The Role of Consumers in Driving Demand for Recycled Materials: New Influence
The Rise of Conscious Consumption

Understanding the Shift
The modern consumer landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, moving away from purely transactional purchasing towards a more conscious and ethically driven approach. This shift, often referred to as conscious consumption, is driven by a multitude of factors, including growing awareness of environmental and social issues, a desire for authenticity, and a yearning for products that align with personal values. Consumers are increasingly looking beyond the price tag and are actively seeking brands and products that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
This conscious consumer is not just focused on eco-friendly products; they also consider fair labor practices, ethical sourcing, and transparent supply chains. They are demanding more than just a product; they are seeking a connection with the brand and its values. This evolution in consumer behavior is fundamentally altering the business landscape and forcing companies to adapt.
Drivers of Conscious Consumption
Several factors are fueling this rise in conscious consumption. Environmental concerns, such as climate change and pollution, are prompting consumers to seek eco-friendly alternatives and to reduce their environmental footprint. Ethical considerations, such as fair trade and responsible labor practices, are also driving consumers to choose products and brands that align with their values.
Moreover, a desire for authenticity and transparency is pushing consumers to support brands that are transparent about their processes and values. The rise of social media and increased access to information has empowered consumers to research and make informed decisions, leading them to question the practices of businesses and demand greater accountability.
Impact on Businesses
The rise of conscious consumption is impacting businesses across various sectors. Companies are now realizing that they need to adapt their strategies to meet the demands of this new consumer segment. This includes incorporating sustainability into their operations, sourcing materials responsibly, and promoting ethical labor practices. By prioritizing these aspects, businesses can build stronger brand loyalty and attract a growing consumer base.
This is not simply about marketing; it's about changing the core of how businesses operate. From supply chains to product development, conscious consumption requires a fundamental shift in mindset. Companies that fail to adapt risk losing market share to those that embrace the values of their conscious consumers.
The Future of Conscious Consumption
The future of conscious consumption appears promising, with continued growth and evolution expected. Consumers are becoming increasingly sophisticated in their choices, demanding even higher levels of transparency and accountability from brands. This trend will likely push businesses to innovate and create more sustainable and ethical products and practices. This evolution will also force consumers to consider the full lifecycle of their purchases and to advocate for positive change.
The integration of conscious consumption into mainstream culture is only going to increase, impacting everything from fashion to food to technology. This shift is not just a trend; it's a fundamental change in how we interact with the world around us, requiring both businesses and consumers to adapt and evolve.
Motivations for Recycling-Conscious Purchases

Environmental Benefits of Recycling
Recycling plays a crucial role in mitigating the environmental impact of our consumption habits. By diverting waste from landfills, we reduce the strain on natural resources and decrease the amount of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere. Landfills, which often contain harmful chemicals, leach toxins into the soil and groundwater, contaminating our ecosystems and posing risks to human health. Recycling also conserves valuable resources like timber, water, and minerals, reducing the need for extraction and processing, which, in turn, minimizes habitat destruction and pollution.
Recycling significantly reduces pollution from manufacturing. Producing new materials from raw materials requires substantial energy and often involves releasing pollutants into the air and water. Recycling existing materials drastically reduces the energy consumption and pollution associated with manufacturing processes, contributing to a healthier planet. This reduction in pollution directly benefits air and water quality, protecting human health and the well-being of wildlife.
Economic Advantages of Recycling
Recycling creates employment opportunities in collection, processing, and manufacturing sectors. Recycling facilities require skilled labor for sorting, cleaning, and processing materials, providing jobs for communities and contributing to economic development. Moreover, the demand for recycled materials stimulates the growth of related industries, including those involved in manufacturing products using recycled content.
Recycling programs can generate revenue for municipalities and businesses. Collected materials can be sold to recycling facilities, providing valuable income streams for local governments and industries. This revenue can be reinvested in public infrastructure, waste management programs, or other community initiatives.
Social Responsibility and Community Impact
Recycling fosters a sense of community responsibility and environmental awareness. By participating in recycling programs, individuals contribute to a collective effort to protect the environment and promote sustainable practices. This shared commitment strengthens social bonds and promotes a sense of shared responsibility towards the common good.
