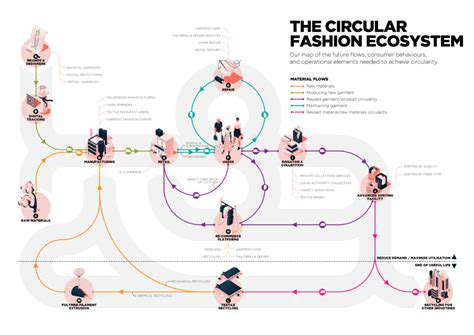
The Circularity of Regenerative Agriculture in Fashion: New Connections
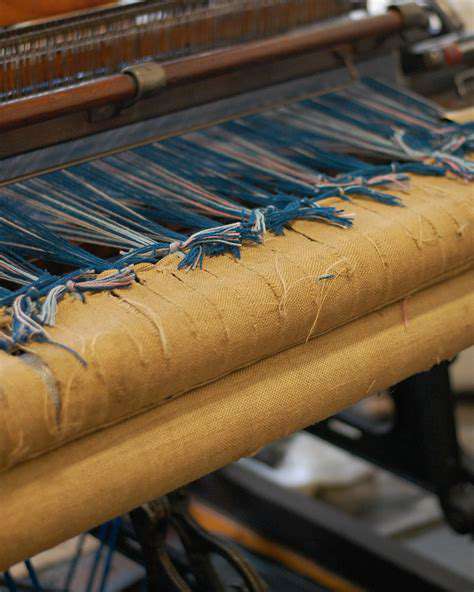

From Seed to Sustainable Style
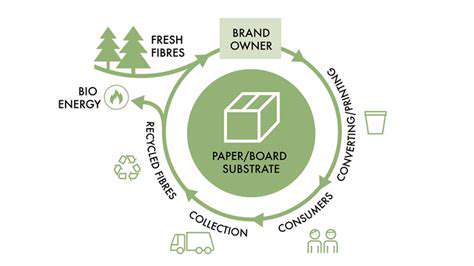
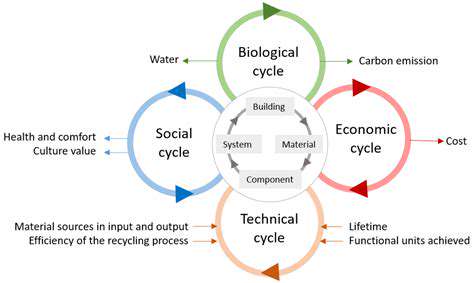
The journey of textiles from farm to fabric is often shrouded in complexity and environmental impact. However, the circular economy offers a pathway to a more sustainable approach, where resources are valued and reused, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency. This shift in thinking is crucial for addressing the growing environmental concerns associated with traditional textile production.
From the initial cultivation of raw materials to the final product, each stage presents opportunities for optimization. By embracing circular principles, we can significantly reduce our reliance on virgin resources and create a more resilient and responsible textile industry.
Cultivating Sustainable Raw Materials
The foundation of sustainable textiles lies in the cultivation of raw materials. This involves innovative agricultural practices that prioritize soil health, water conservation, and biodiversity. For example, using organic farming techniques reduces the need for harmful pesticides and fertilizers, minimizing environmental damage. These practices also contribute to the overall health of the ecosystem and promote long-term sustainability.
Innovative Manufacturing Processes
Moving beyond the farm, innovative manufacturing processes are critical to achieving a circular textile economy. These processes encompass everything from optimizing dyeing techniques to exploring innovative weaving and knitting methods. Efficient water usage in dyeing processes and the adoption of closed-loop systems are paramount in minimizing environmental impact.
Moreover, exploring alternative fibers like recycled or plant-based materials can further reduce the environmental footprint of textile production. This transition is vital for reducing reliance on traditional, resource-intensive methods.
Designing for Durability and Longevity
Durability and longevity are essential aspects of a circular textile economy. Designing garments and textiles with a longer lifespan in mind can significantly reduce the demand for new products and minimize waste. This approach involves using high-quality materials that can withstand repeated use and promoting repair and reuse initiatives. Consumers can also play a crucial role by prioritizing durable and well-made items.
Promoting Repair and Reuse
Repair and reuse are fundamental components of the circular economy. Promoting initiatives that encourage garment repair and reuse not only extends the lifespan of clothing but also reduces textile waste. This can be achieved through community repair workshops, clothing swap events, and initiatives that encourage consumers to mend and repurpose existing garments. Such efforts foster a culture of conscious consumption and resource conservation.
