Sustainable Packaging from Recycled Ocean Plastic

Material Selection for Eco-Friendly Packaging
Choosing sustainable materials is crucial in manufacturing eco-friendly packaging. Recyclable and compostable materials like paper, cardboard, and plant-based plastics are excellent options. Minimizing the use of virgin materials and maximizing the use of recycled content significantly reduces the environmental footprint of the packaging.
Evaluating the lifecycle impact of various materials is essential. This includes considering the energy consumption during production, the potential for reuse or recycling, and the overall waste generation from the packaging itself.
Design for Reduced Waste and Reusability
Packaging design plays a vital role in minimizing waste and maximizing reusability. A well-designed package should be easy to open and close, minimizing the use of unnecessary components like excessive adhesives or complex closures. Streamlining the design process to prioritize simplicity and efficiency is key to reducing material waste during production.
Consider incorporating features that encourage reuse. This could involve designing packages that can be refilled, repurposed, or returned for recycling. This approach can significantly reduce the overall environmental impact of the product and its associated packaging.
Minimizing Packaging Size and Weight
Reducing the size and weight of packaging is essential for minimizing material consumption and transportation costs. Efficient use of space and lightweight materials can dramatically reduce the environmental impact of the shipping process. This results in lower fuel consumption and a smaller carbon footprint.
Optimizing the package shape and structure is critical for minimizing material use while maintaining product integrity. Employing sophisticated design software and simulations can help identify areas where size and weight can be reduced without compromising product safety.
Sustainable Production Processes
Implementing sustainable production processes is paramount in reducing the environmental impact of packaging manufacturing. This includes optimizing energy efficiency within the factory, using renewable energy sources, and minimizing water usage in the production process.
Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability
Ensuring transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain is essential for building consumer trust and promoting sustainable practices. Consumers are increasingly demanding information about the origin and environmental impact of the materials used in their products. This transparency is crucial for building trust and fostering a responsible supply chain.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Conducting a thorough environmental impact assessment is vital for evaluating the sustainability of packaging solutions. This process involves analyzing all stages of the packaging's lifecycle, from material sourcing to disposal. Understanding the environmental impact of each stage is key to pinpointing areas for improvement and making informed decisions about sustainable packaging.
Consumer Engagement and Education
Engaging consumers and educating them about the importance of sustainable packaging is crucial for promoting responsible consumption. Effective communication strategies can help consumers understand the environmental benefits of choosing sustainable packaging options. Educating consumers about the lifecycle impact of packaging choices empowers them to make more environmentally conscious decisions.

Future Outlook and Consumer Engagement
Sustainable Packaging Innovations
The future of packaging hinges on innovation, moving beyond traditional materials to embrace sustainable alternatives. Recycling ocean plastics, while a crucial step, is just one facet of a broader strategy. We need to explore and develop new materials derived from recycled ocean plastic, agricultural waste, or even mycelium, ensuring these materials are not only environmentally friendly but also economically viable for large-scale production. This innovative approach is crucial for achieving a circular economy and minimizing waste.
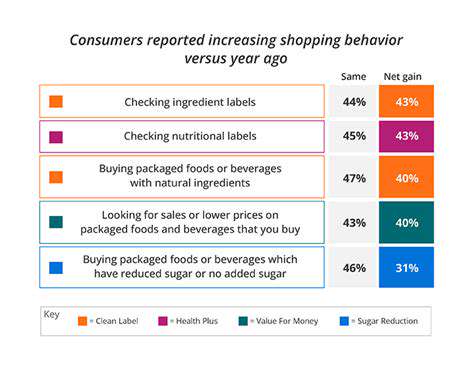
Consumer Demand and Education
Consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of packaging and are demanding more sustainable options. Educating consumers about the benefits of recycled ocean plastic packaging and the importance of responsible consumption is essential. Transparency about the sourcing and recycling process will foster trust and encourage adoption of sustainable packaging choices. This includes clear labeling, easy-to-understand information, and accessible educational resources.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are paving the way for more efficient and effective recycling processes. Developments in sorting technologies, chemical recycling methods, and advanced material science are crucial for maximizing the recovery and reuse of ocean plastics. This allows for a more comprehensive approach to the circular economy, reducing reliance on traditional incineration and landfill disposal.
Economic Viability and Market Trends
The economic viability of sustainable packaging solutions is a critical factor in their widespread adoption. Government incentives, subsidies, and tax credits can stimulate demand and reduce the cost of these materials. Market trends indicate a growing demand for eco-friendly products, creating opportunities for businesses to capitalize on this trend and develop innovative solutions that cater to consumer preferences. This includes collaboration with businesses to create sustainable packaging supply chains.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Sustainable packaging solutions require collaboration among various stakeholders. Partnerships between governments, businesses, and research institutions are essential to drive innovation, develop infrastructure, and implement effective policies. This includes collaborative research into new materials, recycling processes, and the development of industry standards for sustainable packaging.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
Stronger environmental policies and regulations are necessary to accelerate the transition to sustainable packaging. This includes extending the scope of existing regulations to cover ocean plastic waste, incentivizing the use of recycled materials, and enforcing stricter penalties for unsustainable practices. These policies must be supported by robust monitoring and enforcement mechanisms to ensure compliance and promote the adoption of sustainable packaging solutions throughout the supply chain.