Recycling programs can promote community engagement and foster a sense of pride in environmental stewardship. Educational initiatives and community outreach programs can highlight the importance of recycling and engage residents in effective waste management practices. This active participation builds a sense of ownership and responsibility within the community.
Health Benefits of Recycling
Reduced pollution from manufacturing processes associated with recycling translates into improved air and water quality. This, in turn, leads to better public health outcomes, reducing respiratory illnesses and other health problems linked to air and water contamination. By promoting recycling, we contribute to a healthier environment for ourselves and future generations.
Recycling reduces the risk of exposure to hazardous materials in landfills. Landfills often contain hazardous waste, which can leach toxins into the environment and pose risks to human health. Recycling reduces the volume of waste in landfills, minimizing the risk of exposure and contamination. By opting for recycling, we are actively working towards a healthier and safer environment for ourselves and our communities.
The Power of Collective Action
The Ripple Effect of Consumer Choice
Consumer choices, seemingly small and individual, create a powerful ripple effect throughout the supply chain. When consumers actively seek out recycled products, they signal a clear demand to manufacturers and businesses. This demand fosters innovation in recycling processes and encourages the development of new, sustainable materials. The more consumers choose recycled options, the more companies are incentivized to invest in recycling infrastructure and sustainable practices.
Driving Investment in Recycling Infrastructure
Significant investment in recycling infrastructure is often dependent on the projected demand for recycled materials. When consumers demonstrate a consistent preference for recycled products, manufacturers and retailers recognize the potential for profit and sustainability. This translates to increased investment in sorting facilities, processing plants, and the overall recycling network. The financial backing fuels improvements in technology and efficiency, leading to a more robust and effective recycling system.
Promoting Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
The demand for recycled materials directly impacts manufacturing practices. Companies are compelled to incorporate recycled content into their products, reducing their reliance on virgin materials. This shift encourages innovation in material science and manufacturing processes, pushing for more sustainable and environmentally friendly production methods. A strong consumer demand for recycled goods ultimately compels the entire industry to embrace sustainability.
Encouraging Innovation in Recycling Technologies
Consumer demand for recycled materials acts as a catalyst for innovation in recycling technologies. The need to efficiently and effectively process diverse materials drives research and development in sorting, processing, and material recovery techniques. This leads to advancements in technology, which in turn improve the quality and quantity of recycled materials available for use in new products. A continuous cycle of innovation is fueled by consumer engagement.
Reducing Waste and Environmental Impact
By choosing recycled products, consumers directly contribute to reducing waste and minimizing the environmental footprint of consumption. Every recycled product is a step towards diverting waste from landfills and reducing the demand for extracting virgin resources. This translates to less pollution from mining and manufacturing, preserving natural habitats, and conserving precious resources.
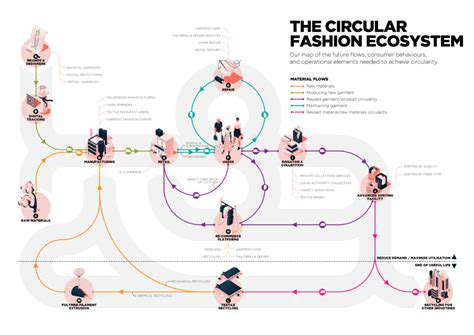
Supporting Circular Economy Models
Consumer preferences for recycled products are crucial for the success of circular economy models. These models prioritize the reuse and recycling of materials, fostering a closed-loop system where waste is minimized and resources are conserved. By supporting circular economy principles, consumers contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future, where products are designed for durability, recyclability, and reuse.
Empowering Consumers as Agents of Change
Ultimately, consumers are empowered as agents of change when they choose recycled products. Their conscious decisions send powerful signals throughout the supply chain, driving positive environmental and economic outcomes. By becoming informed and active consumers, individuals contribute to a more sustainable future and demonstrate their commitment to environmental stewardship. This empowers individuals to effect real change by making conscious choices.