Sustainable Fashion and the Future of Work
The Rise of Conscious Consumption in the Apparel Industry

The Growing Awareness of Sustainability
Consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental and social impacts of their purchasing decisions. This growing awareness is driving a shift in consumer behavior, leading to a demand for more sustainable and ethical products and services. Understanding the ethical production and sourcing of goods is becoming a significant factor in consumer choice. This heightened awareness is a crucial element in the rise of conscious consumption.
The Impact of Social Media and Influencer Marketing
Social media platforms and influencer marketing have significantly impacted consumer behavior. These platforms provide a powerful platform for brands and individuals to share information and opinions about products and services. This constant exposure to diverse perspectives has made consumers more discerning about brands and their values, fostering greater scrutiny of marketing claims and promoting a more conscious approach to purchasing. Consumers are actively seeking out brands that align with their values.
The Importance of Transparency and Traceability
Consumers are demanding greater transparency and traceability in the supply chain. They want to know where their products come from, how they are made, and the conditions under which they were produced. This desire for transparency is a key driver in the conscious consumer movement, with consumers actively seeking out brands that can demonstrate ethical and sustainable practices throughout their operations. This demand creates a pressure for businesses to be more accountable and transparent.
The Role of Ethical and Sustainable Brands
Ethical and sustainable brands are rapidly gaining popularity. These brands prioritize environmental protection and social responsibility in their operations. Consumers are actively supporting brands that align with their values, creating a demand for products that are produced ethically and sustainably. This trend is leading to a wider range of sustainable options available in the marketplace, encouraging more businesses to adopt sustainable practices.
The Influence of Eco-Friendly Packaging and Materials
Consumers are increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly packaging and materials. They are looking for products that are packaged in sustainable materials and that minimize waste. This growing preference for eco-friendly packaging is a powerful driver of change in the market, influencing companies to adopt more sustainable practices. The conscious consumer demands that the entire lifecycle of the product be considered.
The Growing Interest in Local and Handmade Products
There's a noticeable surge in interest in local and handmade products. Consumers are seeking out goods that are produced locally or by small, artisan businesses. This preference reflects a desire to support local communities and to connect with the people who create the products. This interest in local and handmade products is part of a broader trend towards supporting businesses with transparent and ethical practices. It is a way for consumers to actively contribute to local economies.
The Challenges and Opportunities for Businesses
The rise of conscious consumption presents both challenges and opportunities for businesses. Companies must adapt to the changing demands of consumers, incorporating sustainable practices into their operations and communicating their commitment transparently. This requires a shift in mindset and a willingness to invest in sustainable practices. However, businesses that successfully meet these demands can gain a competitive advantage and build stronger customer relationships. Ultimately, understanding and responding to the values of conscious consumers can lead to long-term success.
Innovative Manufacturing Processes and Circular Economy Models
Innovative Manufacturing Processes for Sustainable Fashion
Innovative manufacturing processes are crucial for achieving sustainability in the fashion industry. These processes must prioritize resource efficiency, reduce waste, and minimize the environmental impact of production. This involves exploring alternative materials, such as recycled and bio-based fibers, and implementing closed-loop systems to maximize the use of existing resources and minimize the need for virgin materials. The goal is to create a system where garments are designed for disassembly and reuse, significantly reducing the environmental footprint associated with textile production and consumption.
Circular Economy Models in Sustainable Fashion
Circular economy models offer a transformative approach to fashion production, focusing on minimizing waste and maximizing resource utilization. This includes concepts like product life extension, material reuse, and the development of innovative business models that prioritize the lifecycle of garments. The ultimate aim is to move away from a linear take-make-dispose model to a circular one, where resources are kept in use for as long as possible, and waste is minimized or eliminated entirely. This approach reduces the environmental burden of textile production and consumption.
Design for Disassembly and Repair in Sustainable Fashion
Designing garments for disassembly and repair is an essential aspect of sustainable fashion. This involves considering the materials used, the construction techniques, and the overall design to facilitate easy dismantling and reuse of components. By implementing this principle, consumers can extend the lifespan of garments, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing textile waste. It also promotes a culture of repair and maintenance, reducing the pressure on the production system.
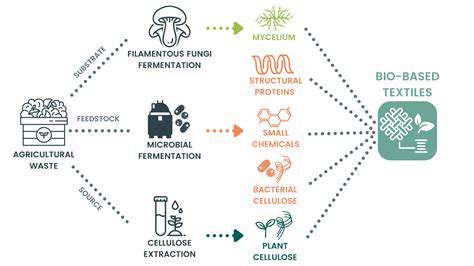
Bio-Based Materials and Sustainable Textile Production
The exploration and adoption of bio-based materials are vital for creating sustainable textile production. These materials, derived from renewable sources, offer a promising alternative to conventional petroleum-based fibers, reducing the environmental impact of textile manufacturing. Examples include plant-based fibers, such as hemp and linen, as well as innovative biopolymers. This transition can significantly lessen the reliance on fossil fuels and promote environmental responsibility in the fashion industry.
Waste Reduction and Recycling in Textile Manufacturing
Waste reduction and effective recycling are critical components of sustainable fashion manufacturing. Implementing strategies to minimize textile waste throughout the production process, from material selection to garment disposal, is paramount. This includes optimizing cutting patterns, reducing textile scraps, and promoting the use of recycled materials. Moreover, establishing robust recycling systems for used garments and textiles is essential for closing the loop and achieving a truly circular fashion system.
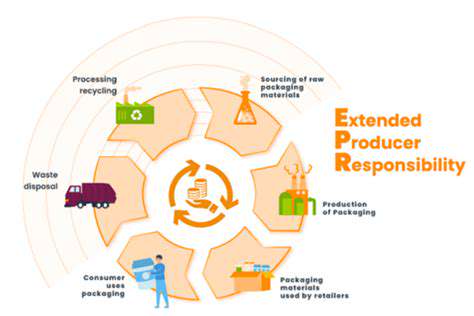
Sustainable Supply Chains and Ethical Practices
Sustainable supply chains are essential for promoting ethical and environmentally conscious practices in the fashion industry. These chains must prioritize transparency and traceability throughout the production process, from raw material sourcing to final product delivery. Implementing fair labor practices and ensuring safe working conditions for workers in all stages of production are also key components of a sustainable supply chain. This creates a responsible and ethical framework for the entire fashion ecosystem.
Consumer Education and Awareness for Sustainable Fashion
Educating consumers about sustainable fashion choices is vital for driving widespread adoption of eco-friendly practices. Raising awareness about the environmental and social impact of clothing choices empowers consumers to make informed decisions. This includes providing information about the materials used, the manufacturing processes, and the ethical considerations involved in the production of garments. Educating consumers about the benefits of repairing, reusing, and recycling clothing can encourage sustainable consumption patterns.