The Thrill of the Hunt: Finding Sustainable Treasures: New Tips
Understanding the Ethical Quandary
The modern consumer often prioritizes sustainable and ethical practices when making purchasing decisions. This extends beyond the readily apparent, like fair trade certifications or organic labeling. A critical examination of the entire supply chain is essential to truly understand the ethical implications of our consumption habits. This is particularly crucial in industries with complex production processes and potentially exploitative labor practices, such as the fishing industry.
Evaluating ethical sourcing goes beyond surface-level assessments. It requires a deep dive into the conditions under which the product is obtained, from the initial catch to the final consumer. This includes considering the welfare of the animals involved, the treatment of workers, and the environmental impact of the fishing practices employed.
Assessing Fishing Practices
Sustainable fishing practices are paramount for maintaining healthy marine ecosystems. Overfishing depletes fish populations, disrupts marine food webs, and threatens the livelihoods of communities reliant on fishing. Evaluating the fishing methods employed is crucial. Does the fishing operation adhere to catch limits and quotas established by regulatory bodies? Are selective fishing techniques employed to minimize bycatch, the unintentional capture of non-target species? How does the fishing operation manage its waste and ensure responsible disposal?
Labor Practices and Fair Treatment
Fishing often involves a complex web of labor practices, from the fishermen themselves to those working in processing plants and distribution centers. Ethical sourcing demands fair wages, safe working conditions, and respect for workers' rights. Evaluating these factors is vital, as exploitative labor practices can undermine the entire ethical sourcing initiative. Does the fishing operation ensure fair compensation for all workers involved in the process, from those on the boats to those in the factories?
Transparency in labor practices and the ability to trace the labor chain back to its origin are critical components of ethical sourcing. Documentation and verification of these practices are necessary to ensure that workers are treated with dignity and respect throughout the entire process.
Environmental Impact of Fishing
Fishing, like many industries, has a significant environmental footprint. The methods employed, the bycatch rates, and the overall impact on marine ecosystems are crucial factors in evaluating the ethical nature of the sourcing. Overfishing is a major concern, as it can disrupt entire marine ecosystems and threaten biodiversity. The use of destructive fishing techniques, such as bottom trawling, can significantly damage the seafloor and harm non-target species.
Assessing the environmental impact of fishing requires understanding the specific fishing techniques used, the areas where fishing takes place, and the overall impact on the marine environment. This includes analyzing the potential for habitat destruction, pollution from discarded fishing gear, and the risk of introducing invasive species.
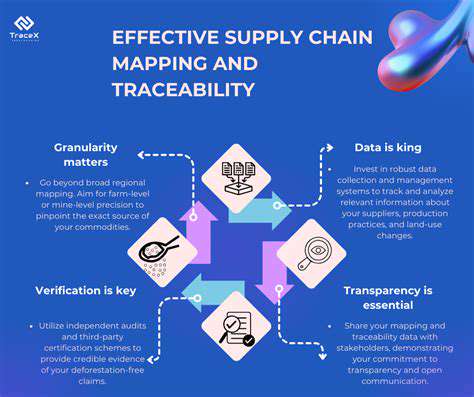
Transparency and Traceability
Transparency in the supply chain is essential for evaluating ethical sourcing practices. Consumers need to understand where their food comes from and how it is produced. Traceability allows consumers to follow the product from the source to the point of purchase, revealing the details of its journey. This includes understanding the fishing methods, the location of the catch, and the treatment of workers involved in the production.
Lack of transparency and traceability creates significant ethical concerns. Without clarity in the supply chain, it's difficult to assess the ethical implications of a product's origin. Consumers have a right to know the details of how their food is sourced and produced.
Consumer Responsibility and Action
Beyond evaluating the sourcing practices of individual companies, consumers play a crucial role in driving ethical change. By making informed choices and demanding transparency from businesses, consumers can encourage sustainable practices in the fishing industry. Supporting companies committed to ethical sourcing and avoiding those with questionable practices are key steps.
Consumer education and advocacy are vital in promoting ethical consumption. By understanding the issues involved and actively supporting sustainable practices, consumers can contribute to a more ethical and environmentally responsible fishing industry.
Exploring Alternative Materials and Production Methods
Exploring Bio-Based Plastics
Bio-based plastics, derived from renewable resources like plants and agricultural waste, offer a compelling alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics. These materials hold significant promise for reducing our reliance on finite fossil fuels and mitigating the environmental impact of plastic production. The development of bio-based polymers allows for the creation of diverse materials with varying properties, opening up possibilities for applications across various industries, from packaging to construction.
The process of creating bio-based plastics often involves converting plant-based feedstocks into biopolymers. This conversion process can be optimized to yield materials with desired strength, flexibility, and durability. Research into sustainable feedstocks and improved conversion technologies is critical to realizing the full potential of bio-based plastics and reducing their environmental footprint.
Innovative 3D Printing Techniques
3D printing, a rapidly evolving technology, is revolutionizing manufacturing processes. The use of alternative materials in 3D printing is transforming design possibilities, allowing for the creation of complex geometries and customized parts. The ability to print directly from a digital model eliminates the need for traditional tooling, drastically reducing production time and costs.
Exploring innovative 3D printing techniques, such as fused deposition modeling (FDM), selective laser sintering (SLS), and stereolithography (SLA), opens doors to producing intricate parts with enhanced precision and functionality. The interplay between material selection and printing parameters is crucial for optimizing the final product's performance and achieving desired characteristics.
