The Craft of Textile Manipulation: Innovative Upcycling Techniques: New Methods
Beyond Garments: Expanding the Horizons of Textile Art
Beyond the Loom: Exploring Three-Dimensional Textile Forms
Textile art extends far beyond the confines of flat garments. Exploring three-dimensional forms allows artists to manipulate textiles in new and exciting ways, creating sculptural pieces that command attention and evoke a wide range of emotions. These forms, often incorporating techniques like felting, knitting, weaving, or knotting, can take on abstract shapes, represent natural objects, or even mimic architectural structures. The possibilities are limitless, and the resulting pieces offer a tangible connection to the artistry and craft involved in their creation.
Embroidered Narratives: Storytelling Through Textile Detail
Embroidery, with its intricate stitches and meticulous designs, provides a powerful medium for storytelling. Artists can create elaborate narratives, weaving tales of personal experiences, historical events, or fantastical adventures into the fabric. Each thread, each carefully placed stitch, contributes to a visual narrative that unfolds before the viewer, inviting contemplation and interpretation. The act of embroidery, itself a meticulous process, embodies the commitment to detail and the profound connection between art and personal expression.
The Fusion of Fiber and Functionality: Textile Design for Everyday Use
Textile art is not solely confined to aesthetic objects. Contemporary designers are increasingly incorporating textile principles into everyday functional items. From intricately woven placemats to beautifully embroidered backpacks, textiles can enhance the beauty and utility of everyday objects. This fusion of form and function showcases the versatility and adaptability of textile craft, demonstrating that beauty and practicality can coexist seamlessly.
Dyeing and Pigment Manipulation: Transforming Fibers Through Color
The world of textile art is deeply intertwined with the art of dyeing and pigment manipulation. Artists experiment with natural dyes derived from plants and minerals, creating unique color palettes and expressions. They also utilize synthetic dyes, exploring a vast spectrum of hues and effects. Through careful control of these elements, artists can transform the raw material of fiber into vibrant and captivating artworks, highlighting the beauty and transformative power of color.
Textiles in the Digital Age: Innovative Techniques and Emerging Trends
Technology is rapidly changing the landscape of textile art. Digital tools are now being used to create intricate patterns, design complex structures, and even manipulate the very fibers themselves. This fusion of traditional textile techniques with digital design offers exciting new avenues for exploration and innovation. Artists are pushing the boundaries of what is possible, creating unique and visually arresting works that reflect the ever-evolving nature of textile art in the 21st century.
The Cultural Significance of Textiles: Preserving Heritage and Celebrating Identity
Textiles often hold significant cultural importance, acting as repositories of history and identity. Traditional weaving techniques, embroidery styles, and dyeing methods are often passed down through generations, preserving cultural heritage and celebrating unique artistic expressions. These handcrafted textiles provide a tangible link to the past, connecting us to the stories, traditions, and artistic heritage of various cultures. This cultural significance deepens our appreciation for the craft and its ability to communicate across generations and geographical boundaries.
The Future of Sustainable Fashion: Weaving a New Narrative

Circular Economy Principles in Sustainable Fashion
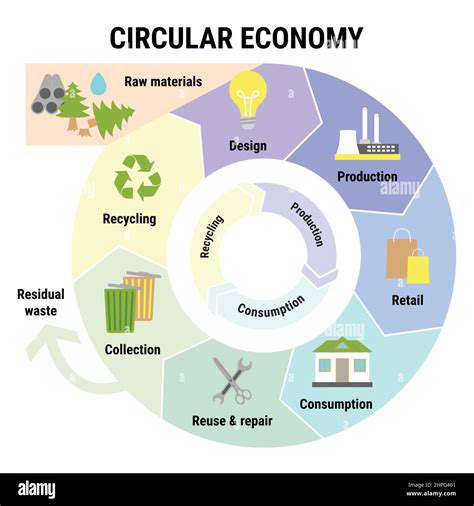
A crucial aspect of the future of sustainable fashion lies in embracing circular economy principles. This involves designing garments for durability and repairability, promoting reuse and recycling, and minimizing waste throughout the entire lifecycle of the product. By shifting from a 'take-make-dispose' model to a circular one, the fashion industry can significantly reduce its environmental footprint and move towards a more sustainable future. This transition requires a fundamental shift in mindset, from a focus on fast fashion to one that values quality and longevity.
