The Power of Consumer Pressure for Ethical Change in Fashion: New Influence
The Growing Demand for Ethical Practices
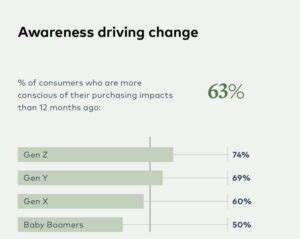
Consumers are increasingly aware of the impact their purchasing decisions have on the environment, social justice, and animal welfare. This growing awareness is driving a significant shift in consumer behavior, pushing companies to adopt more sustainable and ethical practices. Consumers are demanding transparency and accountability from brands, wanting to know the origin of their products and the working conditions of those who produced them. This heightened scrutiny is forcing companies to reassess their supply chains and production methods, ultimately leading to a more responsible and conscious approach to business.
The Influence of Social Media and Online Communities
Social media platforms and online communities have played a pivotal role in shaping the conscious consumer movement. These digital spaces provide a powerful platform for consumers to connect, share experiences, and advocate for their values. Users can easily access information about brands and products, fostering a sense of collective responsibility and empowering them to make informed choices. Reviews, testimonials, and social activism campaigns are often amplified online, influencing the purchasing decisions of a wider audience.
Environmental Concerns and Sustainable Choices
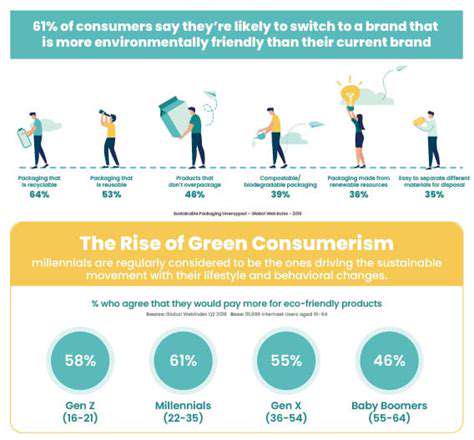
Environmental concerns are a major driving force behind the rise of conscious consumers. From plastic pollution to deforestation, consumers are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of their consumption habits. This concern is prompting a desire for sustainable products and services, such as reusable items, eco-friendly packaging, and brands committed to reducing their carbon footprint. Consumers are actively seeking out products that minimize waste and contribute to a healthier planet.
The Impact of Social Justice Issues on Consumer Choices
Social justice issues are another key factor influencing conscious consumerism. Consumers are increasingly aware of issues like fair labor practices, human rights, and ethical sourcing. They are actively seeking out brands that uphold these values and support fair trade practices, ensuring fair wages and safe working conditions for all involved in the production process. This growing awareness fosters a desire to align their purchasing power with their values.
The Importance of Transparency and Traceability
Transparency and traceability are crucial elements for conscious consumers. Consumers want to know the complete journey of a product, from origin to consumer. This desire for transparency extends to the entire supply chain, enabling consumers to understand the ethical and environmental impact of each step. Knowing the origin and production process allows consumers to make informed decisions aligned with their values.
The Rise of Direct-to-Consumer Brands and Local Businesses
The rise of direct-to-consumer brands and local businesses has empowered conscious consumers. These brands often prioritize ethical sourcing, sustainable practices, and transparent communication. Supporting local businesses allows consumers to directly connect with the people behind the products and experience a more personalized and ethical shopping experience. This trend is further fueled by a desire to reduce reliance on large multinational corporations and support smaller, more accountable businesses.
The Future of Conscious Consumption
The conscious consumer movement is evolving rapidly, constantly pushing brands and businesses to adapt and innovate. The future of conscious consumption will likely see an even greater emphasis on transparency, sustainability, and social responsibility. Consumers will continue to demand more ethical and sustainable options, influencing the direction of the entire retail landscape and demanding more accountability from all businesses. This trend is likely to continue and deepen in the years to come.
The Impact of Social Media on Fashion Activism

The Rise of Social Media Influencers
Social media has fostered a new breed of fashion influencers, individuals who leverage platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube to showcase and promote specific fashion styles, brands, or trends. These influencers have built dedicated followings, often with the power to significantly impact purchasing decisions and drive sales for the brands they endorse. Their reach extends beyond traditional advertising, creating a more personal and engaging connection with consumers.
The rise of social media influencers has revolutionized the fashion industry, offering a more direct and immediate connection between designers, brands, and consumers. Influencers often act as fashion tastemakers, introducing new trends and styles to their followers, and shaping the fashion landscape in unprecedented ways.
Evolving Fashion Trends
Social media platforms are dynamic spaces where trends emerge and evolve rapidly. Users constantly share images and videos of their outfits, creating a ripple effect that quickly translates into broader fashion trends. This constant flow of visual content allows for the rapid dissemination of new styles and influences, enabling fashion to adapt and change at an unprecedented pace.
The ability for trends to spread across vast communities in near real-time allows designers and brands to react quickly to shifts in consumer preferences, which has become crucial for staying competitive in the market.