Sustainable Sourcing of Raw Materials
Sustainable sourcing of raw materials is fundamental to responsible production. Focusing on materials derived from recycled content or waste streams can significantly minimize environmental impact and reduce reliance on virgin resources. Implementing strategies for responsible sourcing ensures that materials are obtained ethically and without jeopardizing ecosystems or impacting communities.
Careful consideration of the entire lifecycle of raw materials, from extraction to processing to disposal, is vital. Companies can implement traceability systems to ensure transparency in their supply chains, allowing consumers to make informed choices and fostering trust in sustainable practices. This approach promotes the use of renewable and recyclable resources, reducing the strain on finite resources.
Advanced Manufacturing Processes
Advanced manufacturing processes, such as additive manufacturing and bio-replication, are transforming traditional production methods. These techniques offer significant potential for creating customized products with high precision and efficiency. The use of these methods can lead to reduced material waste and a more sustainable production cycle.
Exploring and implementing these advanced techniques involves careful consideration of the environmental impact of each stage of the production process. Minimizing energy consumption, optimizing material usage, and reducing waste are crucial aspects of achieving truly sustainable manufacturing practices. The integration of advanced processes with sustainable materials promises a future of more environmentally conscious and efficient production systems.
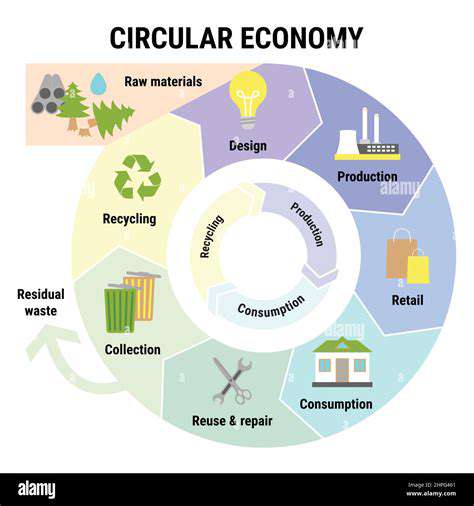
Circular Economy Models
Implementing circular economy models is crucial for minimizing waste and maximizing resource utilization. These models emphasize the concept of designing products for disassembly and reuse, fostering a closed-loop system where materials are continuously recycled and repurposed. This approach extends beyond the product itself to include the entire supply chain, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal.
Developing and implementing circular economy models requires a collaborative effort among producers, consumers, and policymakers. Encouraging the design of products with inherent recyclability and promoting the development of advanced recycling technologies are essential steps towards a circular economy. This approach aims to reduce waste, conserve resources, and minimize environmental impact, creating a more sustainable future for all.
Environmental sustainability is no longer a niche concept but a fundamental necessity for the future of our planet. The escalating pressures of climate change, resource depletion, and biodiversity loss demand urgent and comprehensive action from individuals, businesses, and governments alike. We are witnessing the consequences of ignoring environmental concerns in the form of extreme weather events, dwindling natural resources, and the collapse of ecosystems. This necessitates a shift towards sustainable practices that prioritize the well-being of both humans and the environment.
The Power of Conscious Consumption: Building a Sustainable Future

Understanding the Impact
Conscious consumption isn't just about buying less; it's about making informed decisions that align with your values and have a positive impact on the world. This involves considering the environmental footprint of products, the labor conditions under which they were made, and the ethical implications of your purchases. Understanding these factors empowers you to make choices that contribute to a more sustainable and equitable future.
Prioritizing Sustainability
Sustainable practices are crucial in today's world. Considering the environmental impact of your choices, from the materials used to manufacture a product to the energy required for its transportation and use, is a key aspect of conscious consumption. By supporting businesses committed to sustainability, you're actively reducing your contribution to environmental problems.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical consumption extends beyond the environment. It involves considering the labor conditions in which products are made. Supporting fair trade practices ensures that workers receive fair wages and safe working conditions, preventing exploitation and fostering a more just global economy. Conscious consumers actively research and choose products from companies with demonstrably ethical labor practices.
Reducing Waste and Consumption
One of the most impactful ways to practice conscious consumption is to reduce your overall consumption. This includes evaluating your needs before making purchases and choosing products with a longer lifespan. By actively reducing our consumption, we diminish the amount of waste sent to landfills and the strain on natural resources. This conscious effort contributes to a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Supporting Local Businesses
Buying from local businesses directly supports local economies. This translates to jobs and economic growth within your community. This is a tangible way to positively impact your community, while also frequently finding higher quality products and often with a smaller environmental footprint.
Promoting Transparency and Accountability
Transparency in supply chains is essential for conscious consumers. Knowing where products come from, how they are made, and who made them allows you to make informed decisions. Companies that prioritize transparency are often more accountable for their actions, leading to improved labor practices and environmental responsibility. Consumers are empowered to support businesses that are committed to open communication and ethical practices.
Embracing a Minimalist Mindset
Embracing a minimalist mindset encourages a deeper understanding of your needs versus your wants. This approach helps you prioritize quality over quantity, leading to fewer purchases and a more intentional approach to consumption. By focusing on essential items and experiences, you can reduce your environmental impact and cultivate a more fulfilling life. This practice often leads to a more intentional lifestyle.