Implementing circular economy principles necessitates a comprehensive approach. This includes collaborating with designers, manufacturers, retailers, and consumers to develop sustainable practices. Innovative solutions such as repair cafes and clothing swaps can also play a key role in promoting the reuse and recycling of garments.
Technological Advancements in Sustainable Materials
Technological advancements are paving the way for the development of innovative and sustainable materials. Scientists are exploring new fibers derived from renewable resources like seaweed and agricultural waste, creating fabrics with exceptional performance and eco-friendly attributes. The use of recycled materials, such as plastic bottles and textile scraps, is becoming increasingly prevalent, offering a viable solution to reduce textile waste and reliance on virgin resources.
Ethical Production Practices and Labor Conditions
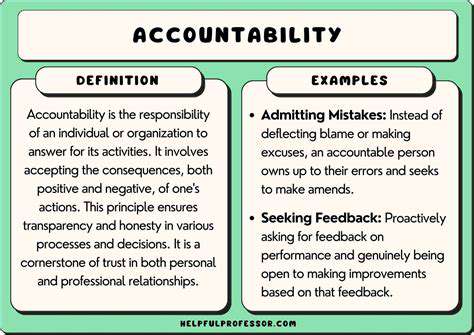
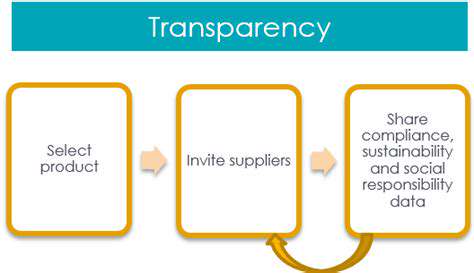
Sustainable fashion is not just about environmental concerns; it also encompasses ethical production practices and fair labor conditions. Transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain are paramount to ensure that workers are treated fairly and receive fair wages. Promoting ethical production involves supporting factories that adhere to labor standards, ensuring safe working conditions, and guaranteeing fair compensation for all involved in the creation of garments.
Small-scale and local production methods are gaining traction, allowing for closer monitoring of labor practices and fostering stronger relationships between producers and consumers. This enhances traceability and accountability, thus reducing the risk of exploitation and promoting fairer working conditions.
Consumer Awareness and Conscious Consumption
Consumer awareness and conscious consumption are key drivers of the sustainable fashion movement. Consumers are increasingly seeking out brands and products that align with their values. This demand for transparency, ethical practices, and environmental responsibility is pushing brands to adopt sustainable business models and practices.
Educating consumers about the environmental and social impacts of their fashion choices is crucial. Raising awareness about the lifecycle of garments, from material sourcing to disposal, empowers consumers to make more informed purchasing decisions. This includes understanding the impact of fast fashion and promoting mindful consumption.
The Role of Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations play a significant role in shaping the future of sustainable fashion. Implementing policies that incentivize sustainable practices, such as tax breaks for eco-friendly materials and production methods, can encourage businesses to adopt more sustainable approaches. This includes regulations that address textile waste management and promote responsible consumption.
Clearer labeling and regulations regarding sustainable materials and ethical production practices would provide consumers with more information and empower them to make better choices. Governments can play a pivotal role in driving the adoption of sustainable practices within the fashion industry and encouraging a more sustainable future.
The Future of Sustainable Fashion Retail
Sustainable fashion retail is evolving to meet the needs of conscious consumers. Retailers are increasingly showcasing eco-friendly brands and offering innovative services like repair workshops and clothing swaps. This shift towards a more circular retail model is crucial for promoting the longevity and sustainability of the industry.
E-commerce platforms are also playing a critical role in connecting consumers with sustainable brands and facilitating ethical and environmentally conscious purchasing. Innovative business models in fashion retail are crucial to ensure that the industry transitions towards a sustainable and ethical future.