understanding these tailored metrics is essential for a comprehensive evaluation of progress and future strategies.
Analyzing Past Performance
A critical aspect of measuring success is analyzing historical performance data. Reviewing past trends, identifying patterns, and pinpointing areas of strength and weakness provides valuable insights for future planning and decision-making. This analysis allows for the identification of factors that contributed to success and those that hindered it, ultimately informing strategies for optimization.
Historical data can reveal seasonal variations, cyclical patterns, and the impact of external factors on performance. This analysis is not just about identifying past successes; it also helps to understand the reasons behind failures, allowing for the development of more robust strategies and mitigating potential risks.
Predictive Modeling and Forecasting
Utilizing predictive modeling and forecasting techniques allows for a proactive approach to measuring success. These sophisticated methods analyze historical data, identify trends, and project future outcomes based on various scenarios. This foresight is invaluable for anticipating potential challenges and opportunities and enabling informed decision-making.
Emerging Technologies and Innovation
The rapid advancement of technology is constantly reshaping industries and influencing success metrics. The integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics is dramatically altering how businesses operate and measure success. Embracing these technological advancements is crucial for staying ahead of the curve and achieving optimal results.
Companies that effectively leverage emerging technologies can gain a competitive advantage, optimize processes, and gain deeper insights into customer behavior, leading to more effective strategies.
Adapting to Future Market Trends
The business landscape is constantly evolving, requiring continuous adaptation to emerging market trends. Understanding these shifts and their potential impact on success metrics is paramount. This includes staying informed about evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and regulatory changes.
Adaptability is a key trait for success in a dynamic environment. Companies that are flexible and responsive to change are better positioned to identify and capitalize on opportunities while mitigating potential threats. This involves a continuous process of learning, adapting, and refining strategies.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations
Beyond traditional metrics, a growing emphasis on sustainability and ethical practices is influencing how success is measured. Companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of environmental responsibility, social equity, and ethical sourcing in their operations. These factors are now integrated into success metrics, reflecting a broader understanding of long-term value creation.
Integrating sustainability and ethical considerations into business strategies not only aligns with societal values but also enhances long-term value and reputation. Companies that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability often attract and retain customers who prioritize ethical and responsible practices.