The Consumer's Role in Circularity
Ultimately, the success of a circular textile economy hinges on the active participation of consumers. Educating consumers about the environmental impact of textile production and encouraging them to make informed choices is crucial. This includes supporting brands that prioritize sustainable practices, choosing durable and well-made garments, and embracing repair and reuse initiatives. Consumers can actively contribute to minimizing waste and maximizing the lifecycle of textiles.
The metaverse, as a burgeoning entertainment platform, necessitates a paradigm shift in how we consume and interact with digital content. Immersive experiences are key to its success, moving beyond traditional two-dimensional screens to envelop users in virtual worlds. This requires advanced technologies like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) to create believable and engaging environments.
Consumer Engagement and Transparency: Driving the Circularity Movement

Consumer Trust and Brand Loyalty
Building consumer trust is paramount in today's market. Consumers are increasingly discerning, demanding transparency and authenticity from brands. This trust, fostered by open communication and ethical practices, directly translates to brand loyalty and repeat business. Consumers who feel valued and understood are more likely to become advocates for a brand.
Transparency in operations, sourcing, and pricing helps establish credibility and fosters a stronger connection with the consumer base. This, in turn, leads to a more engaged and loyal customer base.
Effective Communication Strategies
Clear and consistent communication is crucial for driving engagement. Brands need to tailor their messaging to resonate with their target audience, employing various channels to reach them effectively. This includes utilizing social media, email marketing, and interactive content to foster meaningful interactions.
Understanding the nuances of different communication styles and platforms is vital for achieving optimal impact. A brand's voice should be consistent across all channels, projecting a unified and authentic image.
Data-Driven Insights
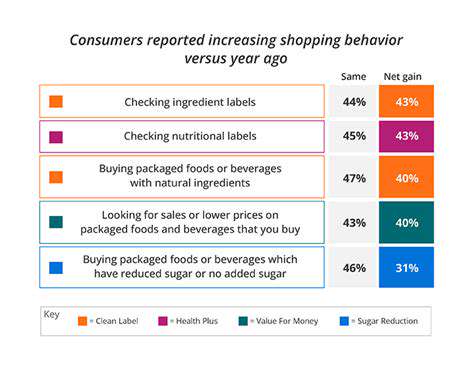
Analyzing consumer data provides valuable insights into preferences, behaviors, and pain points. Understanding these insights allows brands to personalize their offerings and tailor their communication strategies, ultimately leading to increased engagement. This data-driven approach enables brands to understand what resonates with their consumers on an individual level.
Employing advanced analytics tools can help identify trends and patterns in consumer behavior, allowing brands to make informed decisions about product development, marketing campaigns, and customer service initiatives.
Personalized Experiences
Offering personalized experiences is key to capturing consumer attention in today's market. This means adapting products, services, and communication to cater to individual needs and preferences. By recognizing and responding to individual customer needs, brands can foster a deeper connection with their customers.
Interactive Content and Engagement
Interactive content, such as quizzes, polls, and surveys, can significantly boost consumer engagement. These tools encourage active participation and foster a sense of community around the brand. This two-way communication allows for deeper understanding of consumer needs and preferences.
Customer Feedback and Feedback Mechanisms
Actively soliciting and responding to customer feedback is essential for continuous improvement. Open channels for feedback, like surveys and social media monitoring, provide invaluable insights into consumer perceptions and expectations. This feedback can be used to refine products, services, and overall brand strategy.
Implementing feedback mechanisms that are easy to access and utilize is crucial for gathering honest and meaningful insights from customers. This commitment to listening and responding shows consumers that their opinions matter.
Building a Community
Cultivating a sense of community around a brand fosters loyalty and advocacy. Creating platforms for interaction and shared experiences, such as online forums or social media groups, allows consumers to connect with each other and the brand. Strong brand communities demonstrate a shared passion and value proposition that drives engagement and reinforces loyalty.