The Power of Visual Storytelling
Fashion is inherently visual, and social media platforms excel at showcasing the aesthetic appeal of clothing and accessories. High-quality images and videos allow users to virtually experience different styles and trends, giving them a more immersive understanding of how clothes look and feel. This visual storytelling is key to driving engagement and fostering a sense of community around fashion.
The visual nature of social media allows brands to tell compelling stories about their products, effectively communicating their values and unique selling propositions. This visual storytelling fosters a deeper connection with consumers, often leading to greater brand loyalty and increased sales.
The Impact on Consumer Behavior
Social media has transformed the way consumers discover, research, and ultimately purchase fashion items. Consumers often turn to social media platforms to seek inspiration, research brands, and compare prices before making a purchase. This shift in consumer behavior necessitates a new approach to marketing and branding for fashion companies.
The immediacy and accessibility of social media have empowered consumers, giving them more control over their fashion choices and access to a wider range of options. This heightened consumer awareness has led to more informed purchasing decisions and a greater emphasis on ethical and sustainable fashion choices.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Fashion
Social media platforms have broken down geographical barriers, making fashion more accessible to a global audience. The ability to showcase a diverse range of styles and body types online has broadened perceptions of beauty and inclusivity in fashion. This exposure to diverse representations of fashion has a powerful impact on personal style choices.
Social media has become a platform for marginalized communities to express themselves creatively through fashion, fostering a more inclusive and diverse fashion landscape. This increased representation challenges traditional beauty standards and promotes a wider spectrum of aesthetic choices.
Assessing the evolving landscape of [topic] requires a deep understanding of the fundamental concepts that underpin its development and trajectory. This involves scrutinizing historical trends, identifying key drivers of change, and recognizing potential future implications. A comprehensive analysis necessitates a multi-faceted approach, considering both the internal and external factors influencing the landscape.
The Power of Collective Action: Boycotts and Campaigns
Understanding the Mechanics of Boycotts
Boycotts, as a form of consumer activism, leverage the collective power of individuals to exert pressure on businesses or organizations. This pressure is often applied due to perceived unethical practices, poor labor conditions, environmental damage, or social injustices. By collectively refusing to purchase products or services, boycotters aim to disrupt the financial viability of the targeted entity, forcing a change in their behavior. Understanding the mechanics of a successful boycott involves recognizing the importance of widespread participation and sustained effort. A single individual's action has limited impact; a collective movement creates the ripple effect needed to instigate change.
The success of a boycott often depends on clear communication and a shared understanding of the goals. Effective communication strategies mobilize support, explain the rationale behind the boycott, and keep participants informed of progress. This transparency is vital for maintaining momentum and ensuring that the boycott remains focused on the desired outcomes. A well-organized boycott can leverage social media, community forums, and traditional media outlets to spread awareness and engage a wider audience.
The Impact of Campaigns on Consumer Behavior
Consumer campaigns, encompassing a wider range of actions than boycotts, can profoundly influence consumer behavior. These campaigns often target specific issues, promoting sustainable practices, ethical sourcing, or supporting marginalized communities. By educating consumers about the positive and negative impacts of their purchasing decisions, these campaigns foster a more conscious approach to consumption. A successful campaign highlights the interconnectedness of our choices and the power we hold as consumers to drive positive change.
Furthermore, campaigns can reshape the perception of products and services. By associating a particular brand or product with a specific issue, campaigns can influence consumer attitudes and preferences. Consumers, increasingly aware of the ethical and environmental implications of their purchasing decisions, are more receptive to campaigns that address these concerns. Effective campaigns successfully link consumer choices to broader social and environmental issues, empowering individuals to make informed and responsible decisions.
Strategies for Effective Collective Action
Effective collective action requires a well-defined strategy. This involves identifying clear objectives, outlining specific tactics, and developing a comprehensive communication plan. A robust organizational structure is crucial to coordinating efforts, ensuring accountability, and maintaining momentum. This structure could include volunteer roles, communication channels, and decision-making processes. By establishing clear roles and responsibilities, collective action can avoid fragmentation and increase its overall effectiveness.
Building alliances and partnerships with other organizations or groups is another key aspect of successful collective action. This collaborative approach allows campaigns to leverage diverse resources, expertise, and networks. By working together, different groups can amplify their message, garner wider support, and achieve greater impact. Building coalitions broadens the reach and strengthens the collective voice, making it more difficult for the target to ignore the concerns raised.
Measuring the Success of Boycotts and Campaigns
Evaluating the success of boycotts and campaigns is critical to understanding their impact and refining future strategies. This assessment should consider various metrics, including changes in consumer behavior, shifts in corporate practices, and the overall achievement of campaign objectives. Quantifiable data, such as sales figures, media coverage, and public opinion polls, can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of the campaign. Analyzing the long-term consequences of these actions is equally important, as the impact of consumer pressure can manifest in subtle ways over time.
Monitoring the impact on the targeted company or organization is a crucial component of evaluation. Assessing changes in their policies, practices, or public statements provides evidence of the campaign's influence. This data provides valuable feedback for future campaigns and highlights the importance of sustained pressure in achieving meaningful change.