The Future of Fashion: A Regenerative Paradigm
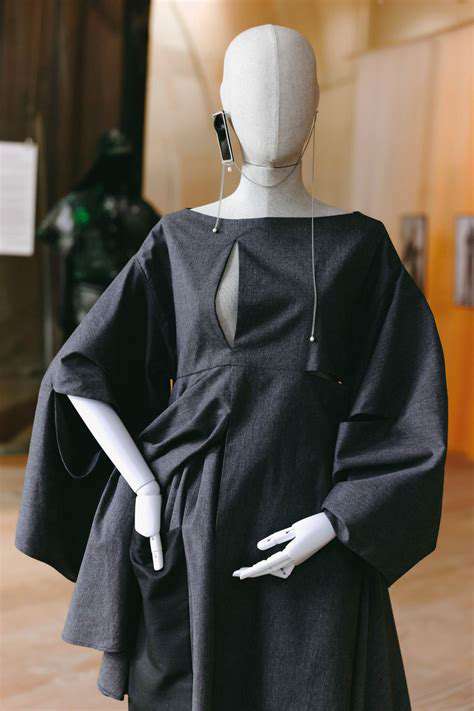

Sustainable Practices in Design
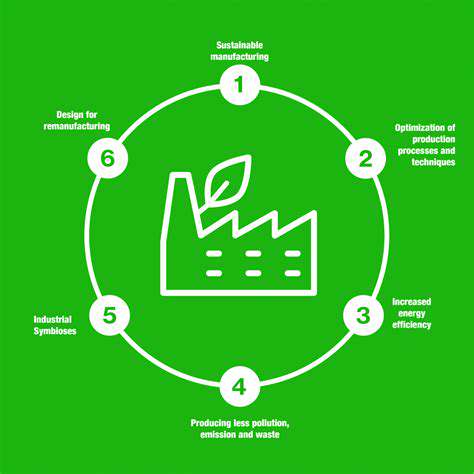
The fashion industry is increasingly recognizing the urgent need for sustainable practices. This involves a radical shift in design thinking, moving away from fast fashion models towards a circular economy approach. Designers are exploring innovative materials like recycled fabrics, organic cotton, and innovative bio-based textiles. This commitment to sustainability extends beyond the materials themselves, encompassing the entire production lifecycle, from sourcing to manufacturing to waste management.
Sustainable practices also include reducing water consumption and minimizing the environmental impact of dyeing processes. This requires collaboration across the entire supply chain, from farmers to manufacturers to retailers. Ultimately, a truly sustainable approach will prioritize minimizing waste and maximizing the lifespan of garments.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are rapidly transforming the fashion industry, offering exciting possibilities for innovation and sustainability. 3D printing, for example, is allowing designers to create intricate and personalized garments with significantly reduced material waste. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the way garments are designed and produced, offering greater customization and efficiency.
Smart textiles are another area of rapid development, incorporating sensors and connectivity into clothing. These advanced fabrics can monitor vital signs, adjust to temperature fluctuations, and even provide real-time feedback on user activity. These advancements hold the promise of creating highly personalized and interactive fashion experiences.
The Rise of Inclusivity
The future of fashion is increasingly embracing inclusivity and diversity. This means moving beyond traditional size and gender norms to cater to a wider range of body types and preferences. The industry is recognizing the importance of representation and celebrating diverse aesthetics, creating clothing that empowers individuals to express themselves authentically.
This shift towards inclusivity extends beyond simply offering a wider range of sizes. It also involves promoting body positivity, challenging harmful beauty standards, and featuring diverse models and designers in campaigns and collections. This evolution is crucial for creating a more equitable and representative fashion landscape.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are becoming increasingly important in the fashion industry. Consumers are demanding transparency and accountability regarding the labor practices and environmental impact of their purchases. This includes fair wages for garment workers, safe working conditions, and environmentally responsible manufacturing practices.
Transparency is key to building trust and ensuring ethical production. Consumers want to know where their clothes come from, how they were made, and who made them. Brands that embrace ethical sourcing and manufacturing practices will be better positioned to resonate with conscientious consumers and drive positive change in the industry.
The Role of E-commerce and Digitalization
E-commerce and digitalization are transforming the fashion industry by connecting brands with consumers in new and innovative ways. Online platforms are providing greater accessibility to a wider range of styles and brands, while also streamlining the shopping experience for consumers. This digital evolution allows brands to connect directly with their customers, fostering a deeper understanding of their preferences and needs.
Digitalization is also impacting the design and production processes. Virtual fashion shows, digital design tools, and online communities are helping to accelerate innovation and foster collaboration across the industry. This digital evolution is essential for staying competitive and adapting to the changing demands of the modern consumer.